Posterior superior alveolar artery
The posterior superior alveolar artery (posterior dental artery) is a branch of the maxillary artery.[1][2] It is one of two or three superior alveolar arteries. It provides arterial supply to the molar and premolar teeth, maxillary sinus and adjacent bone, and the gingiva.[2]
| Posterior superior alveolar artery | |
|---|---|
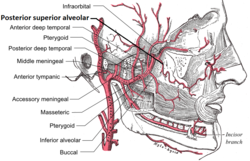 Plan of branches of maxillary artery | |
 Plan of branches of maxillary artery. (Post. sup. alveolar in lower right.) | |
| Details | |
| Branches | Branches to alveolar canals branches to gingiva |
| Supplies | Molar and premolar teeth lining of the maxillary sinus gingiva |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | arteria alveolaris superior posterior |
| TA98 | A12.2.05.075 |
| TA2 | 4444 |
| FMA | 49757 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Anatomy
editOrigin
editThe artery typically arises from maxillary artery within the pterygopalatine fossa. It frequently arises in conjunction with the infraorbital artery.[2]
Course
editIt passes inferior-ward upon the infratemporal surface of maxilla before ramifying.[2]
Branches
editIt emits branches that pass through foramina on the posterior aspect of the maxilla alongside the posterior superior alveolar nerves.[1]
Some branches enter the alveolar canals to supply the upper molar and premolar teeth as well as the maxillary sinus and adjacent bone.[2]
Some branches pass anterior-ward[citation needed] across the alveolar process to supply the gingiva.[2]
See also
editAdditional images
edit-
Left maxilla. Outer surface.
References
edit- ^ a b Sinnatamby, Chummy S. (2011). Last's Anatomy (12th ed.). pp. 362–364. ISBN 978-0-7295-3752-0.
- ^ a b c d e f Standring, Susan (2020). Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice (42th ed.). New York. p. 653. ISBN 978-0-7020-7707-4. OCLC 1201341621.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 562 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
edit- lesson4 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (infratempfossaart)