This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. (September 2019) |
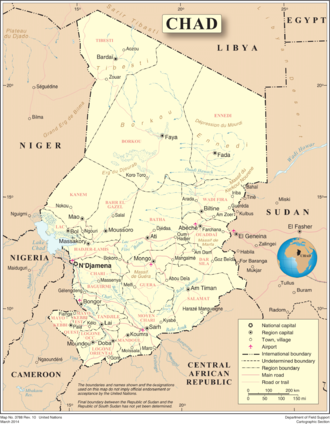
Chad is one of the 47 landlocked countries in the world and is located in North Central Africa, measuring 1,284,000 square kilometers (495,755 sq mi), nearly twice the size of France and slightly more than three times the size of California. Most of its ethnically and linguistically diverse population lives in the south, with densities ranging from 54 persons per square kilometer in the Logone River basin to 0.1 persons in the northern B.E.T. (Borkou-Ennedi-Tibesti) desert region, which itself is larger than France. The capital city of N'Djaména, situated at the confluence of the Chari and Logone Rivers, is cosmopolitan in nature, with a current population in excess of 700,000 people.

Chad has four climatic zones. The northernmost Saharan zone averages less than 200 mm (7.9 in) of rainfall annually. The sparse human population is largely nomadic, with some livestock, mostly small ruminants and camels. The central Sahelian zone receives between 200 and 700 mm (7.9 and 27.6 in) rainfall and has vegetation ranging from grass/shrub steppe to thorny, open savanna. The southern zone, often referred to as the Sudan zone, receives between 700 and 1,000 mm (27.6 and 39.4 in), with woodland savanna and deciduous forests for vegetation. Rainfall in the Guinea zone, located in Chad's southwestern tip, ranges between 1,000 and 1,200 mm (39.4 and 47.2 in).
The country's topography is generally flat,[1] with the elevation gradually rising as one moves north and east away from Lake Chad. The highest point in Chad is Emi Koussi, a mountain that rises 3,100 m (10,171 ft) in the northern Tibesti Mountains. The Ennedi Plateau and the Ouaddaï highlands in the east complete the image of a gradually sloping basin, which descends towards Lake Chad. There are also central highlands in the Guera region rising to 1,500 m (4,921 ft).
Lake Chad is the second largest lake in west Africa[2] and is one of the most important wetlands on the continent.[3] Home to 120 species of fish and at least that many species of birds, the lake has shrunk dramatically in the last four decades due to increased water usage from an expanding population and low rainfall. Bordered by Chad, Niger, Nigeria, and Cameroon, Lake Chad currently covers only 1350 square kilometers, down from 25,000 square kilometers in 1963. The Chari and Logone Rivers, both of which originate in the Central African Republic and flow northward, provide most of the surface water entering Lake Chad. Chad is also next to Niger.
Geographical placement
editLocated in north-central Africa, Chad stretches for about 1,800 kilometers from its northernmost point to its southern boundary.[4] Except in the far northwest and south, where its borders converge, Chad's average width is about 800 kilometers.[4] Its area of 1,284,000 square kilometers is roughly equal to the combined areas of Idaho, Wyoming, Utah, Nevada, and Arizona.[4] Chad's neighbors include Libya to the north, Niger and Nigeria to the west, Sudan to the east, Central African Republic to the south, and Cameroon to the southwest.[4]
Chad exhibits two striking geographical characteristics.[4] First, the country is landlocked.[4] N'Djamena, the capital, is located more than 1,100 kilometers northeast of the Atlantic Ocean; Abéché, a major city in the east, lies 2,650 kilometers from the Red Sea; and Faya-Largeau, a much smaller but strategically important center in the north, is in the middle of the Sahara Desert, 1,550 kilometers from the Mediterranean Sea.[4] These vast distances from the sea have had a profound impact on Chad's historical and contemporary development.[4]
The second noteworthy characteristic is that the country borders on very different parts of the African continent: North Africa, with its Islamic culture and economic orientation toward the Mediterranean Basin; and West Africa, with its diverse religions and cultures and its history of highly developed states and regional economies.[4]
Chad also borders Northeast Africa, oriented toward the Nile Valley and the Red Sea region - and Central or Equatorial Africa, some of whose people have retained classical African religions while others have adopted Christianity, and whose economies were part of the great Congo River system.[4] Although much of Chad's distinctiveness comes from this diversity of influences, since independence the diversity has also been an obstacle to the creation of a national identity.[4]
