The examples and perspective in this article deal primarily with the United States and do not represent a worldwide view of the subject. (September 2018) |
Cyclospora cayetanensis is a coccidian parasite that causes a diarrheal disease called cyclosporiasis in humans and possibly in other primates. Originally reported as a novel pathogen of probable coccidian nature in the 1980s[1] and described in the early 1990s,[1] it was virtually unknown in developed countries until awareness increased due to several outbreaks linked with fecally contaminated imported produce. C. cayetanensis has since emerged as an endemic cause of diarrheal disease in tropical countries and a cause of traveler's diarrhea and food-borne infections in developed nations.[1] This species was placed in the genus Cyclospora because of the spherical shape of its sporocysts. The specific name refers to the Cayetano Heredia University in Lima, Peru, where early epidemiological and taxonomic work was done.[2]
| Cyclospora cayetanensis | |
|---|---|
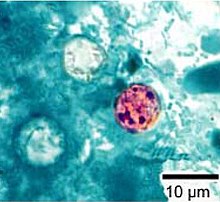
| |
| Cyclospora cayetanensis oocysts | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Clade: | Diaphoretickes |
| Clade: | SAR |
| Clade: | Alveolata |
| Phylum: | Apicomplexa |
| Class: | Conoidasida |
| Order: | Eucoccidiorida |
| Family: | Eimeriidae |
| Genus: | Cyclospora |
| Species: | C. cayetanensis
|
| Binomial name | |
| Cyclospora cayetanensis Ortega, Gilman & Sterling, 1994
| |
History
editAs originally recognized by Markus & Frean (1993),[3] the first published report of Cyclospora cayetanensis in humans appears to be by Ashford (1979), who found unidentified Isospora-like coccidia in the feces of three individuals in Papua, New Guinea. They referenced Ashford's article. The photomicrographs in his paper reveal an organism morphologically identical to that seen nowadays. Markus had perceived the probable coccidial nature of Cyclospora in the 1980s but did not formally publish his ideas on the matter. Later, Narango et al. (1989) reported what may be the same organism from several Peruvians with chronic diarrhea and termed the organism Cryptosporidium muris–like. Other investigators thought the unsporulated oocysts appeared more similar to cyanobacteria, and the name "cyanobacterium-like body" or CLB became prevalent in the literature (occasionally, authors also used the term "coccidian-like body", or CLB). Eventually, Ortega et al. (1992) published an abstract reporting that they had sporulated and excysted the oocysts, resulting in placement of the parasite in the genus Cyclospora. They also created the name Cyclospora cayetanensis at this time. However, since no morphologic information was presented in the abstract, C. cayetanensis technically became a nomen nudum (a named species without a description). Although Ortega et al. (1993) later published additional details about this coccidian, a complete morphologic description was not published to validate the name until 1994.[4] Thus, the correct name for this parasite is Cyclospora cayetanensis Ortega, Gilman, & Sterling, 1994, and the etymology of the nomen triviale is derived from Cayetano Heredia University in Lima, Peru. During this two-year period when C. cayetanensis was a nomen nudum, anyone wishing to publish a complete morphologic description and change the name would have been free to do so.[2]
Characterization
editCyclospora cayetanensis is an apicomplexan, cyst-forming coccidian protozoan that causes a self-limiting diarrhea. In terms of morphology, It has spherical oocysts that are between 7.5 and 10 μm in diameter that also have a 50-nm-thick wall with an outer thread-like coat that has been called a wrinkle by some researchers. The oocyst formula is O.2.2 because one oocyst contains two sporocysts and each sporocyst contains two sporozoites.[5]
