In number theory, the Pólya conjecture (or Pólya's conjecture) stated that "most" (i.e., 50% or more) of the natural numbers less than any given number have an odd number of prime factors. The conjecture was set forth by the Hungarian mathematician George Pólya in 1919,[1] and proved false in 1958 by C. Brian Haselgrove. Though mathematicians typically refer to this statement as the Pólya conjecture, Pólya never actually conjectured that the statement was true; rather, he showed that the truth of the statement would imply the Riemann hypothesis. For this reason, it is more accurately called "Pólya's problem".

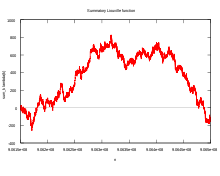

The size of the smallest counterexample is often used to demonstrate the fact that a conjecture can be true for many cases and still fail to hold in general,[2] providing an illustration of the strong law of small numbers.
Statement
editThe Pólya conjecture states that for any n > 1, if the natural numbers less than or equal to n (excluding 0) are partitioned into those with an odd number of prime factors and those with an even number of prime factors, then the former set has at least as many members as the latter set. Repeated prime factors are counted repeatedly; for instance, we say that 18 = 2 × 3 × 3 has an odd number of prime factors, while 60 = 2 × 2 × 3 × 5 has an even number of prime factors.
Equivalently, it can be stated in terms of the summatory Liouville function, with the conjecture being that
for all n > 1. Here, λ(k) = (−1)Ω(k) is positive if the number of prime factors of the integer k is even, and is negative if it is odd. The big Omega function counts the total number of prime factors of an integer.
Disproof
editThe Pólya conjecture was disproved by C. Brian Haselgrove in 1958. He showed that the conjecture has a counterexample, which he estimated to be around 1.845 × 10361.[3]
A (much smaller) explicit counterexample, of n = 906,180,359 was given by R. Sherman Lehman in 1960;[4] the smallest counterexample is n = 906,150,257, found by Minoru Tanaka in 1980.[5]
The conjecture fails to hold for most values of n in the region of 906,150,257 ≤ n ≤ 906,488,079. In this region, the summatory Liouville function reaches a maximum value of 829 at n = 906,316,571.
References
edit- ^ Pólya, G. (1919). "Verschiedene Bemerkungen zur Zahlentheorie". Jahresbericht der Deutschen Mathematiker-Vereinigung (in German). 28: 31–40. JFM 47.0882.06.
- ^ Stein, Sherman K. (2010). Mathematics: The Man-Made Universe. Courier Dover Publications. p. 483. ISBN 9780486404509..
- ^ Haselgrove, C. B. (1958). "A disproof of a conjecture of Pólya". Mathematika. 5 (2): 141–145. doi:10.1112/S0025579300001480. ISSN 0025-5793. MR 0104638. Zbl 0085.27102.
- ^ Lehman, R. S. (1960). "On Liouville's function". Mathematics of Computation. 14 (72): 311–320. doi:10.1090/S0025-5718-1960-0120198-5. JSTOR 2003890. MR 0120198.
- ^ Tanaka, M. (1980). "A Numerical Investigation on Cumulative Sum of the Liouville Function". Tokyo Journal of Mathematics. 3 (1): 187–189. doi:10.3836/tjm/1270216093. MR 0584557.