The island of Borneo, located in southeast Asia at the southern edge of the South China Sea, is home to one endemic bird family, three endemic bird genera and 61 endemic bird species. All but one of the latter are forest dwellers, with most restricted to the spine of hills and mountains running down the middle of the island. The avian endemism has been shaped by the island's geological history. Borneo sits on a continental shelf. During glacial periods, when water levels were lower, Borneo was linked with other islands on the shelf and with the Malay Peninsula in a large landmass known as Sundaland. This allowed bird species to move freely throughout the region until the waters rose again as the glaciers melted. Separated from their relatives by the sea, some of these species evolved over millennia into the endemics now found on the island. BirdLife International has designated the mountainous central spine of the island as an Endemic Bird Area (EBA) because of the number of endemic species found there, and has further designated several lowland regions and nearby islands as secondary EBAs. Habitat destruction is a major threat to Borneo's endemic birds, as forests are lost to palm oil plantations and timber harvesting.
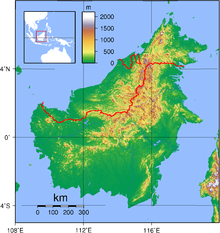
Geology and geological history
editBorneo is an island located in southeast Asia, on the continental shelf at the southern edge of the South China Sea. It lies south of the Philippines, west of Sulawesi, north of Java, and east of Peninsular Malaysia. With an area of 748,168 km2 (288,869 sq mi), it is the world's third largest island. More than half of the island is lowlands, rising to less than 150 m (490 ft). However, a spine of mountains runs down much of the central portion of the island. These include Mount Kinabalu, which at 4,095 m (13,435 ft) is the tallest mountain between the Himalayas and West Papua. The island is shared by three countries: Indonesia, Malaysia, and Brunei.[1] While the lowlands are the most productive habitat in terms of the number of bird species found there, the mountains are the seat of Borneo's endemism.[2] This is in large part due to the island's geological history.[3]
During the Pleistocene, the world's polar caps repeatedly advanced and retreated, alternately locking vast amounts of water into ice, and releasing it back into the world's oceans. This caused the water level in the oceans to repeatedly rise and fall. During glacial periods, when water levels were at their lowest, much of the Sunda Shelf was exposed. This linked what are now discrete islands (including Borneo, Java, Sumatra, and a host of smaller islands) with the Malay Peninsula in one large landmass known as Sundaland. During periods when the shelf was exposed, birds could move freely across the whole landmass. When the waters rose again, these birds were cut off from their relatives, and evolved in isolation on the various islands. Temperatures were cooler overall during glacial periods, so montane birds (those generally restricted to the slopes of mountains) could move lower and spread across larger areas. During interglacial periods, they retreated to higher elevations and were separated again from other populations, including birds in the lowlands.[3][4] Studies have shown that some endemic montane species are most closely related to species in Borneo's lowlands, while others are more closely related to montane species on other Sundaland islands.[5]
Endemism and threats
editThe island is home to a single endemic family: Pityriaseidae, which contains a single endemic genus (Pityriasis) with a single endemic species, the Bornean bristlehead.[6] In addition, the island holds two other endemic genera, both of which are also monotypic: Chlamydochaera (the fruithunter) and Haematortyx (the crimson-headed partridge).[6] Two other monotypic genera formerly considered to be endemic to the island—Chlorocharis and Oculocincta—have since been merged into more widespread genera. Chlorocharis was merged into the large white-eye genus Zosterops after molecular studies showed it nested comfortably within that genus. The same studies showed that Oculocincta was embedded within the smaller white-eye genus Heleia, leading it to be moved as well.[7][8][9]