The only confirmed hosts for C. cayetanensis are humans. The protozoan lives out its lifecycle intracellularly within the host's epithelial cells and gastrointestinal tract. Infection is transmitted through the fecal-oral route, and begins when a person ingests oocysts in feces-contaminated food or water. Various chemicals in the host's gastrointestinal tract cause the oocysts to excyst and release sporozoites; generally, two are observed per oocyst. After these sporozoites invade the epithelial cells, they undergo merogony, a form of asexual reproduction that results in many daughter merozoites. These daughter cells may either infect new host cells and initiate yet another round of merogony or take on a sexual track via gametogony: Daughter merozoites become male macrogamonts—which form many microgametes—and female macrogamonts. After fertilization has occurred via male microgamete fusion with female macrogamont, the zygote matures into an oocyst and ruptures the host cell, from which point it is passed with the stool. The oocysts that are passed are not, however, immediately infectious. Sporulation can take from one to several weeks, meaning person-to-person transmission is not a likely event. This differentiates C. cayetanensis from Cryptosporidium parvum—a closely related organism that causes a similar disease—since C. parvum oocysts are immediately infectious upon release from the host.[6]
Symptoms
editC. cayetanensis causes gastroenteritis, with the extent of the illness varying based on age, condition of the host, and size of the infectious dose. Symptoms include "watery diarrhea, loss of appetite, weight loss, abdominal bloating and cramping, increased flatulence, nausea, fatigue, and low-grade fever", though this can be augmented in more severe cases by vomiting, substantial weight loss, excessive diarrhea, and muscle aches. Typically, patients with a persistent watery diarrhea lasting over several days may be suspected of harboring the disease, especially if they have traveled to a region where the protozoan is endemic. The incubation period in the host is typically around a week, and illness can last six weeks before self-limiting. Unless treated, illness may relapse. The more severe forms of the disease can occur in immunocompromised patients, such as those with AIDS.[7] Human cyclosporiasis is clinically similar to cryptosporidiosis, isosporiasis, giardiasis and microsporidiosis because of the similar clinical features. Flu like syndrome with myalgias and arthralgias may precede the onset of diarrhea. Fever is low grade and is unusual. There is presence of moderate to severe dehydration, compensatory tachycardia, systolic blood pressure (SBP<90 mmHg) and decreased skin turgor may occur. But mild infection produces few or no clinical symptoms. The immune system may determine the appearance of symptoms; that is, from symptomatic to asymptomatic stage depends on resistivity of the immune system.[8]
Risk factors
editPersons living or traveling in developing tropical or subtropical areas may be at an increased risk of acquiring C. cayetanensis, as it is endemic in these areas. Infections in endemic regions tend to show a marked seasonality that is poorly understood, whereas North American outbreaks occur most frequently in late spring and summer, correlating with increased import of produce from the tropics.[2] Consuming food or water while visiting developing countries is a well-documented way of developing traveler's diarrhea. Travelers are often warned against such actions, but over 70 percent of certain produce items consumed in the United States are imported from developing countries, making "traveler's diarrhea" possible without international travel.[9] Since oocysts are shed in the feces of infected persons and then must mature in the environment 2–14 days before they can become infectious, it is unlikely for a person to get an infection directly from another person, such as an infected food handler.[1]
Recognition
editDue to its small size, intracellular habitat, and inability to properly take up many histological stains, diagnosis of C. cayetanensis can be very difficult. Four methods have thus far been established for positive diagnosis of the protozoan: microscopic detection in stool samples of oocysts; recovering oocysts in intestinal fluid/small bowel biopsy specimens; demonstration of oocyst sporulation; and amplification by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) of C. cayetanensis DNA. Since detection is so hard, one negative result should not discount the possibility of C. cayetanensis: tests involving fresh stool samples over the next few days should also be considered.[citation needed]
