The Syrian brown bear (Ursus arctos syriacus or Ursus arctos arctos)[2] is a medium-sized and endangered subspecies of Eurasian brown bear native to the Middle East and West-Central Asia, particularly around the Caucasus Mountains.[3]
| Syrian brown bear | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Family: | Ursidae |
| Genus: | Ursus |
| Species: | |
| Subspecies: | U. a. syriacus
|
| Trinomial name | |
| Ursus arctos syriacus | |
| |
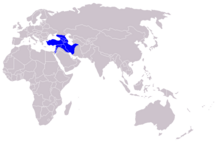
| Historical Distribution | |
| Synonyms | |
|
caucasicus Smirnov, 1919 | |
Characteristics
editThe Syrian brown bear's fur is usually very light brown and straw-coloured.[4] The hair on the withers is longer, with a grey-brown base, and is often a different shade from the rest of the body, seen in some individuals as a dark stripe running across the back. The lighter colors usually appear at higher altitudes. Their legs are commonly darker than the rest of their body. It is the only known bear in the world to have white claws. It is a rather small bear. Adult males have skulls measuring approximately 30–40 cm (12–16 inches). The Syrian brown bear weighs up to 1,102 lb (500 kilograms), and measures from 101–140 cm (40–55 inches) from nose to tail.
Populations in the Caucasus were thought to belong to Ursus arctus syriacus, and to overlap parts of the Eurasian brown bear's range. Eurasian brown bears are larger in size with coats that are considerably darker, likely due to living in more frigid climates, as darker pigmentation helps to absorb heat from the sun.[citation needed] It was thought that these mixed bears originated during the Holocene, when Syrian brown bears supposedly migrated northward and interbred with the larger northern brown bears. Today, that hypothesis is considered by experts to be unfounded. After breeding, the highly protective mother bear gives birth in a den; litter sizes range from one to three cubs.[5]
Distribution and habitat
editHistorically, the brown bear occurred in the Middle East from Turkey to Turkmenistan.[6][7] Today, the brown bear is considered extremely rare (possibly absent) in its namesake Syria, and has been extirpated from Israel, Jordan, Palestine, and the Sinai Peninsula. The bear survives only in Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, Iran, Iraq, Turkey, and Turkmenistan.[8][9] In Syria, brown bear tracks were recorded in the snow in the Anti-Lebanon Mountains in 2004 for the first time in five decades. In February 2011, bear tracks were again recorded in this area.[10]
In Turkey, important habitats are Mediterranean belt forests, deciduous and conifer forests in the Black Sea region and northeastern Turkey, oak and pine forests in the hinterlands of the Black Sea, and dry forests in East Anatolia. In elevation, these habitats range from 500 to 2,700 m (1,600 to 8,900 ft).[11] In Iran, it is present in the Central Alborz Protected Area (south of the Caspian Sea), and in the Zagros Mountains.[5] In these regions, it prefers higher altitudes and northern aspects with access to water resources.[12]
Threats
editIn Turkey, the bear is threatened by large-scale forest fragmentation, degradation of habitat, and persecution in areas where it damages beehives and livestock. Local people in the Black Sea region hunt bears illegally for bear fat, which is thought to have medicinal value. Occasionally, bears are killed during hunts for wild boar using dogs, and by poisoned baits and snares set illegally for red deer, roe deer, wolf or lynx.[11]
In 2018, a sleeping Syrian brown bear was killed by Iraqi forces at the Iraq-Syria border.[13]
In the spring of 2015, three Syrian brown bears were shot and killed in the Northern Iranian county of Savadkuh.[14]
In culture
editThe Syrian brown bear is the bear mentioned in the Bible. The protectiveness of a mother bear towards her cubs is cited proverbially three times (2 Sam. 17:8; Prov. 17:12; Hos. 13:8) in the Hebrew Bible.[15] The Syrian brown bear is also mentioned in 2 Kings 2:23-25 mauling 42 young men who were threatening Elisha.[16]
Wojtek (1942–1963) was a Syrian brown bear. Purchased by Polish soldiers in Iran during World War II, Wojtek became the company mascot. Initially given the rank of private in order to justify his presence in the military camp, he was subsequently promoted to corporal[17] and assisted the soldiers in loading artillery. After the war, Wojtek retired to the Edinburgh Zoo where he became a popular and beloved attraction. His military service is memorialized in Poland, Scotland, England, and Italy.
