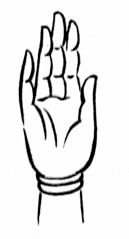
The abhayamudra (Sanskrit: अभयमुद्रा, romanized: abhayamudrā, lit. 'gesture of fearlessness')[2] is a mudra (gesture) that is the gesture of reassurance and safety, which dispels fear and accords divine protection and bliss in Hinduism, Buddhism, and other Indian religions. The right hand is raised to shoulder height, with the palm is facing outward and the fingers pointing upwards [3] This is one of the earliest mudras found depicted on a number of Hindu, Buddhist, Jain, and Sikh images.

Description
editThe abhayamudra represents protection, peace, benevolence and the dispelling of fear. A form of the Hindu god Shiva, Nataraja, is depicted with the second right hand making the abhayamudra, bestowing protection from both evil and ignorance to those who follow the righteousness of dharma. In Theravada Buddhism, it is usually made with the right hand raised to shoulder height, the arm bent and the palm facing outward with the fingers upright and joined and the left hand hanging down while standing. In Thailand and Laos, this mudra is associated with the Walking Buddha, often shown having both hands making a double abhayamudra that is uniform.
The abhayamudra was probably used before the onset of Buddhism as a symbol of good intentions proposing friendship when approaching strangers. In the art of Gandhara, it is present when showing the action of preaching. It was also used in China during the Northern Wei and Sui eras of the 4th and 7th centuries.[citation needed]
The gesture was used by Gautama Buddha to subdue the elephant when attacked by a drunk elephant set off by Devadatta (some says by Ajātasattu),[4] as shown in several frescos and scripts.[citation needed] In Mahayana Buddhism, deities often paired it with another mudra using the other hand.
References
edit- ^ Yves Bonnefoy (1993). Asian Mythologies. University of Chicago Press. pp. 178–179. ISBN 978-0-226-06456-7.
- ^ Buswell, Robert Jr., ed. (2013). Princeton Dictionary of Buddhism. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. p. 2. ISBN 9780691157863.
- ^ "Abhaya Mudra". 17 March 2015. Archived from the original on 18 July 2015. Retrieved 10 February 2015.
- ^ From Dhammapada, Buddhacharita, and Arśapraśamanasūtra
Bibliography
edit- Dallapiccola, Anna L. (2002). Dictionary of Hindu Lore and Legend. Thames & Hudson. ISBN 978-0-500-28402-5.
External links
edit- Media related to Abhayamudra at Wikimedia Commons