Birnaviridae is a family of double-stranded RNA viruses.[1] Salmonid fish, birds and insects serve as natural hosts. There are currently 11 species in this family, divided among seven genera.[2] Diseases associated with this family include infectious pancreatic necrosis in salmonid fish, which causes significant losses to the aquaculture industry, with chronic infection in adult salmonid fish and acute viral disease in young salmonid fish.[2][3]
| Birnaviridae | |
|---|---|
| |
| Infectious bursal disease virus particle | |
| Virus classification | |
| (unranked): | Virus |
| Realm: | Riboviria |
| Kingdom: | Orthornavirae |
| Phylum: | incertae sedis |
| Family: | Birnaviridae |
Structure
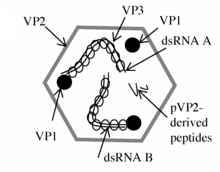
editViruses in family Birnaviridae are non-enveloped, with icosahedral single-shelled geometries, and T=13 symmetry. The diameter is around 70 nm.[2][3]
Genome
editThe genome is composed of linear, bi-segmented, double-stranded RNA. It is around 5.9–6.9 kbp in length and codes for five to six proteins. Birnaviruses encode the following proteins:
RNA-directed RNA polymerase (VP1), which lacks the highly conserved Gly-Asp-Asp (GDD) sequence, a component of the proposed catalytic site of this enzyme family that exists in the conserved motif VI of the palm domain of other RNA-directed RNA polymerases.[4]
The large RNA segment, segment A, of birnaviruses codes for a polyprotein (N-VP2-VP4-VP3-C) [5] that is processed into the major structural proteins of the virion: VP2, VP3 (a minor structural component of the virus), and into the putative protease VP4.[5] VP4 protein is involved in generating VP2 and VP3.[5] recombinant VP3 is more immunogenic than recombinant VP2.[6]
Infectious pancreatic necrosis virus (IPNV), a birnavirus, is an important pathogen in fish farms. Analyses of viral proteins showed that VP2 is the major structural and immunogenic polypeptide of the virus.[7][8] All neutralizing monoclonal antibodies are specific to VP2 and bind to continuous or discontinuous epitopes. The variable domain of VP2 and the 20 adjacent amino acids of the conserved C-terminal are probably the most important in inducing an immune response for the protection of animals.[7]
Non structural protein VP5 is found in RNA segment A.[citation needed] The function of this small viral protein is unknown. It is believed to be involved in influencing apoptosis, but studies are not completely concurring. The protein can not be found in the virion.[citation needed]
Viral Replication
editViral replication is cytoplasmic. Entry into the host cell is achieved by cell receptor endocytosis. Replication follows the double-stranded RNA virus replication model in the cytoplasm. Double-stranded RNA virus transcription is the method of transcription in cytoplasm. The virus is released by budding. Salmonid fish (Aquabirnavirus), young sexually immature chickens (Avibirnavirus), insects (Entomobirnavirus), and blotched snakehead fish (Blosnavirus) are the natural hosts. Transmission routes are contact.[2][3]
Taxonomy
editThe following genera are recognized:
References
edit- ^ Delmas, B; Attoui, H; Ghosh, S; Malik, YS; Mundt, E; Vakharia, VN; Ictv Report, Consortium (January 2019). "ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Birnaviridae". The Journal of General Virology. 100 (1): 5–6. doi:10.1099/jgv.0.001185. PMID 30484762.
- ^ a b c d "Birnaviridae—Birnaviridae—dsRNA Viruses". International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV). Retrieved 16 October 2019.[dead link]
- ^ a b c "Viral Zone". ExPASy. Retrieved 12 June 2015.
- ^ Shwed PS, Dobos P, Cameron LA, Vakharia VN, Duncan R (May 2002). "Birnavirus VP1 proteins form a distinct subgroup of RNA-dependent RNA polymerases lacking a GDD motif". Virology. 296 (2): 241–250. doi:10.1006/viro.2001.1334. PMID 12069523.
- ^ a b c Jagadish MN, Staton VJ, Hudson PJ, Azad AA (March 1988). "Birnavirus precursor polyprotein is processed in Escherichia coli by its own virus-encoded polypeptide". J. Virol. 62 (3): 1084–7. doi:10.1128/JVI.62.3.1084-1087.1988. PMC 253673. PMID 2828658.
- ^ Moon CH, Do JW, Cha SJ, Bang JD, Park MA, Yoo DJ, Lee JM, Kim HG, Chung DK, Park JW (October 2004). "Comparison of the immunogenicity of recombinant VP2 and VP3 of infectious pancreatic necrosis virus and marine birnavirus". Arch. Virol. 149 (10): 2059–68. doi:10.1007/s00705-004-0339-2. PMID 15669113. S2CID 22958612.
- ^ a b Heppell J, Tarrab E, Lecomte J, Berthiaume L, Arella M (December 1995). "Strain variability and localization of important epitopes on the major structural protein (VP2) of infectious pancreatic necrosis virus". Virology. 214 (1): 40–9. doi:10.1006/viro.1995.9956. PMID 8525637.
- ^ Nobiron I, Galloux M, Henry C, Torhy C, Boudinot P, Lejal N, Da Costa B, Delmas B (February 2008). "Genome and polypeptides characterization of Tellina virus 1 reveals a fifth genetic cluster in the Birnaviridae family". Virology. 371 (2): 350–61. doi:10.1016/j.virol.2007.09.022. PMID 17976679.