Land
editAlthough Chadian society is economically, socially, and culturally fragmented, the country's geography is unified by the Lake Chad Basin.[4] Once a huge inland sea (the Pale-Chadian Sea) whose only remnant is shallow Lake Chad, this vast depression extends west into Nigeria and Niger.[4] The larger, northern portion of the basin is bounded within Chad by the Tibesti Mountains in the northwest, the Ennedi Plateau in the northeast, the Ouaddaï Highlands in the east along the border with Sudan, the Guéra Massif in central Chad, and the Mandara Mountains along Chad's southwestern border with Cameroon.[4] The smaller, southern part of the basin falls almost exclusively in Chad.[4] It is delimited in the north by the Guéra Massif, in the south by highlands 250 kilometers south of the border with Central African Republic, and in the southwest by the Mandara Mountains.[4]
Lake Chad, located in the southwestern part of the basin at an altitude of 282 meters, surprisingly does not mark the basin's lowest point; instead, this is found in the Bodele and Djourab regions in the north-central and northeastern parts of the country, respectively.[4] This oddity arises because the great stationary dunes (ergs) of the Kanem region create a dam, preventing lake waters from flowing to the basin's lowest point.[4] At various times in the past, and as late as the 1870s, the Bahr el Ghazal Depression, which extends from the northeastern part of the lake to the Djourab, acted as an overflow canal; since independence, climatic conditions have made overflows impossible.[4]
North and northeast of Lake Chad, the basin extends for more than 800 kilometers, passing through regions characterized by great rolling dunes separated by very deep depressions.[4] Although vegetation holds the dunes in place in the Kanem region, farther north they are bare and have a fluid, rippling character.[4] From its low point in the Djourab, the basin then rises to the plateaus and peaks of the Tibesti Mountains in the north.[4] The summit of this formation—as well as the highest point in the Sahara Desert—is Emi Koussi, a dormant volcano that reaches 3,414 meters above sea level.[4]
The basin's northeastern limit is the Ennedi Plateau, whose limestone bed rises in steps etched by erosion.[4] East of the lake, the basin rises gradually to the Ouaddaï Highlands, which mark Chad's eastern border and also divide the Chad and Nile watersheds.[4] These highland areas are part of the East Saharan montane xeric woodlands ecoregion.
Southeast of Lake Chad, the regular contours of the terrain are broken by the Guéra Massif, which divides the basin into its northern and southern parts.[4] South of the lake lie the floodplains of the Chari and Logone rivers, much of which are inundated during the rainy season.[4] Farther south, the basin floor slopes upward, forming a series of low sand and clay plateaus, called koros, which eventually climb to 615 meters above sea level.[4] South of the Chadian border, the koros divide the Lake Chad Basin from the Ubangi-Zaire river system.[4]
Water systems
editPermanent streams do not exist in northern or central Chad.[4] Following infrequent rains in the Ennedi Plateau and Ouaddaï Highlands, water may flow through depressions called enneris and wadis.[4] Often the result of flash floods, such streams usually dry out within a few days as the remaining puddles seep into the sandy clay soil.[4] The most important of these streams is the Batha, which in the rainy season carries water west from the Ouaddaï Highlands and the Guéra Massif to Lake Fitri.[4]
Chad's major rivers are the Chari and the Logone and their tributaries, which flow from the southeast into Lake Chad.[4] Both river systems rise in the highlands of Central African Republic and Cameroon, regions that receive more than 1,250 millimeters of rainfall annually.[4] Fed by rivers of Central African Republic, as well as by the Bahr Salamat, Bahr Aouk, and Bahr Sara rivers of southeastern Chad, the Chari River is about 1,200 kilometers long.[4] From its origins near the city of Sarh, the middle course of the Chari makes its way through swampy terrain; the lower Chari is joined by the Logone River near N'Djamena.[4] The Chari's volume varies greatly, from 17 cubic meters per second during the dry season to 340 cubic meters per second during the wettest part of the year.[4]
