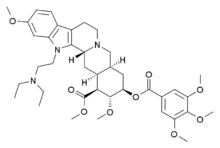
Bietaserpine (INN), or 1-[2-(diethylamino)ethyl]reserpine, is a derivative of reserpine used as an antihypertensive agent. Like reserpine, bietaserpine is a VMAT inhibitor.[1]
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Methyl 1-[2-(diethylamino)ethyl]-11,17α-dimethoxy-18β-[(3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoyl)oxy]-3β,20α-yohimban-16β-carboxylate
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
Methyl (1S,2R,3R,4aS,13bR,14aS)-13-[2-(diethylamino)ethyl]-2,11-dimethoxy-3-[(3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoyl)oxy]-1,2,3,4,4a,5,7,8,13,13b,14,14a-dodecahydroindolo[2′,3′:3,4]pyrido[1,2-b]isoquinoline-1-carboxylate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.151 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C39H53N3O9 | |
| Molar mass | 707.865 g·mol−1 |
| Pharmacology | |
| C02AA07 (WHO) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
References
edit- ^ Buckingham J et al. (eds.) (1993). Dictionary of Natural Products, vol. 5, p. 4923, Boca Raton: Chapman & Hall/CRC. ISBN 978-0-412-46620-5. Retrieved on June 22, 2009 through Google Book Search.