Except for PCR amplification, once a sample with suspected oocysts has been recovered, standard tests are followed to identify C. cayetanensis. These tests include phase contrast microscopy to check for the spherical oocysts described earlier, modified acid-fast staining to check for variable staining (from pale to red), and autofluorescence with UV lights. Obtaining these oocysts is usually the challenge, though recent studies show easier methods of obtaining them. In a recent study on different techniques used in fecal exams to identify oocysts, centrifuging a sample of feces in a sucrose solution and then transferring a small amount to a slide was found to be remarkably effective—both in oocysts found and relative ease of labor—in detecting C. cayetanensis oocysts: indeed, the paper concluded the positive samples obtained were around 84%.[10]
C. cayetanensis has been confused with other protozoan infections in the past, most commonly being misidentified as Cryptosporidium parvum. Several differences can be noted between the two, however, to ensure proper diagnosis. These differences include: size difference—C. parvum is smaller; differing results from modified acid-fast staining—C. parvum has consistent red staining, whereas C. cayetanensis shows variable staining; and autofluorescence under UV light—C. cayetanensis exhibits this, whereas C. parvum does not.[citation needed]
Cases of C. cayetanensis infection often go unexplained, partly because of the difficulties associated with epidemiologic investigations of such cases and the lack of genotyping methods. Recent attempts at a better genotyping characterisation include multilocus sequence typing based on microsatellite markers [11] and single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of nuclear markers.[12]
Treatment
editMost people who have healthy immune systems will recover without treatment. If not treated, the illness may last for a few days to a month or longer. Symptoms may seem to go away and then return one or more times (relapse). Antidiarrheal medicine may help reduce diarrhea, but consult with a health care provider before the medicine is taken. People who are in poor health or who have weakened immune systems may be at higher risk for severe or prolonged illness.[13] To date, the most effective drug for the treatment of the protozoan is a seven-day course of oral trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX). Effects of the drug include a significant decrease in the duration of oocyst excretion, cessation of diarrhea, and stool samples negative for oocysts within two to three days.[13] TMP-SMX is classified as a Category C during pregnancy, meaning potential adverse effects (such as teratogenic or embryocidal or other) could results and should only be given if the potential benefit significantly justifies the risk. The drug should be avoided near-term, as high potentials exist for hyperbilirubinemia and kernicterus in newborns. Additionally, TMP-SMX can be excreted in breast milk, which is compatible in healthy, full-term newborns, but should be avoided in premature, ill, stressed, or jaundiced infants.[14] No highly alternative antibiotic regimen has been discovered yet for patients who possess a sulfa-allergy.[15]
Prevention
editNo vaccine against this pathogen is available.[16] Since infection occurs via fecally contaminated food and water in endemic environments, several simple solutions have been suggested for the prevention of C. cayetanensis infections. The simplest is to warn travelers not to visit regions where the protozoan is endemic (in general, tropical and subtropical regions where sanitation is poor, such as Peru, Brazil, and Haiti), especially when the season is best for spreading: Travelers also should be aware that treatment of water or food with chlorine or iodine is unlikely to kill Cyclospora oocysts.[17] Additionally, better health practices in the originating agricultural setting—such as making sure produce watering systems are not pulling water that has access to human feces. Additionally, using filtering systems such as a 1 micron absolute carbon filtration system will reduce the presence of Cyclospora, drastically decreasing the incidence of the spread of this parasite.[1] The odds of becoming infected with Cyclospora, and many other foodborne pathogens, can be greatly diminished by thoroughly washing fruits and vegetables in clean water prior to consumption. However, simply washing foods does not remove 100% of the oocysts present.[2]