The Logone River is formed by tributaries flowing from Cameroon and Central African Republic.[4] Both shorter and smaller in volume than the Chari, it flows northeast for 960 kilometers; its volume ranges from five to eighty-five cubic meters per second.[4] At N'Djamena the Logone empties into the Chari, and the combined rivers flow together for thirty kilometers through a large delta and into Lake Chad.[4] At the end of the rainy season in the fall, the river overflows its banks and creates a huge floodplain in the delta.[4]
The seventh largest lake in the world (and the fourth largest in Africa), Lake Chad is located in the sahelian zone, a region just south of the Sahara Desert.[4] The Chari River contributes 95 percent of Lake Chad's water, an average annual volume of 40 billion cubic meters, 95% of which is lost to evaporation.[4] The size of the lake is determined by rains in the southern highlands bordering the basin and by temperatures in the Sahel.[4] Fluctuations in both cause the lake to change dramatically in size, from 9,800 square kilometers in the dry season to 25,500 at the end of the rainy season.[4]
Lake Chad also changes greatly in size from one year to another.[4] In 1870 its maximum area was 28,000 square kilometers.[4] The measurement dropped to 12,700 in 1908.[4] In the 1940s and 1950s, the lake remained small, but it grew again to 26,000 square kilometers in 1963.[4] The droughts of the late 1960s, early 1970s, and mid-1980s caused Lake Chad to shrink once again, however.[4] The only other lakes of importance in Chad are Lake Fitri, in Batha Prefecture, and Lake Iro, in the marshy southeast.[4]
Climate
editThe Lake Chad Basin embraces a great range of tropical climates from north to south, although most of these climates tend to be dry.[4] Apart from the far north, most regions are characterized by a cycle of alternating rainy and dry seasons.[4] In any given year, the duration of each season is determined largely by the positions of two great air masses—a maritime mass over the Atlantic Ocean to the southwest and a much drier continental mass.[4]
During the rainy season, winds from the southwest push the moister maritime system north over the African continent where it meets and slips under the continental mass along a front called the "intertropical convergence zone".[4] At the height of the rainy season, the front may reach as far as Kanem Prefecture.[4] By the middle of the dry season, the intertropical convergence zone moves south of Chad, taking the rain with it.[4] This weather system contributes to the formation of three major regions of climate and vegetation.[4]
Saharan region
editThe Saharan region covers roughly the northern half of the country, including Borkou-Ennedi-Tibesti Prefecture along with the northern parts of Kanem, Batha, and Biltine prefectures.[4] Much of this area receives only traces of rain during the entire year; at Faya-Largeau, for example, annual rainfall averages less than 12 millimeters (0.47 in), and there are nearly 3800 hours of sunshine.[4] Scattered small oases and occasional wells provide water for a few date palms or small plots of millet and garden crops.[4]
In much of the north, the average daily maximum temperature is about 32 °C (89.6 °F) during January, the coolest month of the year, and about 45 °C (113 °F) during May, the hottest month.[4] On occasion, strong winds from the northeast produce violent sandstorms.[4] In northern Biltine Prefecture, a region called the Mortcha plays a major role in animal husbandry.[4] Dry for eight months of the year, it receives 350 millimeters (13.8 in) or more of rain, mostly during July and August.[4]
A carpet of green springs from the desert during this brief wet season, attracting herders from throughout the region who come to pasture their cattle and camels.[4] Because very few wells and springs have water throughout the year, the herders leave with the end of the rains, turning over the land to the antelopes, gazelles, and ostriches that can survive with little groundwater.[4] Northern Chad averages over 3500 hours of sunlight per year, the south somewhat less.
