Bithionol is an antibacterial, anthelmintic, and algaecide. It is used to treat Anoplocephala perfoliata (tapeworms) in horses[1] and Fasciola hepatica (liver flukes).
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
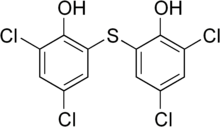
| Other names | 2,4-dichloro- 6-(3,5-dichloro- 2-hydroxyphenyl)sulfanylphenol |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.333 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H6Cl4O2S |
| Molar mass | 356.04 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 188 °C (370 °F) |
| |
| |
| | |
Mechanism of action
editBithionol has been shown to be a potent inhibitor of soluble adenylyl cyclase,[2] an intracellular enzyme important in the catalysis of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). Soluble adenylyl cyclase is uniquely activated by bicarbonate. The cAMP formed by this enzyme is associated with capacitation of sperm, eye pressure regulation, acid-base regulation, and astrocyte/neuron communication.[citation needed]
It is related to the organochlorine hexachlorophene, which has been shown to be an isomer-specific inhibitor of soluble adenylyl cyclase. Bithionol has two aromatic rings with a sulfur atom bonded between them and multiple chlorine ions and hydroxyl groups attached to the phenyl groups. These functional groups are capable of hydrophobic, ionic, and polar interactions.[citation needed]
These intermolecular interactions are responsible for the binding of bithionol to the bicarbonate binding site of soluble adenylyl cyclase efficiently enough to cause competitive inhibition with the usual bicarbonate substrate. The side chain of arginine 176 within the bicarbonate binding site interacts significantly with the aromatic ring of the bithionol molecule. This allosteric, conformational change interferes with the ability of the active site of soluble adenylyl cyclase to adequately bind ATP to convert it into cAMP. Arginine 176 usually interacts with the ATP and other catalytic ions at the active site, so when it turns from its normal position to interact with the bithionol inhibitor, it no longer functions in keeping the ATP bound to the active site.[citation needed]
In another form of inhibition, bithionol is a much larger molecule than simple sodium bicarbonate, so it is large enough to reach through a small channel in the soluble adenylyl cyclase and interfere with binding of ATP, preventing its conversion to cAMP.[citation needed]
This inhibition of the soluble adenylyl cyclase by bithionol at the bicarbonate binding site is demonstrated through a mixed-inhibition graph, where higher concentrations of bithionol have a lower Vmax and a larger Km. This translates to a decreased rate of reaction and a decreased affinity between substrates when bithionol is in higher concentrations.[citation needed]
However, concentrations of bithionol that are required inhibit soluble adenylyl cyclase at clinically relevant levels are also cytotoxic in vivo. Thus, it cannot be used as the therapeutic drug needed to inhibit soluble adenylyl cyclase and therefore decrease the accumulation of cAMP within the cell. However, it sheds light on the search for a compound that will eventually be able to target the bicarbonate binding site of soluble adenylyl cyclase. Bithionol is the first known soluble adenylyl cyclase inhibitor to act through the bicarbonate binding site via a mostly allosteric mechanism.[citation needed]
Safety and regulation
editLD50 (oral, mouse) is 2100 mg/kg.[3]
Bithionol was formerly used in soaps and cosmetics until the U.S. FDA banned it for its photosensitizing effects. The compound has been known to cause photocontact sensitization.[4]
References
edit- ^ Sanada Y, Senba H, Mochizuki R, Arakaki H, Gotoh T, Fukumoto S, Nagahata H (May 2009). "Evaluation of marked rise in fecal egg output after bithionol administration to horse and its application as a diagnostic marker for equine Anoplocephala perfoliata infection". The Journal of Veterinary Medical Science. 71 (5): 617–620. doi:10.1292/jvms.71.617. PMID 19498288.
- ^ Kleinboelting S, Ramos-Espiritu L, Buck H, Colis L, van den Heuvel J, Glickman JF, et al. (April 2016). "Bithionol Potently Inhibits Human Soluble Adenylyl Cyclase through Binding to the Allosteric Activator Site". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 291 (18): 9776–9784. doi:10.1074/jbc.M115.708255. PMC 4850313. PMID 26961873.
- ^ Fiege H, Voges HW, Hamamoto T, Umemura S, Iwata T, Miki H, et al. (2007). "Phenol Derivatives". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a19_313. ISBN 978-3527306732.
- ^ Morton IK, HallJM (1999). Concise Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents. doi:10.1007/978-94-011-4439-1. ISBN 978-94-010-5907-7. S2CID 25401949.