Outbreaks
editThe examples and perspective in this section may not represent a worldwide view of the subject. (May 2022) |
U.S. foodborne outbreaks of cyclosporiasis: 2000–2014
editFoodborne outbreaks of cyclosporiasis have been reported in the United States since the mid-1990s and have been linked to various types of imported fresh produce, including raspberries, basil, snow peas, mesclun lettuce, and cilantro; no commercially frozen produce has been implicated to date. U.S. foodborne outbreaks of cyclosporiasis that occurred before 2000 were summarized previously, as were the major documented outbreaks in 2013 and 2014. Foodborne outbreaks during the 15-year period of 2000–2014 are summarized in table. The table provides information about 31 reported foodborne outbreaks of cyclosporiasis that occurred in the United States during 2000–2014; the total case count was 1,562. No outbreaks were reported in 2003, 2007, or 2010. Overall, a median of two outbreaks were reported per year, with a median of 20 cases per outbreak (range, 3 to 582 cases). Although the outbreaks occurred during 8 different months (December through July), the peak months were May, June, and July. As indicated in the table, a food vehicle of infection was identified for 15 of the 31 outbreaks.[citation needed]
Summary of U.S. foodborne outbreaks of cyclosporiasis, 2000–2014 [18]
| Year(s)* | Month(s)* | Jurisdiction(s)* | No. of cases† | Food vehicle and source, if identified‡ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | May | Georgia | 19 | Raspberries and/or blackberries (suspected) |
| 2000 | June | Pennsylvania | 54 | Raspberries |
| 2001 | January–February | Florida | 39 | |
| 2001 | January | New York City | 3 | |
| 2001–02 | December–January | Vermont | 22 | Raspberries (likely) |
| 2002 | April–May | Massachusetts | 8 | |
| 2002 | June | New York | 14 | |
| 2004 | February | Texas | 38 | |
| 2004 | February | Illinois | 57 | Basil (likely) |
| 2004 | May | Tennessee | 12 | |
| 2004 | May–June | Pennsylvania | 96 | Snow peas from Guatemala |
| 2005 | March–May | Florida | 582 ¶ | Basil from Peru |
| 2005 | May | South Carolina | 6 | |
| 2005 | April | Massachusetts | 58 | |
| 2005 | May | Massachusetts | 16 | |
| 2005 | June | Connecticut | 30 | Basil (suspected) |
| 2006 | June | Minnesota | 14 | |
| 2006 | June | New York | 20 | |
| 2006 | July | Georgia | 3 | |
| 2008 | March | Wisconsin | 4 | Sugar snap peas (likely) |
| 2008 | July | California | 45 ¶ | Raspberries and/or blackberries (likely) |
| 2009 | June | District of Columbia | 34 | |
| 2011 | June | Florida | 12 | |
| 2011 | July | Georgia | 100 | |
| 2012 | June–July | Texas | 16 | |
| 2013** | June | Iowa and Nebraska | 161 | Bagged salad mix from Mexico |
| 2013** | June–July | Texas | 38 | Cilantro from Mexico |
| 2013 | July | Wisconsin | 8 | Berry salad (suspected) |
| 2014 | June | Michigan | 14 | |
| 2014†† | June–July | Texas | 26 | Cilantro from Mexico |
| 2014 | July | South Carolina | 13 |
* The entries in the first three columns refer to the known or likely year(s), month(s), and jurisdiction(s) in which the exposure(s) to Cyclospora occurred.
** For additional details, see summary information about the outbreak investigations in 2013. For the purposes of this table, the exposure month(s) and case counts are limited to those explicitly linked in the investigations to the food item specified in the last column.
† The case counts include laboratory-confirmed and probable cases of cyclosporiasis. By definition, each outbreak included at least two linked cases, at least one of which was laboratory confirmed.
‡ A food vehicle is specified only if a single ingredient or commodity was identified in an outbreak investigation.
¶ Cases that occurred in Canadian travelers to the United States were not included.
†† For additional perspective, see summary information about outbreak investigations in 2014. For the purposes of this table, the exposure months and the case count for the outbreak in Texas are limited to those explicitly linked in the investigations to the food item specified in the last column.