| Climate data for Faya-Largeau (1961–1990) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 39 (102) |
43 (109) |
44 (111) |
49 (120) |
49 (120) |
49 (120) |
47 (117) |
46 (115) |
46 (115) |
47 (117) |
39 (102) |
36 (97) |
49 (120) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 26.4 (79.5) |
29.4 (84.9) |
33.6 (92.5) |
39.1 (102.4) |
41.0 (105.8) |
42.1 (107.8) |
41.0 (105.8) |
40.2 (104.4) |
39.8 (103.6) |
36.5 (97.7) |
31.1 (88.0) |
27.6 (81.7) |
35.7 (96.3) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 20.0 (68.0) |
22.2 (72.0) |
26.0 (78.8) |
30.8 (87.4) |
33.0 (91.4) |
34.1 (93.4) |
33.4 (92.1) |
33.1 (91.6) |
32.7 (90.9) |
29.5 (85.1) |
24.5 (76.1) |
21.0 (69.8) |
28.4 (83.1) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 13.6 (56.5) |
15.0 (59.0) |
18.4 (65.1) |
22.4 (72.3) |
25.0 (77.0) |
26.1 (79.0) |
25.8 (78.4) |
26.0 (78.8) |
25.9 (78.6) |
22.5 (72.5) |
17.9 (64.2) |
14.4 (57.9) |
21.1 (70.0) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 4 (39) |
7 (45) |
11 (52) |
14 (57) |
17 (63) |
17 (63) |
16 (61) |
16 (61) |
17 (63) |
12 (54) |
9 (48) |
3 (37) |
3 (37) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.1 (0.00) |
0.4 (0.02) |
0.3 (0.01) |
3.0 (0.12) |
7.0 (0.28) |
0.8 (0.03) |
0.1 (0.00) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
11.7 (0.46) |
| Average rainy days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 10 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 25 | 20 | 18 | 18 | 17 | 20 | 27 | 33 | 22 | 25 | 23 | 25 | 23 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 306.9 | 291.2 | 306.9 | 309.0 | 344.1 | 333.0 | 334.8 | 319.3 | 312.0 | 319.3 | 309.0 | 306.9 | 3,792.4 |
| Mean daily sunshine hours | 9.9 | 10.4 | 9.9 | 10.3 | 11.1 | 11.1 | 10.8 | 10.3 | 10.4 | 10.3 | 10.3 | 9.9 | 10.4 |
| Source 1: World Meteorological Organization (temperatures and precipitation days)[5] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: NOAA (sun and humidity),[6] Annales de Géographie[7][8] | |||||||||||||
Sahelian region
editThe semiarid sahelian zone, or Sahel, forms a belt about 500 kilometers (311 mi) wide that runs from Lac and Chari-Baguirmi prefectures eastward through Guéra, Ouaddaï, and northern Salamat prefectures to the Sudanese frontier.[4] The climate in this transition zone between the desert and the southern sudanian zone is divided into a rainy season (from June to September) and a dry period (from October to May).[4]
In the northern Sahel, thorny shrubs and acacia trees grow wild, while date palms, cereals, and garden crops are raised in scattered oases.[4] Outside these settlements, nomads tend their flocks during the rainy season, moving southward as forage and surface water disappear with the onset of the dry part of the year.[4] The central Sahel is characterized by drought-resistant grasses and small woods.[4] Rainfall is more abundant there than in the Saharan region.[4] For example, N'Djamena records a maximum annual average rainfall of 580 millimeters (22.8 in), while Ouaddaï Prefecture receives just a bit less.[4]
During the hot season, in April and May, maximum temperatures frequently rise above 40 °C (104 °F).[4] In the southern part of the Sahel, rainfall is sufficient to permit crop production on unirrigated land, and millet and sorghum are grown.[4] Agriculture is also common in the marshlands east of Lake Chad and near swamps or wells.[4] Many farmers in the region combine subsistence agriculture with the raising of cattle, sheep, goats, and poultry.[4]
| Climate data for N'Djamena (1961-1990, extremes 1904-present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 41.8 (107.2) |
47.6 (117.7) |
46.5 (115.7) |
48.3 (118.9) |
49.1 (120.4) |
44.0 (111.2) |
46.0 (114.8) |
38.6 (101.5) |
40.5 (104.9) |
