Anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPAs) are autoantibodies (antibodies to an individual's own proteins) that are directed against peptides and proteins that are citrullinated. They are present in the majority of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clinically, cyclic citrullinated peptides (CCP) are frequently used to detect these antibodies in patient serum or plasma (then referred to as anti–citrullinated peptide antibodies).[1]
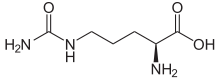
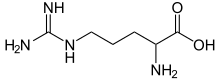
During inflammation, arginine amino acid residues can be enzymatically converted into citrulline residues in proteins such as vimentin, by a process called citrullination. If their shapes are significantly altered, the proteins may be seen as antigens by the immune system, thereby generating an immune response.[2]
ACPAs have proved to be powerful biomarkers that allow the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) to be made at a very early stage.[1] In July 2010, the 2010 ACR/EULAR Rheumatoid Arthritis Classification Criteria were introduced.[3] These new classification criteria include ACPA testing, and overruled the "old" ACR criteria of 1987 and are adapted for early RA diagnosis.
History
editThe presence of autoantibodies against citrullinated proteins in rheumatoid arthritis patients was first described in the mid-1970s when the biochemical basis of antibody reactivity against keratin and filaggrin was investigated.[4][5] Subsequent studies demonstrated that autoantibodies from RA patients react with a series of different citrullinated antigens, including fibrinogen, deiminated Epstein-Barr Virus Nuclear Antigen 1 and vimentin,[6][7][8] which is a member of the intermediate filament family of proteins. Several assays for detecting ACPAs were developed in the following years, employing mutated citrullinated Vimentin (MCV-assay), filaggrin-derived peptides (CCP-assay)[9][10] and viral citrullinated peptides (VCP-assay).
A 2006 clinical study showed that anti viral citrullinated peptide (VCP) antibodies of the IgG and IgA isotypes represent a discriminating specific marker of rheumatoid arthritis from other chronic arthritides and disease controls, suggesting an independent production of each isotype.[11] In 2010, ACPA testing has become substantial part of The 2010 ACR-EULAR classification criteria for rheumatoid arthritis.[3]
Clinical significance
editIn a comparative study (in 2007), various detection kits had a sensitivity between 69.6% and 77.5% and a specificity between 87.8% and 96.4%.[12] Despite the excellent performance of these immunoassays, for example CCP-assays, they only provide a sensitivity comparable with that of rheumatoid factor (RF). Moreover, analysis of the correlation of anti-CCP antibody titre with RA disease activity yielded conflicting results.[13][14]
However, novel test systems utilizing ACPA have been developed. Citrullinated vimentin is a very promising autoantigen in RA, and a suitable tool for studying this systemic autoimmune disease. Vimentin is secreted and citrullinated by macrophages in response to apoptosis, or by pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha).[15] [16] A newly developed ELISA system utilises genetically modified citrullinated vimentin (MCV), a naturally occurring isoform of vimentin to optimize the performance of the test.[6][17] Noteworthy are the findings of a recently published study that highly valuates anti-MCV test systems for diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis in anti-CCP-negative patients. However, data from all around the world vary substantially.[18] Anti-CCP is also very useful in the early diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis in high-risk groups, such as relatives of RA patients,[19] although Silman and co-workers found that the concordance rate of developing RA was 15.4% among identical (monozygotic) twins and was 3.6% among fraternal (dizygotic) twins.[20]
Given that ACPA are more specific than rheumatoid factor, they are used to distinguish various causes of arthritis.[21] Novel assays may be useful for monitoring disease activity and effects of RA therapy.[22]
The reference ranges for blood tests of anti–citrullinated protein antibodies are:
| Negative | Low/weak positive | Moderate positive | High/strong positive | Unit |
| < 20[23] | 20–39[23] | 40–59[23] | > 60[23] | EU[23] |
Anti-CCP is part of the 2010 ACR/EULAR classification criteria for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Anti-CCP positivity is also a good prognostic marker for future radiographic damage, and possibly a marker to B-cell therapy responses including rituximab.[24]
Combination of anti-CCP with other serological markers like rheumatoid factor, 14-3-3η (YWHAH) not only enhances the diagnostic capture rate but together with acute phase reactants either in early disease or at the time of diagnosis may be useful in predicting future outcomes.