2013 United States outbreak
editAt least 285 people in 11 states had been affected as of July 26, 2013. The exact cause of the outbreak had not yet been identified according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). The majority of cases were located in the Midwest, with 138 reported cases in Iowa and 70 in Nebraska. The other states affected are: Texas, Florida, Georgia, Wisconsin, Connecticut, Illinois, Kansas, Minnesota, New Jersey, and Ohio.[citation needed]
As of July 29, 2013, the CDC reported 373 people in 15 states had been affected by the outbreak, and 21 patients from three states had been hospitalized, with no deaths reported. No food source had been identified, but health officials in Iowa—the state reporting the most cases—said they suspected imported vegetables.[19]
On July 30, 2013, the Nebraska Department of Health & Human Services and the Iowa Department of Health announced that a restaurant chain's packaged salad was the disease vector for the parasite.[20] However, the CDC and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) continued to assess information from other states to see if the findings applied to illnesses there.[21]
In an August 1, 2013, update, the CDC reported 397 cases, while Iowa and Texas added another 22 more. This pushed the unofficial count to over 400 cases. Additionally, Louisiana reported its first case, bringing the total number of states affected to 16.[22]
On August 3, 2013, CNN reported that the outbreak was traced to packaged salad served at Olive Garden and Red Lobster restaurants that was manufactured by Taylor Farms de Mexico.
On August 15, 2013, the CDC reported nine more Cyclospora infections, raising its case count to 548. The number of affected states remained at 19, but the CDC said that not all cases were confirmed to be linked to an outbreak in Iowa and Nebraska traced to a contaminated salad mix from Mexico.[23]
On August 19, 2013, the CDC reported 10 more Cyclospora cases, raising the unofficial count to over 600. Tennessee also reported its first case, bringing the number of states affect to 20. The CDC still cautions that whether cases in all of the states are related to outbreaks in Iowa and Nebraska is not clear.[24]
As of August 27, 2013, the origin of the outbreak still remained a mystery. The FDA said it found no food safety violations at the Taylor Farms de Mexico salad plant that was linked to some of the illnesses.[25]
2015 Texas outbreak
editIn an FDA statement, the CDC is quoted, "there is currently (in July 2015) another ongoing outbreak of cyclosporiasis in the United States in which both the Texas Department of State Health Services and the Wisconsin Department of Health Services and the Wisconsin Department of Agriculture, Trade and Consumer Protection have identified cilantro from the Mexican state of Puebla as a suspect vehicle with respect to separate illness clusters." Last year, Texas had 200 cases, some of which were associated with cilantro from the Puebla region.[26]
2016 Texas outbreak
editHealth officials said more than a dozen cases of cyclosporiasis had been confirmed in North Texas' four major counties and that the source was likely contaminated food. The Texas Department of State Health Services said Wednesday the parasite was found in Dallas, Tarrant, Collin and Denton counties and that the origin may have been linked to a fresh produce item.[citation needed]
County officials told NBC 5 there were four cases recorded in Dallas County, three in Collin County, four in Denton County and seven in Tarrant County. The Denton County cases and at least four of the Tarrant County cases had recently traveled out of the country—calling into question the point of origin.
Across the state, there were currently 66 confirmed cases of cyclosporiasis—though the sources of infection were unconfirmed. For most people, the symptoms were not serious. "But for those who are very young and those who are older, or those who have a suppressed immune system, this illness can cause major problems," said Dr. Khang Tran, chief medical officer at The Medical Center of Plano. In recent years, 2012–2015, cyclospora outbreaks were associated with fresh cilantro imported from Puebla, Mexico. Since the summer of 2015, the Food and Drug Administration has instituted ban on imports from that region between from April through August.[27]
2018 Midwestern Del Monte vegetable outbreak
editDel Monte recalled packaged Del Monte Fresh Produce vegetable trays, which contained broccoli, carrots, cauliflower, celery sticks, and dill dip, from certain retailers, including Kwik Trip and Peapod, according to the CDC. Residents in four states — Iowa, Michigan, Minnesota, and Wisconsin got sick from Cyclospora.[28]
2018 Midwestern McDonald's salad outbreak
editMcDonald's stopped selling salads[28] supplied by Fresh Express at some 3,000 locations across the country mostly in the Midwest United States due to a multistate parasite outbreak that had sickened 551 people caused by Cyclospora.[29]
2020 Midwestern Fresh Express bagged garden salad outbreak
editIn June 2020, the CDC and other regulatory bodies began investigating an outbreak of Cyclosporiasis in the Midwestern United States linked to bagged salad mix.[30] On June 27, 2020, Fresh Express announced a voluntary recall of over 91 Fresh Express and private label salad products.[31]
| Year | Case Count | Incidence Rate |
|---|---|---|
| 2015 | 316 | |
| 2014* | 200 | 0.7 |
| 2013* | 351 | 1.3 |
| 2012* | 44 | 0.2 |
| 2011* | 14 | 0.1 |
| 2010 | 9 | 0.0 |
| 2009 | 10 | 0.0 |
| 2008 | 6 | 0.0 |
| 2007 | 2 | 0.0 |
| 2006 | 1 | 0.0 |
| 2005 | 1 | 0.0 |
| 2004 | 4 | 0.0 |
| 2003 | 1 | 0.0 |
| 2002 | 1 | 0.0 |
| 2001 | 0 | 0.0 |
IR=incidence rate per 100,000
* incidence rates are based on projected census data obtained from the DSHS Center for Health Statistics.