43.6 (110.5) |
47.5 (117.5) |
40.5 (104.9) |
49.1 (120.4) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 32.4 (90.3) |
35.2 (95.4) |
38.7 (101.7) |
41.0 (105.8) |
39.9 (103.8) |
37.2 (99.0) |
33.5 (92.3) |
31.6 (88.9) |
33.7 (92.7) |
36.9 (98.4) |
35.8 (96.4) |
33.5 (92.3) |
35.8 (96.4) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 23.4 (74.1) |
25.9 (78.6) |
29.9 (85.8) |
32.9 (91.2) |
32.9 (91.2) |
30.9 (87.6) |
28.3 (82.9) |
27.0 (80.6) |
28.2 (82.8) |
29.4 (84.9) |
26.8 (80.2) |
24.2 (75.6) |
28.3 (83.0) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 14.3 (57.7) |
16.6 (61.9) |
21.0 (69.8) |
24.8 (76.6) |
25.8 (78.4) |
24.7 (76.5) |
23.1 (73.6) |
22.4 (72.3) |
22.7 (72.9) |
21.8 (71.2) |
17.8 (64.0) |
14.8 (58.6) |
20.8 (69.5) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 6.5 (43.7) |
8.0 (46.4) |
11.3 (52.3) |
16.2 (61.2) |
16.8 (62.2) |
18.2 (64.8) |
17.7 (63.9) |
18.5 (65.3) |
15.1 (59.2) |
13.5 (56.3) |
10.3 (50.5) |
8.4 (47.1) |
6.5 (43.7) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.3 (0.01) |
10.3 (0.41) |
25.8 (1.02) |
51.0 (2.01) |
143.8 (5.66) |
174.4 (6.87) |
84.3 (3.32) |
20.3 (0.80) |
0.1 (0.00) |
0.0 (0.0) |
510.3 (20.1) |
| Average rainy days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 6 | 9 | 13 | 15 | 9 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 60 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 29 | 23 | 21 | 28 | 39 | 52 | 68 | 76 | 72 | 49 | 33 | 31 | 43 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 297.6 | 277.2 | 282.1 | 273.0 | 285.2 | 258.0 | 213.9 | 201.5 | 228.0 | 285.2 | 300.0 | 303.8 | 3,205.5 |
| Mean daily sunshine hours | 9.6 | 9.9 | 9.1 | 9.1 | 9.2 | 8.6 | 6.9 | 6.5 | 7.6 | 9.2 | 10.0 | 9.8 | 8.8 |
| Source 1: World Meteorological Organization (precipitation)[9] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: NOAA (sun, humidity, temperatures),[10] Meteo Climat (record highs and lows)[11] | |||||||||||||
Sudanian region
editThe humid sudanian zone includes the Sahel,[12] the southern prefectures of Mayo-Kebbi, Tandjilé, Logone Occidental, Logone Oriental, Moyen-Chari, and southern Salamat.[4] Between April and October, the rainy season brings between 750 and 1,250 millimeters (29.5 and 49.2 in) of precipitation.[4] Temperatures are high throughout the year.[4] Daytime readings in Moundou, the major city in the southwest, range from 27 °C (80.6 °F) in the middle of the cool season in January to about 40 °C (104 °F) in the hot months of March, April, and May.[4]
The sudanian region is predominantly East Sudanian savanna, or plains covered with a mixture of tropical or subtropical grasses and woodlands.[4] The growth is lush during the rainy season but turns brown and dormant during the five-month dry season between November and March.[4] Over a large part of the region, however, natural vegetation has yielded to agriculture.
| Climate data for Sarh (1961-1990) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 35.8 (96.4) |
38.0 (100.4) |
39.1 (102.4) |
38.5 (101.3) |
36.2 (97.2) |
33.2 (91.8) |
30.9 (87.6) |
30.6 (87.1) |
31.7 (89.1) |
33.6 (92.5) |
35.5 (95.9) |
35.4 (95.7) |
34.9 (94.8) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 16.5 (61.7) |
18.8 (65.8) |
22.6 (72.7) |
24.7 (76.5) |
24.1 (75.4) |
22.6 (72.7) |
21.6 (70.9) |
21.5 (70.7) |
21.5 (70.7) |
21.7 (71.1) |
18.8 (65.8) |
16.4 (61.5) |
20.9 (69.6) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 0.1 (0.00) |
1.6 (0.06) |
9.5 (0.37) |
37.4 (1.47) |
82.1 (3.23) |
135.9 (5.35) |
234.4 (9.23) |
243.7 (9.59) |
165.5 (6.52) |
55.8 (2.20) |
3.3 (0.13) |
0.0 (0.0) |
969.3 (38.16) |
