Inguinal lymph nodes are lymph nodes in the groin. They are situated in the femoral triangle of the inguinal region. They are subdivided into two groups: the superficial inguinal lymph nodes and deep inguinal lymph nodes.
| Inguinal lymph nodes | |
|---|---|

| |
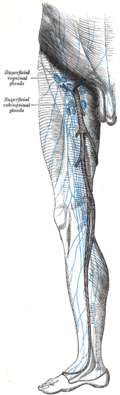 The lymph glands and lymphatic vessels of the lower extremity in males. | |
| Details | |
| System | Lymphatic system |
| Drains from | Most of perineal region |
| Drains to | Abdominal region of lymph nodes |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nodi lymphoidei inguinales superficiales |
| TA98 | A13.3.05.002 |
| FMA | 44226 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Superficial inguinal lymph nodes
editThe superficial inguinal lymph nodes are the inguinal lymph nodes that form a chain immediately inferior to the inguinal ligament. They lie deep to the fascia of Camper that overlies the femoral vessels at the medial aspect of the thigh. They are bounded superiorly by the inguinal ligament in the femoral triangle, laterally by the border of the sartorius muscle, and medially by the adductor longus muscle.
There are approximately 10 superficial lymph nodes. They normally measure up to 2 cm in diameter.[1]
They are divided into three groups:
- inferior – inferior of the saphenous opening of the leg, receive drainage from lower legs
- superolateral – on the side of the saphenous opening, receive drainage from the side buttocks and the lower abdominal wall.
- superomedial – located at the middle of the saphenous opening, take drainage from the perineum and genitals.[2]
Afferents
editThey may receive lymphatic afferents from the following as applicable:
- integument of the penis
- scrotum
- perineum
- buttock
- abdominal wall below the level of the umbilicus
- back below the level of the iliac crest
- vulva
- anus (below the pectinate line)
- the thigh and the medial side of the leg (the lateral leg drains to the popliteal lymph nodes first).
Efferents
editThey drain to the deep inguinal lymph nodes.[1]
Deep inguinal lymph nodes
editThe deep inguinal lymph nodes are 3-5 in number. They lie medial to the femoral vein deep to the cribriform fascia.[3][4]
Size
editThe mean size of an inguinal lymph node, as measured over the short-axis, is approximately 5.4 mm (range 2.1-13.6 mm), with two standard deviations above the mean being 8.8 mm.[5] A size of up to 10 mm is generally regarded as a cut-off value for normal vs abnormal inguinal lymph node size.[6]
Cloquet's node
editThe superior-most node is situated in the groin, deep to the inguinal ligament, and is termed the Cloquet's node (also Rosenmuller's node).[7] It can instead be considered as the inferior-most of the external iliac lymph nodes.[8][citation needed] Cloquet's node is also considered as a potential sentinel lymph node.[7][9]
This node is named for French surgeon Jules Germain Cloquet,[3][4] or for German anatomist Johann Christian Rosenmüller.[10][11]
Efferents
editThe deep inguinal lymph nodes drain superiorly to the external iliac lymph nodes, then to the pelvic lymph nodes and on to the paraaortic lymph nodes.[12]
Clinical significance
editThe presence of swollen inguinal lymph nodes is an important clinical sign because lymphadenopathy (swelling) may indicate an infection, or spread as a metastasis from cancers, such as anal cancer and vulvar cancer. Inguinal lymph nodes may normally be up to 2 cm.[1] The cut-off value for normal sized inguinal nodes is up to 10 mm.[6]
Additional images
edit-
A view of the different inguinal lymph nodes
-
Murine inguinal lymph node beneath the bifurcation of superior epigastric vein. Bright structure visualised by MHC II-GFP construct, is the lymph node
-
Lymph node regions
References
edit- ^ a b c "Assessment of lymphadenopathy". BMJ Best Practice. Retrieved 2017-03-04. Last updated: Last updated: Feb 16, 2017
- ^ "Superficial Inguinal Lymph Nodes -- Medical Definition". www.medilexicon.com. Archived from the original on 2016-05-12. Retrieved 2016-05-09.
- ^ a b synd/2657 at Who Named It?
- ^ a b Loukas M, El-Sedfy A, Tubbs RS, Wartman C (November 2007). "Jules Germain Cloquet (1790-1883)--drawing master and anatomist". Am Surg. 73 (11): 1169–72. PMID 18092657.
- ^ Bontumasi, Nicholas; Jacobson, Jon A.; Caoili, Elaine; Brandon, Catherine; Kim, Sung Moon; Jamadar, David (2014). "Inguinal lymph nodes: size, number, and other characteristics in asymptomatic patients by CT". Surgical and Radiologic Anatomy. 36 (10): 1051–1055. doi:10.1007/s00276-014-1255-0. ISSN 0930-1038. PMID 24435023.
- ^ a b Maha Torabi, MD; , Suzanne L. Aquino & Mukesh G. Harisinghani (2004-09-01). "Current Concepts in Lymph Node Imaging". J Nucl Med. 45 (9): 1509–1518.
- ^ a b Zhu Y, Zhang SL, Ye DW, et al. (May 2009). "Prospectively packaged ilioinguinal lymphadenectomy for penile cancer: the disseminative pattern of lymph node metastasis". J. Urol. 181 (5): 2103–8. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2009.01.041. PMID 19286211.
- ^ "Clinical Sidelights to Core Concepts in Anatomy". Archived from the original on 2010-02-26. Retrieved 2010-03-06.
- ^ Shen P, Conforti AM, Essner R, Cochran AJ, Turner RR, Morton DL (2000). "Is the node of Cloquet the sentinel node for the iliac/obturator node group?". Cancer J. 6 (2): 93–7. PMID 11069226.
- ^ "Whonamedit - dictionary of medical eponyms". www.whonamedit.com.
- ^ "node of Cloquet". TheFreeDictionary.com. Retrieved 2017-09-18.
- ^ "lymph nodes and nerves". www.oganatomy.org. Retrieved 2016-05-09.