References
edit- ^ a b c d e Ortega, Ynés R; Sanchez, Roxana (2010), "Update on Cyclospora cayetanensis, a food-borne and waterborne parasite", Clin Microbiol Rev, 23 (1): 218–234, doi:10.1128/CMR.00026-09, PMC 2806662, PMID 20065331.
- ^ a b c d "Cyclospora cayetanensis". Division of Biology, Kansas State University. Retrieved 31 October 2001.
- ^ Markus, MB; Frean, JA (1993). "Occurrence of human Cyclospora infection in sub-Saharan Africa" (PDF). South African Medical Journal. 83 (11): 862–863. PMID 7839229. Retrieved February 5, 2023.
- ^ (Ortega et al., 1994).
- ^ Ghimire TR, Redescription of Genera of Family Eimeriidae Minchin, 1903. International Journal of Life Sciences. 2010:26-47. https://www.nepjol.info/index.php/IJLS/article/viewFile/3285/3013
- ^ "Parasites-Cyclosporiasis (Cyclospora Infection). Biology". Global Health - Division of Parasitic Diseases and Malaria Notice. Retrieved March 17, 2015.
- ^ "Symptoms of cyclosporiasis. Disease". Global Health - Division of Parasitic Diseases and Malaria Notice. Retrieved January 10, 2013.
- ^ Tirth Raj Ghimire, Jeevan B. Sherchan. Human infection of cyclospora cayetanensis: a review on its medico-biological and epidemiological pattern in global scenario. 2006. Journal of Nepal Health Research Council.25-40
- ^ NaTashua Davis, ed. (Fall 2002). "The McNair Journal" (PDF). University of Missouri-Columbia. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2020-09-26. Retrieved 2015-04-30.
- ^ Riner DK, Mullin AS, Lucas SY, Cross JH, Lindquist HD (2007). "Enhanced concentration and isolation of Cyclospora cayetanensis oocysts from human fecal samples". Journal of Microbiological Methods. 71 (1): 75–77. doi:10.1016/j.mimet.2007.06.021. PMID 17698229.
- ^ Hofstetter, Jessica N.; Nascimento, Fernanda S.; Park, Subin; Casillas, Shannon; Herwaldt, Barbara L.; Arrowood, Michael J.; Qvarnstrom, Yvonne (2019). "Evaluation of Multilocus Sequence Typing of Cyclospora cayetanensis based on microsatellite markers". Parasite. 26: 3. doi:10.1051/parasite/2019004. ISSN 1776-1042. PMC 6354607. PMID 30702060.
- ^ Houghton, Katelyn A.; Lomsadze, Alexandre; Park, Subin; Nascimento, Fernanda S.; Barratt, Joel; Arrowood, Michael J.; VanRoey, Erik; Talundzic, Eldin; Borodovsky, Mark; Qvarnstrom, Yvonne (2020). "Development of a workflow for identification of nuclear genotyping markers for Cyclospora cayetanensis". Parasite. 27: 24. doi:10.1051/parasite/2020022. ISSN 1776-1042. PMC 7147239. PMID 32275020.