| Average rainy days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 9 | 12 | 15 | 18 | 16 | 7 | 1 | 0 | 86 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 33 | 29 | 37 | 50 | 61 | 72 | 79 | 82 | 80 | 73 | 57 | 42 | 58 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 266.6 | 243.6 | 244.9 | 237.0 | 241.8 | 207.0 | 173.6 | 176.7 | 186.0 | 232.5 | 261.0 | 266.6 | 2,737.3 |
| Mean daily sunshine hours | 8.6 | 8.7 | 7.9 | 7.9 | 7.8 | 6.9 | 5.6 | 5.7 | 6.2 | 7.5 | 8.7 | 8.6 | 7.5 |
| Source 1: World Meteorological Organization (temperatures and rainy days)[13] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: NOAA (sun, humidity and precipitation)[14] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Moundou (1961-1990) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 34.1 (93.4) |
36.7 (98.1) |
38.6 (101.5) |
38.0 (100.4) |
35.7 (96.3) |
32.3 (90.1) |
30.2 (86.4) |
29.8 (85.6) |
30.7 (87.3) |
33.1 (91.6) |
35.1 (95.2) |
34.2 (93.6) |
34.0 (93.2) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 15.1 (59.2) |
18.3 (64.9) |
22.5 (72.5) |
24.2 (75.6) |
23.5 (74.3) |
22.1 (71.8) |
21.2 (70.2) |
21.0 (69.8) |
20.8 (69.4) |
21.0 (69.8) |
17.4 (63.3) |
14.6 (58.3) |
20.1 (68.2) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 0.0 (0.0) |
0.2 (0.01) |
4.6 (0.18) |
39.2 (1.54) |
89.8 (3.54) |
147.7 (5.81) |
257.8 (10.15) |
284.8 (11.21) |
200.1 (7.88) |
57.1 (2.25) |
1.5 (0.06) |
0.0 (0.0) |
1,082.8 (42.63) |
| Average rainy days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 9 | 12 | 15 | 19 | 13 | 7 | 2 | 0 | 85 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 36 | 28 | 31 | 50 | 63 | 73 | 80 | 81 | 78 | 73 | 56 | 45 | 58 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 279.0 | 249.2 | 248.0 | 234.0 | 241.8 | 210.0 | 182.9 | 170.5 | 186.0 | 235.6 | 282.0 | 291.4 | 2,810.4 |
| Mean daily sunshine hours | 9.0 | 8.9 | 8.0 | 7.8 | 7.8 | 7.0 | 5.9 | 5.5 | 6.2 | 7.6 | 9.4 | 9.4 | 7.7 |
| Source 1: World Meteorological Organization[15] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: NOAA (sun and humidity)[16] | |||||||||||||
2010 drought
editOn 22 June, the temperature reached 47.6 °C (117.7 °F) in Faya, breaking a record set in 1961 at the same location. Similar temperature rises were also reported in Niger, which began to enter a famine situation.[17]
On 26 July the heat reached near-record levels over Chad and Niger.[18]
Area
editArea:
total:
1.284 million km2
land:
1,259,200 km2
water:
24,800 km2
Area — comparative:
- Canada: slightly less than twice the size of Alberta
- US: slightly more than three times the size of California
- Australia: slightly smaller than the Northern Territory
Boundaries
editLand boundaries:
total:
6,406 km
border countries:
Cameroon 1,116 km, Central African Republic 1,556 km, Libya 1,050 km, Niger 1,196 km, Nigeria 85 km, Sudan 1,403 km
Coastline: 0 km (landlocked)
Maritime claims: none (landlocked)
Elevation extremes:
lowest point:
Bodélé Depression 160 m[19]
highest point:
Emi Koussi 3,415 m[20]
Land use and resources
editNatural resources: petroleum, uranium, natron, kaolin, fish (Chari River, Logone River), gold, limestone, sand and gravel, salt
Land use:
arable land:
3.89%
permanent crops:
0.03%
other:
96.08% (2012)
Irrigated land: 302.7 km2 (2003)
Total renewable water resources: 43 km3 (2011)
Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural):
total:
0.88 km3/yr (12%/12%/76%)
per capita:
84.81 m3/yr (2005)
Environmental issues
editNatural hazards: hot, dry, dusty, Harmattan winds occur in north; periodic droughts; locust plagues
Environment - current issues: inadequate supplies of potable water; improper waste disposal in rural areas contributes to soil and water pollution; desertification
See also
editExtreme points
editThis is a list of the extreme points of Chad, the points that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location.
