Male accessory glands (MAG) are the seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and the bulbourethral glands.[1][better source needed] These glands are found only in mammals.[2] In insects, male accessory glands produce products that mix with the sperm to protect and preserve them, including seminal fluid proteins.[3] Some insecticides can induce an increase in the protein content of the male accessory glands of certain types of insects. This has the unintended effect of increasing the number of offspring they produce.[4]
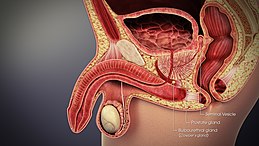
The accessory glands of male mammals secrete fluid for nourishment of sperm and sexual attraction.[2]
Accessory glands
editThis section needs additional citations for verification. (September 2018) |
The male accessory glands are the ampullary gland, seminal vesicle, prostate, bulbourethral gland, and urethral gland.[5]
The products of these glands serve to nourish and activate the spermatozoa, to clear the urethral tract prior to ejaculation, serve as the vehicle of transport of the spermatozoa in the female tract, and to plug the female tract after placement of spermatozoa to help ensure fertilization. Although the glands are usually described as being branched tubular or branched tubuloalveolar, they vary in their organization and in their distribution in different species.
Ampullary glands
editEach of these branched tubular glands lined by simple columnar epithelium is an enlargement of the vas deferens in its terminal portion. These are typical tubular glands in ruminants, horses and dogs; absent in the cat and poorly developed in boars. The function of the white serous secretion is not known.
Seminal vesicles
editThe secretory endpieces of these glands are lined with simple columnar epithelium; the main ducts are lined with stratified columnar epithelium. These glands do not occur in carnivores, but are present in some form in horses, ruminants and swine. Seminal fluid, the product of this gland, serves as a vehicle for the transport of spermatozoa.
Prostate gland
editGrossly the prostate gland can be divided into two parts: the body and the disseminate part. Low cuboidal to low columnar epithelium provides the lining for this compound, tubuloalveolar gland which consists primarily of serous secretory end pieces. The secretion of this gland is more serous in dogs and more mucous in bulls. It serves to promote the movement of spermatozoa and to form a vaginal plug. Additionally, in bulls, the secretion contains high amounts of fructose and citric acid. Concretions may be present in the secretory end pieces as well as parts of the duct system.[citation needed] The prostate and Cowper's glands are the only male accessory glands in marsupials.[6]
Bulbourethral glands
editThe lining of these paired, compound, tubuloalveloar glands is simple columnar epithelium. A capsule of dense connective tissue contains some smooth muscle as well as skeletal muscle of the bulbospongiosus and urethral muscles. All domestic species have these glands except the dog, and their mucus secretion serves to clear the urethra of urine and to lubricate it and the vagina. The product may also serve as an energy source for the spermatozoa.
Urethral glands
editIn some species, branched tubular mucous glands are found along the length of the urethra, especially dorsal to the lumen of the urethra. The exact function of their product is not clear.
Distribution in insects
editThe male accessory gland is also prevalent in some species of butterflies and moths. An example is the cotton leafworm, or Spodoptera litura, in which the males transfer MAG to the females during copulation. This results in a wide range of post-mating behavior in the females, the most noteworthy being the decrease in sexual receptivity in the females. This helps to assure that no other males will mate with that female, allowing her eggs to be fertilized by the current male's own sperm.[7]
See also
edit- Male accessory gland infection (MAGI)
- Female accessory glands: Skene's glands and Bartholin's glands (cf. List of related male and female reproductive organs)
References
edit- ^ Darling, David. "male reproductive accessory glands". male reproductive accessory glands.
- ^ a b Hyman, Libbie Henrietta (1992-09-15). Hyman's Comparative Vertebrate Anatomy. University of Chicago Press. ISBN 978-0-226-87013-7.
- ^ Keeley, Larry. "INSECT ORGANIZATION: STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION". Texas A&M University. Archived from the original on 2010-09-24. Retrieved 2010-09-01.
- ^ Li-Ping Wang, Jun Shen, Lin-Quan Ge, Jin-Cai Wu, Guo-Qin Yang and Gary C. Jahn. Insecticide-induced increase in the protein content of male accessory glands and its effect on the fecundity of females in the brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens Stål (Hemiptera: Delphacidae). Crop Protection 29:1280-1285.
- ^ Knobil, Ernst (2006). Knobil and Neill's Physiology of Reproduction. Gulf Professional Publishing. ISBN 978-0-12-515401-7.
- ^ Renfree, Marilyn; Hugh Tyndale-Biscoe (1987). Reproductive Physiology of Marsupials. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521337922.
- ^ Yu, Jin-Feng; Li, Cong; Xu, Jin; Liu, Jian-Hong; Ye, Hui (2014-01-01). "Male Accessory Gland Secretions Modulate Female Post-Mating Behavior in the Moth Spodoptera litura". Journal of Insect Behavior. 27 (1): 105–116. Bibcode:2014JIBeh..27..105Y. doi:10.1007/s10905-013-9414-4. ISSN 0892-7553.