The House of Representatives (Majlis al-Nuwaab) is the lower house of the Parliament of Yemen. It shares the legislative power with the Shura Council, the upper house.[2][3] The Assembly of Representatives has 301 members, elected for a six-year term in single-seat constituencies. It is one of the rare parliamentary chambers in the world to currently have no female representation.[4]
House of Representatives مجلس النواب اليمني | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | |
| Type | Lower house of the Parliament of Yemen |
| History | |
| Founded | 1990 |
| Leadership | |
| Structure | |
| Seats | 301 |
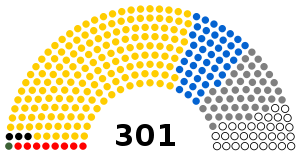 | |
Political groups | Elected in 2003
General People's Congress (168) |
| Committees | Unknown |
Joint committees | Unknown |
| Elections | |
| First-past-the-post | |
Last election | 27 April 2003 |
Next election | TBD (indefinitely postponed) |
| Website | |
| parliament-ye.com (exile government)[1] yemenparliament.gov.ye (Sanaa Government) [2] | |
The House of Representatives was established in 1990 after the unification of Yemen for a transitional period.[5] An election hasn't been held for the body since 2003. An election was set for 27 April 2009, but president Saleh postponed it by two years on 24 February 2009.[6][7] However, the election did not take place on 27 April 2011, and was again postponed until the next presidential election, sometime in February 2014.[8][9] In January 2014, the final session of the National Dialogue Conference (NDC) announced that both elections had been delayed, and would occur within 9 months of a referendum on a new constitution which had yet to be drafted.[10] However both the GPC and Houthi representatives on the National Authority for Monitoring the Implementation of NDC Outcomes have refused to vote on the new constitution drafted by the constitution drafting committee, which submitted it in January 2015.[11]
In February 2015, the Houthis briefly dissolved parliament before reportedly agreeing to reinstate the 301-member assembly in UN-brokered talks. Under the agreement, it will be augmented by a "people's transitional council" serving as the upper house.[12]
Since the civil war, the House of Representatives had held semi-regular sessions in San'aa in Houthi-held territory. In 13 April 2019, the first session was held in Seiyun, in Hadi-controlled Hadhramaut Governorate.[13]
Latest elections
editThe last parliamentary election in Yemen took place in 2003.
| Party | Votes | % | Seats | +/– | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| General People's Congress | 3,465,117 | 57.79 | 229 | +42 | |
| Al-Islah | 1,349,485 | 22.51 | 45 | –8 | |
| Yemeni Socialist Party | 291,541 | 4.86 | 7 | New | |
| Nasserist Unionist People's Organisation | 109,714 | 1.83 | 3 | 0 | |
| Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party | 40,872 | 0.68 | 2 | 0 | |
| Unnamed party | 25,352 | 0.42 | 1 | – | |
| National Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party | 23,745 | 0.40 | 0 | 0 | |
| Nasserist Reform Organisation | 15,257 | 0.25 | 0 | 0 | |
| Union of Popular Forces | 11,967 | 0.20 | 0 | – | |
| Democratic Nasserist Party | 9,829 | 0.16 | 0 | 0 | |
| National Democratic Front | 7,056 | 0.12 | 0 | – | |
| Social Nationalist Party – Yemen | 5,349 | 0.09 | 0 | – | |
| Party of Truth | 4,585 | 0.08 | 0 | 0 | |
| People's Democratic Party | 4,077 | 0.07 | 0 | – | |
| Democratic Union of Popular Forces | 3,003 | 0.05 | 0 | – | |
| Social Green Party | 2,276 | 0.04 | 0 | – | |
| Popular Unity Party | 1,739 | 0.03 | 0 | – | |
| Yemeni League Party | 1,383 | 0.02 | 0 | – | |
| Liberation Front Party | 1,282 | 0.02 | 0 | – | |
| Popular Unionist Liberation Party | 1,241 | 0.02 | 0 | – | |
| Yemeni Unionist Gathering | 483 | 0.01 | 0 | – | |
| Democratic September Organization | 81 | 0.00 | 0 | – | |
| Independents | 620,615 | 10.35 | 14 | –40 | |
| Total | 5,996,049 | 100.00 | 301 | 0 | |
| Valid votes | 5,996,049 | 96.69 | |||
| Invalid/blank votes | 205,205 | 3.31 | |||
| Total votes | 6,201,254 | 100.00 | |||
| Registered voters/turnout | 8,097,514 | 76.58 | |||
| Source: Yemen NIC | |||||
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ "Yemeni Parliament to hold first session Thursday in Seyoun". 10 April 2019.
- ^ "Constitutional history of Yemen". ConstitutionNet. Retrieved 26 June 2019.
- ^ "Yemen". Freedom House. Archived from the original on 13 August 2018. Retrieved 26 June 2019.
- ^ "Monthly ranking of women in national parliaments". Parline: the IPU’s Open Data Platform. Retrieved 2021-09-28.
- ^ "مجلس النواب اليمني".
- ^ Stephen Day (2009-06-02). "Yemen Postpones Its April 2009 Parliamentary Elections". Middle East Institute. Retrieved 2015-04-04.
- ^ Parliament Overwhelmingly Approves Proposal To Extend Term- Yemen Post English Newspaper Online. Yemenpost.net. Retrieved on 2010-11-08.
- ^ "September 2012 Monthly Forecast – Yemen". Security Council Report. 2012-08-31.
- ^ "Foreign Secretary welcomes Yemeni plan for elections in 2014" (Press release). Foreign & Commonwealth Office, UK. 7 March 2013. Retrieved 7 July 2013.
- ^ "Yemen's 'national dialogue' ends in violence, no election scheduled". Archived from the original on 2015-01-21. Retrieved 2016-01-05.
- ^ "Houthis and GPC refuse to vote on constitution". Archived from the original on 2018-07-08. Retrieved 2016-01-05.
- ^ "Yemen feuding parties agree on transitional council". Al Jazeera. 20 February 2015. Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- ^ "Yemeni Parliament to hold first session Thursday in Seyoun". 10 April 2019.