- Northernmost point - an unnamed location on the border with Libya, Borkou-Ennedi-Tibesti region
- Easternmost point - the northern section of the Chad-Sudan border, Borkou-Ennedi-Tibesti region *
- Southernmost point - unnamed location on the border with Central African Republic at a confluence in the Lébé river, Logone Oriental region
- Westernmost point - unnamed location west of the town of Kanirom and immediately north of Lake Chad, Lac Region
*Note: technically Chad does not have an easternmost point, the easternmost section of the border being formed by the 24° of longitude
References
edit- ^ Leonard, Thomas M. (2005). Encyclopedia of the Developing World. Routledge. pp. 311–312. ISBN 978-1-57958-388-0. Retrieved 12 September 2019.
- ^ Mueckenheim, J.K. (2007). Countries of the World & Their Leaders Yearbook 08. Gale virtual reference library. Thomson Gale. p. 390. ISBN 978-0-7876-8107-4. Retrieved 12 September 2019.
- ^ "Lake Chad fishermen pack up their nets". BBC News. 15 January 2007. Retrieved 12 September 2019.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq ar as at au av aw ax ay az ba bb bc bd be bf bg bh bi bj bk bl bm bn bo bp bq br bs bt bu bv bw bx by bz ca cb cc cd ce cf cg This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain: Collelo, Thomas, ed. (1990). Chad: A Country Study (2nd ed.). Washington, D.C.: Federal Research Division, Library of Congress. pp. 35–42. ISBN 0-16-024770-5.
- ^ "World Weather Information Service–Faya-Largeau". World Meteorological Organization. Retrieved 24 June 2015.
- ^ "Faya–Largeau Climate Normals 1961–1990". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 24 June 2015.
- ^ Mainguet, Monique (1968). "Le Borkou. Aspects d'un modèle éolien". Annales de Géographie (in French). 77 (421): 296–322. doi:10.3406/geo.1968.15662.
- ^ http://www.bbc.co.uk/weather/world/city_guides/results.shtml?tt=TT000120 [permanent dead link]
- ^ "World Weather Information Service–Ndjamena". World Meteorological Organization. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 19 October 2015.
- ^ "ND'Jamena Climate Normals 1961–1990". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 19 October 2015.
- ^ "Station N'Djamena" (in French). Meteo Climat. Retrieved 19 October 2016.
- ^ Gorse, J.E.; Steeds, D.R. (1987). Desertification in the Sahelian and Sudanian Zones of West Africa. World Bank. p. 1. ISBN 978-0-8213-0897-4. Retrieved 12 September 2019.
- ^ "World Weather Information Service – Sarh". World Meteorological Organization. Retrieved 24 June 2015.
- ^ "Sarh Climate Normals 1961-1990". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 24 June 2015.
- ^ "World Weather Information Service – Moundou". World Meteorological Organization. Retrieved 24 June 2015.
- ^ "Moundou Climate Normals 1961-1990". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 24 June 2015.
- ^ Masters, Jeff. "NOAA: June 2010 the globe's 4th consecutive warmest month on record". Weather Underground. Jeff Masters' WunderBlog. Archived from the original on 19 July 2010. Retrieved 21 July 2010.
- ^ "Wunder Blog : Weather Underground". Wunderground.com. Archived from the original on 27 June 2010. Retrieved 28 July 2010.
- ^ Bristow, Charlie S.; Drake, Nick; Armitage, Simon (1 April 2009). "Deflation in the dustiest place on Earth: The Bodélé Depression, Chad". Geomorphology. Contemporary research in aeolian geomorphology. 105 (1): 50–58. Bibcode:2009Geomo.105...50B. doi:10.1016/j.geomorph.2007.12.014. ISSN 0169-555X.
- ^ "Emi Koussi". Global Volcanism Program. Smithsonian Institution. Retrieved 3 November 2013.
Sources
edit- This article incorporates public domain material from The World Factbook. CIA.
External links
edit- 15°N 19°E / 15°N 19°E – title=Field Listing: Geographic Coordinates. Geo-links for Geography of Chad.
- Detailed map of Chad from www.izf.net