Berkelium(III) iodide is a binary inorganic compound of berkelium and iodine with the chemical formula BkI3.[1][2]
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
berkelium triiodide
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| BkI3 | |
| Molar mass | 628 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | yellow solid |
| Density | g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 650 °C (1,202 °F; 923 K) |
| Structure | |
| trigonal | |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Radioactive |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Synthesis
editSynthesis of berkelium(III) iodide is by action of hydrogen iodine on berkelium oxide at 650 °C.[3]
Physical properties
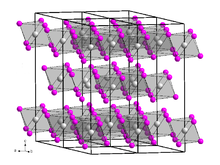
editBerkelium triiodide forms a yellow solid[4] of the trigonal crystal system, space group R3 (No. 148), lattice parameters a = 758.4 pm and c = 2087 pm. Its crystal structure is the same as that of bismuth triiodide.
References
edit- ^ Donnay, Joseph Désiré Hubert (1978). Crystal Data: Inorganic compounds 1967-1969. National Bureau of Standards. p. 192. Retrieved 11 April 2023.
- ^ Yaws, Carl (6 January 2015). The Yaws Handbook of Physical Properties for Hydrocarbons and Chemicals: Physical Properties for More Than 54,000 Organic and Inorganic Chemical Compounds, Coverage for C1 to C100 Organics and Ac to Zr Inorganics. Gulf Professional Publishing. p. 698. ISBN 978-0-12-801146-1. Retrieved 11 April 2023.
- ^ Mi͡asoedov, Boris Fedorovich (1974). Analytical Chemistry of Transplutonium Elements. Wiley. p. 101. ISBN 978-0-470-62715-0. Retrieved 11 April 2023.
- ^ "WebElements Periodic Table » Berkelium » berkelium triiodide". webelements.com. Retrieved 11 April 2023.