A bifid nose (also known as cleft nose) is an uncommon congenital malformation which is characterized by the presence of a cleft between the two nostrils of the nose.[1] It is the result of a disturbance during embryological nose development.[2]
| Bifid nose | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Bifid nose tip, cleft nose, cleft nose tip, median fissure of nose, median cleft of nose. |
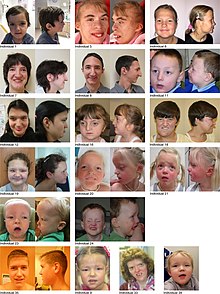 | |
| Individuals with Snijders Blok-Campeau syndrome, one of which (Individual 8) has a noticeable bifid nose tip. | |
| Specialty | Medical genetics, plastic surgery |
| Symptoms | Having a cleft between the two nostrils of the nose. |
| Complications | Usually, there aren't any. |
| Usual onset | Conception |
| Duration | Life-long (unless cosmetic surgery is done) |
| Causes | Genetics |
| Risk factors | Having parents or close relatives with the disorder |
| Diagnostic method | Physical evaluation |
| Prevention | none |
| Treatment | usually, none is necessary |
| Prognosis | Good |
| Frequency | Uncommon |
| Deaths | none |
It is part of the Tessier classification for craniofacial clefts.[3]
Signs and symptoms
editThe visibility of this malformation varies from person to person; from a barely noticeable "line" in the middle of the nose to the complete clefting of the nose which results in two "half noses", the airway is usually adequate.[4][5] Individuals with this birth anomaly don't have any symptoms related to their bifid nose.
Complications
editThis condition is merely cosmetic, and the severity of it doesn't affect a person with the disorder (health-wise) since usually there is a normal and adequate nasal airway.
Diagnosis
editThis condition can be diagnosed by physical examination.
This difference can serve as a diagnostic method since it occurs alongside other malformations, such as frontonasal dysplasia, hypertelorbitism and cleft lips.[6][7]
Bifid noses can also be diagnosed prenatally via a coronal view of the face under ultrasonography, they typically have a broad appearance with "a cleavage between the nostrils resembling a double barrel gun".[8]
Causes
editThis condition is caused due to incomplete fusion of both sides of the nose during embryonic life.[9][10][11]
This anomaly is highly hereditary: autosomal dominant and autosomal recessive inheritance patterns have been observed in multiple families.[12]
If the bifid nose is accompanied by abnormalities of the anorectal and renal systems, it may be part of a different separate genetic disorder (which is characterized by overlapping toes, renal adysplasia and variable anorectal anomalies[13][14]) that is caused by autosomal recessive mutations in the FREM1 gene.[15]
Treatment
editGenerally, sutures and rhinoplasty can be done in order to get rid of a bifid nose tip (though what surgery should be done depends on the severity of the cleft nose).[16][17] Open W-shaped surgical incisions have also proven to be effective.[18] Surgery is usually done before the age of 5.[19]
Prevalence
editThis birth anomaly affects less than 0.0008% of people worldwide, making it the most common midline craniofacial cleft.[20]
8% of people with bifid nose also have hypertelorism.[21]
Bifid nose as a hereditary trait
editTwo forms of inheritance pattern for bifid noses have been described: autosomal recessive and autosomal dominant.
One case per inheritance pattern follows:
History
editThis condition was first described in medical literature in 1939[24] by Esser et al. when they described 5 children (4 siblings and a male first-cousin of theirs) from a single family.[25]
Occurrence in animals
editSee also
editReferences
edit- ^ "Bifid Nose". DoveMed. Retrieved 2022-08-25.
- ^ Lugo-Machado, Juan Antonio; Quintero-Bauman, Alejandra; Barragán-Márquez, Fernanda; Vargas-Cárdenas, Luis Gerardo; Sepúlveda-Martínez, Mario; Jiménez-Rodríguez, Martha; Yocupicio-Hernández, Dalia; Gutiérrez-Pérez, Martha Lucia (2021-01-01). "Nariz bífida: Presentación de caso Translated title: Bifid Nose: Case presentation". Revista del Cuerpo Médico Hospital Nacional Almanzor Aguinaga Asenjo. doi:10.35434/rcmhnaaa.2021.141.885. S2CID 236398187.
- ^ Chauhan, Dinesh Singh; Guruprasad, Yadavalli (2014-01-01). "A rare occurrence of Tessier's 0 cleft in siblings". Medical Journal of Dr. D.Y. Patil University. 7 (1): 104. doi:10.4103/0975-2870.122808. ISSN 0975-2870.
- ^ "SNOMED CT - Bifid nose - Classes | NCBO BioPortal". bioportal.bioontology.org. Retrieved 2022-08-25.
- ^ Miller, Philip J.; Grinberg, Daniel; Wang, Tom D. (1999-07-01). "Midline Cleft". Archives of Facial Plastic Surgery. 1 (3): 200–203. doi:10.1001/archfaci.1.3.200. ISSN 1521-2491. PMID 10937104.
