This article needs additional citations for verification. (April 2021) |
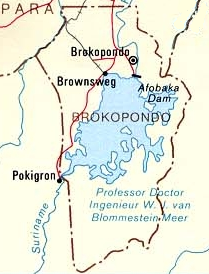
The Brokopondo Reservoir, officially named Professor Doctor Ingenieur W. J. van Blommestein Meer,[1] and also called the Brokopondostuwmeer, is a large reservoir in Suriname. It is named after the Surakarta-born Dutch hydrological engineer Willem Johan van Blommestein. With a surface area of approximately 1,560 km2 (600 sq mi), depending on the current water level, it is one of the largest reservoirs in the world, covering nearly one percent of the country.
| Brokopondo Reservoir | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Coordinates | 4°48′N 55°4′W / 4.800°N 55.067°W |
| Type | Reservoir |
| Primary inflows | Suriname River |
| Primary outflows | Suriname River |
| Catchment area | 12,200 km2 (4,700 sq mi) |
| Basin countries | Suriname |
| Surface area | 1,560 km2 (600 sq mi) |
| Water volume | 20 billion cubic metres (16×106 acre⋅ft) |
History
editThe reservoir was created by constructing Afobaka Dam across the Suriname River between 1961 and 1964. The dam spanning the river is 54 m (177 ft) tall, and is built near the small town of Afobaka. Contrary to the reservoir's long official name, it was quickly rechristened Brokopondomeer by Dutch-speaking locals, after the town of Brokopondo 3 km (2 mi) further downstream from where the dam was constructed. The length of the dam, including secondary dams along the margins of the reservoir, is 12 km (7+1⁄2 mi). The watershed which feeds the reservoir is 12,200 km2 (4,700 sq mi) in area.[2]
The reservoir was put into service in 1965, but did not reach its optimal water level until 1971. Due to the great area of the reservoir, villages home to approximately 5,000 people had to be abandoned. The largest of these, the village of Ganzee, had approximately 1,200 residents.[3] Most displaced residents were moved to new villages (Dutch: transmigratiedorpen) downstream from the dam, in many cases with the same names as the previously abandoned hamlets. The most important being Klaaskreek, Nieuw Ganzee,[3] and Marshallkreek.[4] A separate government operation, "Operation Gwamba," was conducted to save animals from the soon-to-be lake bed.
The dam was constructed in order to provide electricity to plants involved in the processing of bauxite into alumina, and later into purer aluminum metal. These plants were operated by Suralco, the Suriname Aluminum Company, which is a daughter company of Alcoa. About 75% of the dam's electricity was used to power these plants, and the portion of the electricity produced by the dam was used to power Suriname's capital city, Paramaribo. Other advantages of the dam's construction, besides a boost to the aluminum industry, have included the development of the country's inland areas and the surrounding forests, the pushing back of the saltwater boundary in the Suriname River, better irrigation capabilities during times of drought, an increase in tourist activity, and an increase in ease of fishing.
Criticism
editAccording to the 2003 World Bank report Good Dams, Bad Dams, the Brokopondo dam (Afobaka Dam) flooded significantly more hectares of land per megawatt generated than any other large hydropower project analyzed.[5] The report notes that Brokopondo inundated roughly 160,000 hectares of biologically valuable tropical rainforest, while providing only 180 megawatts of capacity, equivalent to 889 ha/MW. For comparison the controversial Three Gorges Dam in China flooded 6 hectares per megawatt, providing 18,000 megawatts while flooding an area smaller than Brokopondo. The global average for all large hydroelectric dams constructed to date is about 60 ha/MW, according to the same report.[6]
Harvesting of trees
editAs a cost reducing measure, the trees of the area were not cut before they started to submerge. This caused problems for shipping activity in the lake. In 2002, Brokopondo Watra Wood International N.V. (BWWI) was given permission by Suralco to a start a pilot investigating the possibility to harvest the remaining trees from the lake. The idea came from the late Paramaribo entrepreneur Orlando Lee On, who read about similar harvesting efforts in the Tucuruí Lake in Brazil when on a plane to Miami.[7][8] In 2004 harvesting began, which resulted in the first shipment of wood from the lake to Europe and the United States in June 2005.[9] The Brokopondo lake wood is marketed in Germany as "Stauseeholz" (English: Reservoir wood).[10] In November 2010, Jens Hahne filmed a documentary about the harvesting activities for the Franco-German channel Arte.[11] This documentary was broadcast on Arte on 22 January 2011.[12]
References
edit- ^ Professor Doctor Ingenieur W.J. van Blommestein Meer: Suriname Geographic.org. Retrieved: 2011-06-07.
- ^ "Afobaka Dam: Suriname". National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency, Bethesda, MD, USA. Retrieved 2013-04-21.
- ^ a b "Rond het sterfbed van mijn dorp". Werkgroep Caraibische Letteren (in Dutch). Retrieved 15 February 2021.
- ^ "Sranan. Cultuur in Suriname". Digital Library for Dutch Literature (in Dutch). Retrieved 16 May 2020.
- ^ World Bank:Good Dams, Bad Dams 2003, p. 22
- ^ George., Ledec (2003). Good dams and bad dams : environmental criteria for site selection of hydroelectric projects. Environmentally and Socially Sustainable Development Sector Management Unit, Latin America and the Caribbean Region, World Bank. OCLC 754104548.
- ^ Armand Snijders - "Duiken naar hout" Archived July 15, 2011, at the Wayback Machine. Parbode. 1 July 2006.
- ^ De Ware Tijd - Orlando Lee On was een zeer gedurfde Surinaamse ondernemer
- ^ Brokopondo Watra Wood International N.V. - Facts Archived October 20, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Stauseeholz.de
- ^ Internationale aandacht voor Surinames onderwaterhoutkap Archived July 24, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Arte.tv - Surinam: le trésor englouti Archived April 3, 2012, at the Wayback Machine
External links
edit- Media related to Brokopondo Reservoir at Wikimedia Commons
