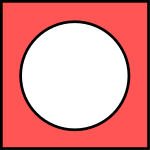
In set theory, the complement of a set A, often denoted by (or A′),[1] is the set of elements not in A.[2]
When all elements in the universe, i.e. all elements under consideration, are considered to be members of a given set U, the absolute complement of A is the set of elements in U that are not in A.
The relative complement of A with respect to a set B, also termed the set difference of B and A, written is the set of elements in B that are not in A.
Absolute complement
editDefinition
editIf A is a set, then the absolute complement of A (or simply the complement of A) is the set of elements not in A (within a larger set that is implicitly defined). In other words, let U be a set that contains all the elements under study; if there is no need to mention U, either because it has been previously specified, or it is obvious and unique, then the absolute complement of A is the relative complement of A in U:[3]
The absolute complement of A is usually denoted by . Other notations include [2] [4]
Examples
edit- Assume that the universe is the set of integers. If A is the set of odd numbers, then the complement of A is the set of even numbers. If B is the set of multiples of 3, then the complement of B is the set of numbers congruent to 1 or 2 modulo 3 (or, in simpler terms, the integers that are not multiples of 3).
- Assume that the universe is the standard 52-card deck. If the set A is the suit of spades, then the complement of A is the union of the suits of clubs, diamonds, and hearts. If the set B is the union of the suits of clubs and diamonds, then the complement of B is the union of the suits of hearts and spades.
- When the universe is the universe of sets described in formalized set theory, the absolute complement of a set is generally not itself a set, but rather a proper class. For more info, see universal set.
Properties
editLet A and B be two sets in a universe U. The following identities capture important properties of absolute complements:
Complement laws:[5]
-
- (this follows from the equivalence of a conditional with its contrapositive).
Involution or double complement law:
Relationships between relative and absolute complements:
Relationship with a set difference:
The first two complement laws above show that if A is a non-empty, proper subset of U, then {A, A∁} is a partition of U.
Relative complement
editDefinition
editIf A and B are sets, then the relative complement of A in B,[5] also termed the set difference of B and A,[6] is the set of elements in B but not in A.
The relative complement of A in B is denoted according to the ISO 31-11 standard. It is sometimes written but this notation is ambiguous, as in some contexts (for example, Minkowski set operations in functional analysis) it can be interpreted as the set of all elements where b is taken from B and a from A.
Formally:
Examples
edit- If is the set of real numbers and is the set of rational numbers, then is the set of irrational numbers.
Properties
editLet A, B, and C be three sets in a universe U. The following identities capture notable properties of relative complements:
-
- with the important special case demonstrating that intersection can be expressed using only the relative complement operation.
- If , then .
- is equivalent to .
Complementary relation
editA binary relation is defined as a subset of a product of sets The complementary relation is the set complement of in The complement of relation can be written Here, is often viewed as a logical matrix with rows representing the elements of and columns elements of The truth of corresponds to 1 in row column Producing the complementary relation to then corresponds to switching all 1s to 0s, and 0s to 1s for the logical matrix of the complement.
Together with composition of relations and converse relations, complementary relations and the algebra of sets are the elementary operations of the calculus of relations.
LaTeX notation
editIn the LaTeX typesetting language, the command \setminus[7] is usually used for rendering a set difference symbol, which is similar to a backslash symbol. When rendered, the \setminus command looks identical to \backslash, except that it has a little more space in front and behind the slash, akin to the LaTeX sequence \mathbin{\backslash}. A variant \smallsetminus is available in the amssymb package, but this symbol is not included separately in Unicode. The symbol (as opposed to ) is produced by \complement. (It corresponds to the Unicode symbol U+2201 ∁ COMPLEMENT.)
See also
edit- Algebra of sets – Identities and relationships involving sets
- Intersection (set theory) – Set of elements common to all of some sets
- List of set identities and relations – Equalities for combinations of sets
- Naive set theory – Informal set theories
- Symmetric difference – Elements in exactly one of two sets
- Union (set theory) – Set of elements in any of some sets
Notes
edit- ^ "Complement and Set Difference". web.mnstate.edu. Retrieved 2020-09-04.
- ^ a b "Complement (set) Definition (Illustrated Mathematics Dictionary)". www.mathsisfun.com. Retrieved 2020-09-04.
- ^ The set in which the complement is considered is thus implicitly mentioned in an absolute complement, and explicitly mentioned in a relative complement.
- ^ Bourbaki 1970, p. E II.6.
- ^ a b c Halmos 1960, p. 17.
- ^ Devlin 1979, p. 6.
- ^ [1] Archived 2022-03-05 at the Wayback Machine The Comprehensive LaTeX Symbol List
References
edit- Bourbaki, N. (1970). Théorie des ensembles (in French). Paris: Hermann. ISBN 978-3-540-34034-8.
- Devlin, Keith J. (1979). Fundamentals of contemporary set theory. Universitext. Springer. ISBN 0-387-90441-7. Zbl 0407.04003.
- Halmos, Paul R. (1960). Naive set theory. The University Series in Undergraduate Mathematics. van Nostrand Company. ISBN 9780442030643. Zbl 0087.04403.