- ^ "Bifid nose".
- ^ "Bifid nose - About the Disease - Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center". rarediseases.info.nih.gov. Retrieved 2022-05-10.
- ^ Padmanabhan, Laxmi Devi; Hamza, V. Zareena; Thampi, Venugopalan Madhavan; Govindankuttymenon, Usha Madathiparambil (2014-12-01). "Double Barrel Sign: A Pointer for Prenatal Detection of Bifid Nose". Journal of Fetal Medicine. 1 (4): 187–188. doi:10.1007/s40556-015-0032-4. ISSN 2348-8859. S2CID 72797381.
- ^ "Bifid nose".
- ^ Mühlbauer, Wolfgang D. (1976-09-01). "A surgical approach to the bifid nose". Chirurgia Plastica. 3 (3): 175–183. doi:10.1007/BF00274291. ISSN 1435-0130. S2CID 37372814.
- ^ WEAVER, D. F.; BELLINGER, D. H. (1946-10-01). "Bifid Nose Associated with Midline Cleft of the Upper Lip". Archives of Otolaryngology. 44 (4): 480–482. doi:10.1001/archotol.1946.00680060501012. ISSN 0276-0673. PMID 21002094.
- ^ "Orphanet: Bifid nose".
- ^ "KEGG DISEASE: Bifid nose with or without anorectal and renal anomalies". www.genome.jp. Retrieved 2022-08-25.
- ^ "Entry - #608980 - BIFID NOSE WITH OR WITHOUT ANORECTAL AND RENAL ANOMALIES; BNAR - OMIM". omim.org. Retrieved 2022-08-25.
- ^ Alazami, Anas M.; Shaheen, Ranad; Alzahrani, Fatema; Snape, Katie; Saggar, Anand; Brinkmann, Bernd; Bavi, Prashant; Al-Gazali, Lihadh I.; Alkuraya, Fowzan S. (2009-11-13). "FREM1 Mutations Cause Bifid Nose, Renal Agenesis, and Anorectal Malformations Syndrome". The American Journal of Human Genetics. 85 (5): 414–418. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2009.10.008. ISSN 0002-9297. PMC 2771533. PMID 19732862.
- ^ "What is a bifid nasal tip ?".
- ^ Tawfik, Ali; El-Sisi, Hossam Elsayed; Abd El-fattah, Ahmed Musaad (2016-07-01). "Surgical correction of bifid nose". International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology. 86: 72–76. doi:10.1016/j.ijporl.2016.04.004. ISSN 0165-5876. PMID 27260584.
- ^ Wei, Jiao; Herrler, Tanja; Yu, Baofu; Chen, Xiaoxue; Dai, Chuanchang (2022-06-23). "Correction of severe bifid nose deformity using an open W-shaped incision". Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery. 75 (9): 3457–3461. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2022.06.060. ISSN 1748-6815. PMID 35941033. S2CID 249998871.
- ^ "Cleft Nasal Deformity". www.rchsd.org. Retrieved 2022-08-25.
- ^ Wang, Xin; Wang, Huan; You, Jianjun; Zheng, Ruobing; Xu, Yihao; Zhang, Xulong; Guo, Junsheng; Fan, Fei (2021). "Morphological Analysis of Nose in Patients of Tessier No. 0 Cleft with a Bifid Nose in China". Frontiers in Pediatrics. 9: 768176. doi:10.3389/fped.2021.768176. PMC 8668193. PMID 34912760.
- ^ "Symptoms: What are the signs and symptoms of autosomal recessive bifid nose? | ThinkGenetic". thinkgenetic.com. Retrieved 2022-08-25.
- ^ Anyane-Yeboa, K.; Raifman, M. A.; Berant, M.; Frogel, M. P.; Travers, H. (1984-03-01). "Dominant inheritance of bifid nose". American Journal of Medical Genetics. 17 (3): 561–563. doi:10.1002/ajmg.1320170303. ISSN 0148-7299. PMID 6711607.
- ^ Boo-Chai, K. (1965-12-01). "The bifid nose. With a report of 3 cases in siblings". Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 36 (6): 626–628. doi:10.1097/00006534-196512000-00007. ISSN 0032-1052. PMID 5845694.
- ^ Lugo-Machado, Juan Antonio (2021). "Bifid Nose: Case presentation".
- ^ "Entry - 210400 - BIFID NOSE, AUTOSOMAL RECESSIVE - OMIM". omim.org. Retrieved 2022-08-25.
- ^ Arzi, B.; Verstraete, F. (2011). "Repair of a bifid nose combined with a cleft of the primary palate in a 1-year-old dog". Veterinary Surgery. 40 (7): 865–869. doi:10.1111/j.1532-950X.2011.00880.x. PMID 22380669. S2CID 3377802.