References
edit- ^ "IUCN Brown Bear subspecies status". Retrieved August 29, 2022.
- ^ Murtskhvaladze, M.; Gavashelishvili, A.; Tarkhnishvili, D. (2010). "Geographic and genetic boundaries of brown bear (Ursus arctos) population in the Caucasus". Molecular Ecology. 19 (9): 1829–1841. Bibcode:2010MolEc..19.1829M. doi:10.1111/j.1365-294X.2010.04610.x. PMID 20345670. S2CID 21347253.
- ^ Masseti, M. (2009-12-28). Neubert, E.; Amr, Z.; Taiti, S.; Gümüs, B. (eds.). "Carnivores of Syria". ZooKeys (31). Aqaba, Jordan: 229–252. Bibcode:2009ZooK...31..229M. doi:10.3897/zookeys.31.170.
- ^ The Syrian Brown Bear
- ^ a b Nezami, B.; Farhadinia, M.S. (2011). "Litter sizes of brown bears in the Central Alborz Protected Area, Iran" (PDF). Ursus. 22 (2): 167–171. doi:10.2192/URSUS-D-10-00026.1. S2CID 83965830. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2019-08-08. Retrieved 2019-08-08.
- ^ Calvignac, S.; Hughes, S.; Hänni, C. (2009). "Genetic diversity of endangered brown bear (Ursus arctos) populations at the crossroads of Europe, Asia and Africa" (PDF). Diversity and Distributions. 15 (5): 1–9. Bibcode:2009DivDi..15..742C. doi:10.1111/j.1472-4642.2009.00586.x.
- ^ Hatt, R. T. (1959). The mammals of Iraq (PDF). Ann Arbor: Museum of Zoology, University of Michigan.
- ^ "Syrian Brown Bear". www.WorldLandTrust.org. Retrieved 29 August 2023.
The Syrian Brown Bear is now extinct in Syria, Israel, Lebanon and the Sinai Peninsula, and survives today in Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, Iraq, Iran, Turkey and Turkmenistan. It lives in mountainous areas where it can be found foraging in forests, grasslands and meadows.
- ^ McLellan, B.N.; Proctor, M.F.; Huber, D.; Michel, S. (2017). "Ursus arctos". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2017: e.T41688A121229971. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-3.RLTS.T41688A121229971.en. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- ^ Garshelis, D.L.; Steinmetz, R.; Hajjar, I.; Tabbaa, D. (2015). "Brown bear(s) do exist in Syria: fuzzy photo generates much interest" (PDF). International Bear News. Vol. 24, no. 1. pp. 5−8.
- ^ a b Can, Ö; Togan, İ. (2004). "Status and management of brown bears in Turkey" (PDF). Ursus. 15 (1): 48−53. doi:10.2192/1537-6176(2004)015<0048:SAMOBB>2.0.CO;2. S2CID 85945926. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2019-08-07. Retrieved 2019-08-07.
- ^ Ataei, F; Karami, M.; Kaboli, M. (2012). "Summer Habitat Suitability Modeling of Brown Bear (Ursus arctos) Southern Alborz Protected Area". Iranian Journal of Natural Resources. 65 (2): 235−245.
- ^ "Iraq forces kill endangered sleeping Syria brown bear". Middle East Monitor. November 9, 2018. Retrieved March 9, 2021.
- ^ Marashi, Mahmoud (25 July 2016). "Seasonal human-brown bear conflicts in northern Iran: implications for conservation". Zoology and Ecology. 27 (2): 100–102. doi:10.1080/21658005.2017.1331786 – via Taylor & Francis Online.
- ^ George Cansdale, "Bear", in Merrill C. Tenney (ed.), The Zondervan Encyclopedia of the Bible, Vol. 1 (Zondervan, 2010).
- ^ American Bible Society. (1986). The Holy Bible : containing the Old and New Testaments; translated out of the original tongues and with the former translations diligently compared and revised. American Bible Society. pp. 2 Kings 2:23–25. OCLC 13621095.
- ^ "Pomnik legendarnego niedźwiedzia Wojtka stanął w Krakowie [Statue of the legendary bear Wojtek unveiled in Krakow]". www.tvp.info (in Polish). Telewizja Polska. 19 May 2014. Retrieved 7 February 2020.