There are 61 endemic bird species on Borneo, according to the taxonomy proposed by the International Ornithologists' Union.[9] Nearly all of these are forest birds; only the dusky munia is not. In all, roughly 10% of Borneo's forest birds are endemic to the island. Of these, 60% are montane species, 30% are found on lower slopes, and 10% are lowland species.[10] However, Borneo's forests are under threat, particularly in the lowlands. Nearly 40% of the island's forests had been completely cleared by 2016, and another 34% had been selectively logged.[11] Some 80% of Kalimantan's forests have been sold to timber concessions.[12] Much of the original lowland forest has been converted to palm oil plantations; these now cover more than 32% of Kalimantan's lowland area.[11] This results in a huge loss of biodiversity. While the original dipterocarp forests are home to more than 220 bird species, for example, palm plantations support only about 14 resident species.[13] Some 80% of Kalimantan's forests have been opened up to timber concessions, even in protected areas.[12][14] Many highland forests fall into protected areas—including national parks and forest reserves—but such gazetting does not always guarantee true protection, with logging occurring even in those areas.[15]
Endemic Bird Areas
editBirdlife International defines Endemic Bird Areas (EBAs) as places where the breeding ranges of two or more range-restricted species—those with breeding ranges of less than 50,000 km2 (19,000 sq mi)—overlap. In order to qualify, the whole of the breeding range of at least two range-restricted species must fall entirely within the EBA.[17] Borneo has one such area. The Bornean mountains EBA (157) comprises 130,000 km2 (50,000 sq mi) of mountain ranges in Borneo's interior, at an altitude above 500 m (1,600 ft) in elevation. These mountains are found in all three countries which share the island. Two of Borneo's three endemic genera are found here; only the Borneo bristlehead is found at lower elevations. In total, 31 range-restricted species occur within this EBA.[18]
BirdLife International has also designated five Secondary EBAs for Borneo: two smaller island groups and three areas on Borneo itself. Secondary EBAs are those which either include the breeding range of only a single range-restricted species, or those which cover only part of a range-restricted bird's breeding area.[19]
- The North-east Bornean islands secondary area (s097) includes a number of small islands off the northern and eastern coasts of Borneo.[20] The grey imperial pigeon, which the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) considers to be a vulnerable species, is found on a dozen or so of the islands; the near threatened, range-restricted Mantanani scops owl is more common and widespread on the small islands off Sabah. Both species also breed on small islands near the Philippines. Three designated Important Bird Areas (IBAs) fall within this area.[20]
- The Sabah lowlands secondary area (s098) encompasses the lowlands of the Malaysian state of Sabah, at the northern end of Borneo. The breeding range of the white-fronted falconet, a near-threatened species, falls entirely within the area. Part of the breeding range of the white-crowned shama is also included. The secondary area includes eight designated IBAs.[21]
- The Kalimantan lowlands secondary area (s099) encompasses the lowland forest thought to contain the breeding range of the black-browed babbler, a presumably threatened species rediscovered in 2020, more than 170 years after the only specimen was collected.[22][23] There are no IBAs in this secondary area.[22]
- The Bornean coastal zone secondary area (s100) includes mangroves, coastal forest, and scrub on the island's western and southern coasts. These lie in the Malaysian state of Sarawak, and the Indonesian provinces of Kalimantan Barat, Kalimantan Selatan and Kalimantan Tengah. Part of the breeding area of the range-restricted Javan white-eye is found here; the vulnerable species also breeds on the Javan coast. The secondary area includes one designated IBA.[24]
- The Natuna Islands secondary area (s101) includes small islands in an archipelago located off the western coast of Borneo. The critically endangered and range-restricted silvery pigeon occurs in very small numbers here; it also occurs on Sumatra and a few smaller islands just off Sumatra's coasts.[25][26] One designated IBA lies within this zone.[26]
List of endemic species
