Bagaraatan (/'ba-ɣa-raa-tan/ meaning 'small' baɣa + 'carnivorous animal, beast of prey' araatan in Mongolian) is a genus of theropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous period. Its fossils were found in the Nemegt Formation of Mongolia. Bagaraatan may have been around 3 to 4 metres (9.8 to 13 ft) in length.
| Bagaraatan Temporal range: Late Cretaceous,
| |
|---|---|
| |
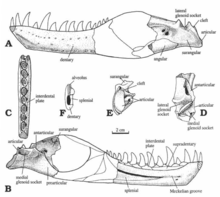
| Lower jaw bones | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Dinosauria |
| Clade: | Saurischia |
| Clade: | Theropoda |
| Clade: | †Pantyrannosauria |
| Genus: | †Bagaraatan Osmólska, 1996 |
| Type species | |
| †Bagaraatan ostromi Osmólska, 1996
| |
History
editThe type species, B. ostromi, was described by Halszka Osmólska in 1996. Initially, the post-cranial (ZPAL MgD-I/108) skeleton had been described as "bird-like", while the skull was noted to exhibit features of several different theropod groups.
The material that warranted this conclusion was later found to be a chimaera of two non-avian dinosaurs, with some of the post-crania (hand bones, left femur, tibiotarsus, and rib) being referred to an indeterminate caenagnathid, possibly Elmisaurus. The material that is considered the holotype, which includes the mandible, axial skeleton, pelvis, and one pedal phalanx, likely indicates that Bagaraatan is an indeterminate tyrannosaurid. Similarities between the material and young specimens of Tyrannosaurus and Tarbosaurus indicate that the holotype represents a juvenile tyrannosaurid, one of the smallest currently known.[1]
Classification
editHoltz classified Bagaraatan as a basal tyrannosauroid, Coria identified it as a troodontid, and Rauhut placed it in Maniraptora.[2] Mark Loewen et al. placed it in basal Tyrannosauroidea, agreeing with the placement by Holtz.[3]
Below is the cladogram by Loewen et al. in 2013.[3]
In their 2024 reassessment of Bagaraatan, Słowiak, Brusatte & Szczygielski determined that the initial material referred to Bagaraatan is chimaeric. They suggested that the material recognized as the holotype can more confidently be identified as a member of the Tyrannosauridae or a closely related tyrannosauroid. When tested in a phylogenetic analysis, Bagaraatan was recovered in a polytomy with derived tyrannosauroids within the Tyrannosauridae. However, they caution that its exact phylogenetic position remains uncertain since juvenile specimens tend to be recovered in more basal positions than adults of the same species. Their results are shown in the cladogram below:[1]
References
edit- ^ a b Słowiak, Justyna; Brusatte, Stephen L; Szczygielski, Tomasz (2024-02-16). "Reassessment of the enigmatic Late Cretaceous theropod dinosaur, Bagaraatan ostromi". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. 202 (3). doi:10.1093/zoolinnean/zlad169. ISSN 0024-4082.
- ^ O. W. M. Rauhut (2003). The interrelationships and evolution of basal theropod dinosaurs. Special Papers in Palaeontology 69: 1-213.
- ^ a b Loewen, M.A.; Irmis, R.B.; Sertich, J.J.W.; Currie, P. J.; Sampson, S. D. (2013). Evans, David C (ed.). "Tyrant Dinosaur Evolution Tracks the Rise and Fall of Late Cretaceous Oceans". PLoS ONE. 8 (11): e79420. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...879420L. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0079420. PMC 3819173. PMID 24223179.
Sources
edit- Osmolska, H. (1996). "An unusual theropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Nemegt Formation of Mongolia". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica 41; 1-38 [1]
External links
edit- Dinosaur Mailing List entry which discusses the genus Archived 2012-02-04 at the Wayback Machine
Media related to Bagaraatan at Wikimedia Commons Data related to Bagaraatan at Wikispecies