This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. (February 2021) |
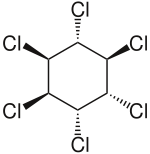
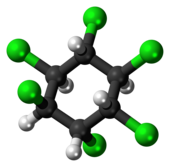
α-Hexachlorocyclohexane (α-HCH) is an organochloride which is one of the isomers of hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH).[1] It is a byproduct of the production of the insecticide lindane (γ-HCH) and it is typically still contained in commercial grade lindane used as insecticide. Lindane, however, has not been produced or used in the United States for more than 20 years.[1] At ambient temperatures it is a stable, white, powdery solid substance. As of 2009, the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants classified (α-HCH) and (β-HCH) as persistent organic pollutants (POPs), due to the chemical's ability to persistence in the environment, bioaccumulative, biomagnifying, and long-range transport capacity.
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(1R,2R,3S,4S,5S,6S)-1,2,3,4,5,6-Hexachlorocyclohexane | |
| Other names
α-HCH
α-Benzenehexachloride α-BHC alpha-hexacloran(e) alpha-Lindane | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.702 |
| EC Number |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2761, 2811, 3082 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H6Cl6 | |
| Molar mass | 290.83 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ a b Toxicological Profile for Alpha-, Beta-, Gamma-, and Delta-Hexachlorocyclohexane, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry, August 2005