Other ACPAs and citrullinated targets in RA
editVimentin, fibrin, filaggrin, enolase and keratin are common citrullination targets. The list of proteins that undergo citrullination and make up the citrullinome continues to increase. The RA associated citrullinome has been reported to include targets from synovial fluid and tissue that range from proteases, receptors, and carrier proteins. These proteins are components of complement, proteolytic activity, cell recognition, endocytosis, and response to biotic stimuli amongst others.[25] 14-3-3η (YWHAH) is also another synovial derived protein that has been reported as a citrullination target.[26]
References
edit- ^ a b Puszczewicz M, Iwaszkiewicz C (May 2011). "Role of anti-citrullinated protein antibodies in diagnosis and prognosis of rheumatoid arthritis". Arch Med Sci. 7 (2): 189–94. doi:10.5114/aoms.2011.22067. PMC 3258718. PMID 22291756.
- ^ Raptopoulou A, Sidiropoulos P, Katsouraki M, Boumpas DT (2007). "Anti-citrulline antibodies in the diagnosis and prognosis of rheumatoid arthritis: evolving concepts". Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 44 (4): 339–63. doi:10.1080/10408360701295623. PMID 17558653. S2CID 1773519.
- ^ a b Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, et al. (September 2010). "2010 rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative" (PDF). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 69 (9): 1580–8. doi:10.1136/ard.2010.138461. PMID 20699241. S2CID 1191830.
- ^ Young BJ, Mallya RK, Leslie RD, Clark CJ, Hamblin TJ (July 1979). "Anti-keratin antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis". Br Med J. 2 (6182): 97–9. doi:10.1136/bmj.2.6182.97. PMC 1596039. PMID 111762.
- ^ Sebbag M, Simon M, Vincent C, et al. (June 1995). "The antiperinuclear factor and the so-called antikeratin antibodies are the same rheumatoid arthritis-specific autoantibodies". J. Clin. Invest. 95 (6): 2672–9. doi:10.1172/JCI117969. PMC 295950. PMID 7539459.
- ^ a b Vossenaar ER, Després N, Lapointe E, et al. (2004). "Rheumatoid arthritis specific anti-Sa antibodies target citrullinated vimentin". Arthritis Research & Therapy. 6 (2): R142–50. doi:10.1186/ar1149. PMC 400433. PMID 15059278.
- ^ Pratesi F, Tommasi C, Anzilotti C, Chimenti D, Migliorini P (March 2006). "Deiminated Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 1 is a target of anti-citrullinated protein antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis". Arthritis Rheum. 54 (3): 733–41. doi:10.1002/art.21629. PMID 16508937.
- ^ Bang H, Egerer K, Gauliard A, et al. (August 2007). "Mutation and citrullination modifies vimentin to a novel autoantigen for rheumatoid arthritis". Arthritis Rheum. 56 (8): 2503–11. doi:10.1002/art.22817. PMID 17665451.
- ^ cyclic+citrullinated+peptide at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- ^ Nishimura K, Sugiyama D, Kogata Y, et al. (June 2007). "Meta-analysis: diagnostic accuracy of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody and rheumatoid factor for rheumatoid arthritis". Annals of Internal Medicine. 146 (11): 797–808. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-146-11-200706050-00008. PMID 17548411. S2CID 6640507.
- ^ C. Anzilotti; L. Riente; F. Pratesi; D. Chimenti; A. Delle Sedie; S. Bombardieri; P. Migliorini (October 2007). "IgG, IgA, IgM antibodies to a viral citrullinated peptide in patients affected by rheumatoid arthritis, chronic arthritides and connective tissue disorders". Rheumatology. 46 (10): 1579–82. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kem193. ISSN 1462-0324. OCLC 173280877. PMID 17717033. Archived from the original on 30 August 2020.
- ^ Coenen D, Verschueren P, Westhovens R, Bossuyt X (March 2007). "Technical and diagnostic performance of 6 assays for the measurement of citrullinated protein/peptide antibodies in the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis". Clin. Chem. 53 (3): 498–504. doi:10.1373/clinchem.2006.078063. PMID 17259232.