- ^ a b Prevention, CDC - Centers for Disease Control and (2018-10-18). "CDC - Cyclosporiasis - Treatment".
- ^ Prevention, CDC - Centers for Disease Control and (2018-05-14). "CDC - Cyclosporiasis - Resources for Health Professionals - Treatment for Cyclosporiasis".
- ^ "Cyclospora infection Treatments and drugs". Mayo Clinic.
- ^ "Cyclosporiasis - Prevention & Control". CDC - Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2018-06-15.
- ^ "CDC - Cyclosporiasis - Epidemiology & Risk Factors". CDC - Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2018-05-10.
- ^ "U.S. Foodborne Outbreaks of Cyclosporiasis—2000–2014". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved 30 June 2015.
- ^ Schnirring, Lisa (July 29, 2013). "More states report Cyclospora cases; total reaches 373". CIDRAP News.
- ^ "Stomach Bug Outbreak Linked to Salad Mix". ABC News. Retrieved 30 July 2013.
- ^ Schnirring, Lisa (July 30, 2013). "Iowa, Nebraska link Cyclospora cases to bagged salad mix". CIDRAP News.
- ^ Lisa, Schnirring (August 1, 2013). "Iowa, Texas cases push Cyclospora count over 400". CIDRAP News.
- ^ "NEWS SCAN: Cyclospora case count rises; Meningitis in NYC". CIDRAP News. August 14, 2013.
- ^ "News Scan for Aug 19, 2013". CIDRAP News. Aug 19, 2013.
- ^ "Salad plant linked to cyclospora outbreak resumes operations". CBS News. Retrieved 27 August 2013.
- ^ "Mexican Cilantro Again Blamed for Texas Cyclospora Outbreak After Feces Found in Growing Field". NBC 5 Dallas-Fort Worth. Retrieved 27 July 2015.
- ^ "Cyclospora Found in North Texas Counties Likely Food Borne". NBC 5 Dallas-Fort Worth. Retrieved 3 August 2016.
- ^ a b "McDonald's pulls salad from thousands of locations after people are sickened by parasite". Washington Post. Retrieved 14 July 2018.
- ^ "McDonald's Fresh Express Salad Cyclospora Outbreak ends". Food Poisoning Bulletin. 2018-09-14. Retrieved 12 July 2019.
- ^ "Cyclosporiasis Outbreak Investigations — United States, 2020". 24 September 2020.
- ^ "Update: New Bagged Salad Products Linked to Cyclospora Outbreak". 30 June 2020.
- Türk M, Türker M, Ak M, Karaayak B, Kaya T (March 2004). "Cyclosporiasis associated with diarrhoea in an immunocompetent patient in Turkey". J. Med. Microbiol. 53 (Pt 3): 255–7. doi:10.1099/jmm.0.45531-0. PMID 14970253.[permanent dead link]
- Kimura K, Kumar Rai S, Takemasa K, et al. (September 2004). "Comparison of three microscopic techniques for diagnosis of Cyclospora cayetanensis". FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 238 (1): 263–6. doi:10.1016/j.femsle.2004.07.045. PMID 15336431.
- Mansfield LS, Gajadhar AA (December 2004). "Cyclospora cayetanensis, a food- and waterborne coccidian parasite". Vet. Parasitol. 126 (1–2): 73–90. doi:10.1016/j.vetpar.2004.09.011. PMID 15567580.
- Yu JR, Sohn WM (October 2003). "A case of human cyclosporiasis causing traveler's diarrhea after visiting Indonesia". J. Korean Med. Sci. 18 (5): 738–41. doi:10.3346/jkms.2003.18.5.738. PMC 3055112. PMID 14555830.