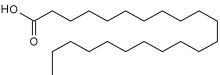
Behenic acid (also docosanoic acid) is a carboxylic acid, the saturated fatty acid with formula C21H43COOH. In appearance, it consists of white solid although impure samples appear yellowish.
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Docosanoic acid | |
| Other names
Behenic acid, Docosanoic acid; 1-Docosanoic acid; n-Docosanoic acid, n-Docosanoate, Glycon B-70, Hydrofol Acid 560, Hydrofol 2022-55, Hystrene 5522, Hystrene 9022, Prifrac 2989, C22:0 (Lipid numbers)
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.646 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C22H44O2 | |
| Molar mass | 340.592 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Melting point | 80.0 °C (176.0 °F; 353.1 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 306 °C (583 °F; 579 K) |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |

Sources
editAt 9%, it is a major component of ben oil (or behen oil), which is extracted from the seeds of the drumstick tree (Moringa oleifera). It is so named from the Persian month Bahman, when the roots of this tree were harvested.[2]
Behenic acid is also present in some other oils and oil-bearing plants, including rapeseed (canola) and peanut oil and skins. It is estimated that one ton of peanut skins contains 13 pounds (5.9 kg) of behenic acid.[3]
Properties
editAs a dietary oil, behenic acid is poorly absorbed. In spite of its low bioavailability compared with oleic acid, behenic acid is a cholesterol-raising saturated fatty acid in humans.[4]
Uses
editCommercially, behenic acid is often used to give hair conditioners and moisturizers their smoothing properties.[3] It is also used in lubricating oils, and as a solvent evaporation retarder in paint removers. Its amide is used as an anti-foaming agent in detergents, floor polishes and dripless candles. Reduction of behenic acid yields behenyl alcohol.
Pracaxi oil (from the seeds of Pentaclethra macroloba) is a natural product with one of the highest concentrations of behenic acid, and is used in hair conditioners.
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ Beare-Rogers, J. L.; Dieffenbacher, A.; Holm, J. V. (2001). "Lexicon of lipid nutrition (IUPAC Technical Report)". Pure and Applied Chemistry. 73 (4): 685–744. doi:10.1351/pac200173040685. S2CID 84492006.
- ^ "History of scientific nomenclature and mathematical symbols - Numericana".
- ^ a b USDA Scientists Find Treasure in Peanut Skins Archived 2006-03-23 at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ Nilo B Cater and Margo A Denke, January 2001, Behenic acid is a cholesterol-raising saturated fatty acid in humans. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, v 73, No. 1, pp 41-44.[unreliable source?].