- ^ van Gaalen F, Ioan-Facsinay A, Huizinga TW, Toes RE (1 November 2005). "The devil in the details: the emerging role of anticitrulline autoimmunity in rheumatoid arthritis". J. Immunol. 175 (9): 5575–80. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.175.9.5575. PMID 16237041.
- ^ Greiner A, Plischke H, Kellner H, Gruber R (June 2005). "Association of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies, anti-citrullin antibodies, and IgM and IgA rheumatoid factors with serological parameters of disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis". Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1050: 295–303. doi:10.1196/annals.1313.031. PMID 16014545. S2CID 12252627.
- ^ Asaga H, Yamada M, Senshu T (February 1998). "Selective deimination of vimentin in calcium ionophore-induced apoptosis of mouse peritoneal macrophages". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 243 (3): 641–6. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1998.8148. PMID 9500980.
- ^ Mor-Vaknin N, Punturieri A, Sitwala K, Markovitz DM (January 2003). "Vimentin is secreted by activated macrophages". Nat. Cell Biol. 5 (1): 59–63. doi:10.1038/ncb898. PMID 12483219. S2CID 30850762.
- ^ Soós L, Szekanecz Z, Szabó Z, et al. (August 2007). "Clinical evaluation of anti-mutated citrullinated vimentin by ELISA in rheumatoid arthritis". J. Rheumatol. 34 (8): 1658–63. PMID 17611988. Archived from the original on 20 February 2008. Retrieved 27 March 2009.
- ^ Iwaszkiewicz C, Puszczewicz M, Białkowska-Puszczewicz G (January 2015). "Diagnostic value of the anti-Sa antibody compared with the anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody in rheumatoid arthritis". International Journal of Rheumatic Diseases. 18 (1): 46–51. doi:10.1111/1756-185X.12544. PMID 25488711. S2CID 12677526.
- ^ Goeldner, I.; Skare, T. L.; De Messias Reason, I. T.; Nisihara, R. M.; Silva, M. B.; Utiyama, S. R. (August 2010). "Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies and rheumatoid factor in rheumatoid arthritis patients and relatives from Brazil". Rheumatology (Oxford). 49 (8): 1590–3. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keq134. PMID 20457731.
- ^ Silman AJ, MacGregor AJ, Thomson W, et al. (October 1993). "Twin concordance rates for rheumatoid arthritis: results from a nationwide study". Br J Rheumatology. 32 (10): 903–7. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/32.10.903. PMID 8402000.
- ^ Avouac J, Gossec L, Dougados M (July 2006). "Diagnostic and predictive value of anti-cyclic citrullinated protein antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic literature review". Ann. Rheum. Dis. 65 (7): 845–51. doi:10.1136/ard.2006.051391. PMC 1798205. PMID 16606649.
- ^ Nicaise Roland P, Grootenboer Mignot S, Bruns A, et al. (2008). "Antibodies to mutated citrullinated vimentin for diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis in anti-CCP-negative patients and for monitoring infliximab therapy". Arthritis Research & Therapy. 10 (6): R142. doi:10.1186/ar2570. PMC 2656247. PMID 19077182.
- ^ a b c d e chronolab.com > Autoantibodies associated with rheumatic diseases > Reference ranges Archived 30 July 2013 at the Wayback Machine Retrieved on 29 April 2010
- ^ Gardette A, Ottaviani S, Tubach F, Roy C, Nicaise-Roland P, Palazzo E, Gill G, Meyer O, Dieudé P (October 2014). "High anti-CCP antibody titres predict good response to rituximab in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis". Joint Bone Spine. 81 (5): 416–20. doi:10.1016/j.jbspin.2014.06.001. PMID 24998790.
- ^ Tilvawala R, Nguyen SH, Maurais AJ, Nemmara VV, Nagar M, Salinger AJ, Nagpal S, Weerapana E, Thompson PR (June 2018). "The Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Citrullinome". Cell Chem Biol. 25 (6): 691–704.e6. doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2018.03.002. PMC 6014894. PMID 29628436.
- ^ Maksymowych WP, Marotta A (2014). "14-3-3η: a novel biomarker platform for rheumatoid arthritis". Clin Exp Rheumatol. 32 (5 Suppl 85): S–35–9. PMID 25365087.