Liver fluke is a collective name of a polyphyletic group of parasitic trematodes under the phylum Platyhelminthes.[1] They are principally parasites of the liver of various mammals, including humans. Capable of moving along the blood circulation, they can occur also in bile ducts, gallbladder, and liver parenchyma. In these organs, they produce pathological lesions leading to parasitic diseases. They have complex life cycles requiring two or three different hosts, with free-living larval stages in water.[2]

Biology
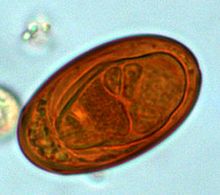
editThe body of liver flukes is leaf-like and flattened. The body is covered with a tegument. They are hermaphrodites having complete sets of both male and female reproductive systems. They have simple digestive systems and primarily feed on blood. The anterior end has the oral sucker opening into the mouth. Inside, the mouth leads to a small pharynx which is followed by an extended intestine that runs the entire length of the body. The intestine is heavily branched and the anus is absent. Instead, the intestine runs along an excretory canal that opens at the posterior end. Adult flukes produce eggs that are passed out through the excretory pore. The eggs infect different species of snails (as intermediate hosts) in which they grow into larvae. The larvae are released into the environment from which the definitive hosts (humans and other mammals) acquire the infection. In some species another intermediate host is required, generally a cyprinid fish, and the definitive hosts are infected from eating infected fish. Hence, these species are food-borne parasites.[3][4]
Pathogenicity
editLiver fluke infections cause serious medical and veterinary diseases. Fasciolosis of sheep, goats and cattle, is the major cause of economic losses in dairy and meat industry.[5] Fasciolosis of humans produces clinical symptoms such as fever, nausea, swollen liver, extreme abdominal pain, jaundice and anemia.[6]
Clonorchiasis and opisthorchiasis (due to Opisthorchis viverrini) are particularly dangerous. They can survive for several decades in humans causing chronic inflammation of the bile ducts, epithelial hyperplasia, periductal fibrosis and bile duct dilatation. In many infections these symptoms cause further complications such as stone formation, recurrent pyogenic cholangitis and cancer (cholangiocarcinoma).[7] Opisthorchiasis is the leading cause of cholangiocarcinoma in Thailand and Laos.[8] Clonorchis sinensis and Opisthorchis viverrini are both categorized by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) as Group 1 carcinogens.[9][10]
Species
editSpecies of liver fluke include:[11][12]
- Clonorchis sinensis (the Chinese liver fluke, or the Oriental liver fluke)
- Dicrocoelium dendriticum (the lancet liver fluke)
- Dicrocoelium hospes
- Fasciola hepatica (the sheep liver fluke)
- Fascioloides magna (the giant liver fluke)
- Fasciola gigantica
- Fasciola jacksoni
- Metorchis conjunctus
- Metorchis albidus
- Protofasciola robusta
- Parafasciolopsis fasciomorphae
- Opisthorchis viverrini (Southeast Asian liver fluke)
- Opisthorchis felineus (Cat liver fluke)
- Opisthorchis guayaquilensis
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ Lotfy, WM; Brant, SV; DeJong, RJ; Le, TH; Demiaszkiewicz, A; Rajapakse, RP; Perera, VB; Laursen, JR; Loker, ES (2008). "Evolutionary origins, diversification, and biogeography of liver flukes (Digenea, Fasciolidae)". The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene. 79 (2): 248–255. doi:10.4269/ajtmh.2008.79.248. PMC 2577557. PMID 18689632.
- ^ Diseases and Disorders Volume 2. Tarrytown, NY: Marshall Cavendish COrporation. 2008. p. 525. ISBN 978-0-7614-7772-3.
- ^ Xiao, Lihua; Ryan, Una; Feng, Yaoyu (2015). Biology of Foodborne Parasites. Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press. pp. 276–282. ISBN 978-1-4665-6885-3.
- ^ Mas-Coma, S.; Bargues, M.D.; Valero, M.A. (2005). "Fascioliasis and other plant-borne trematode zoonoses". International Journal for Parasitology. 35 (11–12): 1255–1278. doi:10.1016/j.ijpara.2005.07.010. PMID 16150452.
- ^ Piedrafita, D; Spithill, TW; Smith, RE; Raadsma, HW (2010). "Improving animal and human health through understanding liver fluke immunology". Parasite Immunology. 32 (8): 572–581. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3024.2010.01223.x. PMID 20626812. S2CID 25000945.
- ^ Carnevale, Silvana; Malandrini, Jorge Bruno; Pantano, María Laura; Sawicki, Mirna; Soria, Claudia Cecilia; Kuo, Lein Hung; Kamenetzky, Laura; Astudillo, Osvaldo Germán; Velásquez, Jorge Néstor (2016). "Fasciola hepatica infection in humans: overcoming problems for the diagnosis". Acta Parasitologica. 61 (4): 776–783. doi:10.1515/ap-2016-0107. PMID 27787223. S2CID 28346356.
- ^ Lim, Jae Hoon (2011). "Liver Flukes: the Malady Neglected". Korean Journal of Radiology. 12 (3): 269–79. doi:10.3348/kjr.2011.12.3.269. PMC 3088844. PMID 21603286.
- ^ Sripa, Banchob; Bethony, Jeffrey M.; Sithithaworn, Paiboon; Kaewkes, Sasithorn; Mairiang, Eimorn; Loukas, Alex; Mulvenna, Jason; Laha, Thewarach; Hotez, Peter J.; Brindley, Paul J. (September 2011). "Opisthorchiasis and Opisthorchis-associated cholangiocarcinoma in Thailand and Laos". Acta Tropica. 120 (Suppl): S158–S168. doi:10.1016/j.actatropica.2010.07.006. PMC 3010517. PMID 20655862.
- ^ "IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans". monographs.iarc.fr. Retrieved 17 July 2017.
- ^ Kim, TS; Pak, JH; Kim, JB; Bahk, YY (2016). "Clonorchis sinensis, an oriental liver fluke, as a human biological agent of cholangiocarcinoma: a brief review". BMB Reports. 49 (11): 590–597. doi:10.5483/BMBRep.2016.49.11.109. PMC 5346318. PMID 27418285.
- ^ Chai, Jong-Yil; Jung, Bong-Kwang (2019). "Epidemiology of Trematode Infections: An Update". Digenetic Trematodes. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. Vol. 1154. pp. 359–409. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-18616-6_12. ISBN 978-3-030-18615-9. PMID 31297768. S2CID 195894725.
- ^ Lotfy, Wael M.; Brant, Sara V.; DeJong, Randy J.; Le, Thanh Hoa; Demiaszkiewicz, Aleksander; Rajapakse, R. P. V. Jayanthe; Perera, Vijitha B. V. P.; Laursen, Jeff R.; et al. (2008). "Evolutionary origins, diversification, and biogeography of liver flukes (Digenea, Fasciolidae)". The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene. 79 (2): 248–255. doi:10.4269/ajtmh.2008.79.248. PMC 2577557. PMID 18689632.