edit| Conservation status | |
|---|---|
| EX | Extinct (0 species) |
| EW | Extinct in the wild (0 species) |
| CR | Critically Endangered (0 species) |
| EN | Endangered (1 species) |
| VU | Vulnerable (5 species) |
| NT | Near threatened (13 species) |
| LC | Least concern (37 species) |
| Other categories | |
| DD | Data deficient (2 species) |
| NE | Not evaluated (2 species) |
| Taxon. order[nb 1] |
Common name | Picture | Scientific name | Habitat | IUCN status[nb 2] |
Notes | EBA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hose's partridge | Rhizothera dulitensis | Hill and lower montane forest[28] | VU IUCN | Also known as Dulit partridge.[29] | ||
| 2 | Red-breasted partridge | Arborophila hyperythra | Hill dipterocarp forest; lower and upper montane forest[30] | LC IUCN | Also known as Bornean partridge.[31] | 157 | |
| 3 | Crimson-headed partridge | Haematortyx sanguiniceps | Hill dipterocarp forest; lower and upper montane forest[30] | LC IUCN | 157 | ||
| 4 | Bulwer's pheasant | Lophura bulweri | Hill and lower montane forest[32][33] | VU IUCN | |||
| 5 | Bornean peacock-pheasant | Polyplectron schleiermacher | Lowland and hill dipterocarp forest[33][34] | EN IUCN | |||
| 6 | Dulit frogmouth | Batrachostomus harterti | Hill dipterocarp forest; lower montane forest[30] | NT IUCN | 157 | ||
| 7 | Bornean frogmouth | Batrachostomus mixtus | Hill dipterocarp forest; lower montane forest[30] | NT IUCN | |||
| 8 | Bornean swiftlet | Collocalia dodgei | Upper montane forest[35][36] | LC IUCN | Sometimes considered to be a subspecies of the cave swiftlet or the glossy swiftlet.[37] | ||
| 9 | Bornean ground cuckoo | Carpococcyx radiceus | Lowland primary dipterocarp and riverine forest[38][39] | NT IUCN | |||
| 10 | Mountain serpent eagle | Spilornis kinabaluensis | Upper montane forest[30] | VU IUCN | 157 | ||
| 11 | Whitehead's trogon | Harpactes whiteheadi | Lower and upper montane forest[30] | NT IUCN | 157 | ||
| 12 | Mountain barbet | Psilopogon monticola | Lower and upper montane forest[30] | LC IUCN | 157 | ||
| 13 | Golden-naped barbet | Psilopogon pulcherrimus | Upper montane forest[30] | LC IUCN | 157 | ||
| 14 | Bornean barbet | Psilopogon eximius | Lower and upper montane forest[30] | LC IUCN | 157 | ||
| 15 | Brown barbet | Caloramphus fuliginosus | Lowland dipterocarp forest and lower hill forest, swamp forest and kerangas forest[40][41] | LC IUCN | Sometimes known as the Bornean brown barbet.[42] | ||
| 16 | White-fronted falconet | Microhierax latifrons | Lowland dipterocarp forest[43][44] | NT IUCN | s098 | ||
| 17 | Hose's broadbill | Calyptomena hosii | Hill dipterocarp forest; lower montane forest[30] | NT IUCN | 157 | ||
| 18 | Whitehead's broadbill | Calyptomena whiteheadi | Lower and upper montane forest[30] | LC IUCN | 157 | ||
| 19 | Bornean banded pitta | Hydrornis schwaneri | Lowland and hill dipterocarp forest[45][46] | LC IUCN | |||
| 20 | Blue-headed pitta | Hydrornis baudii | Lowland dipterocarp forest[45][46] | VU IUCN | |||
| 21 | Black-crowned pitta | Erythropitta ussheri | Lowland dipterocarp forest[45][47] | NT IUCN | |||
| 22 | Blue-banded pitta | Erythropitta arquata | Hill and lower montane forest, particularly bamboo groves[45][47] | LC IUCN | |||
| 23 | Bornean bristlehead | Pityriasis gymnocephala | Lowland and hill dipterocarp forest[48][49] | NT IUCN | |||
| 24 | Bornean whistler | Pachycephala hypoxantha | Lower and upper montane forest[30] | LC IUCN | 157 | ||
| 25 | Black oriole | Oriolus hosii | Lower and upper montane forest[30] | NT IUCN | 157 | ||
| 26 | Bornean black magpie | Platysmurus aterrimus | Lowland forest and swamp forest | LC IUCN | Formerly considered to be a subspecies of the black magpie; split in 2021. | ||
| 27 | Bornean green magpie | Cissa jefferyi | Lower forest[48][50] | LC IUCN | |||
| 28 | Bornean treepie | Dendrocitta cinerascens | Hill dipterocarp forest; lower and upper montane forest[48][50] | LC IUCN | |||
| 29 | Charlotte's bulbul | Iole charlottae | Lowland and hill dipterocarp and peat swamp forests[51][52] | NT IUCN | Sometimes considered to be a subspecies of the buff-vented bulbul.[53] | ||
| 30 | Bornean bulbul | Rubigula montis | Lower and upper montane forest[54][55] | LC IUCN | |||
| 31 | Cream-eyed bulbul | Pycnonotus pseudosimplex | Lowland and hill dipterocarp and peat swamp forests; lower montane forests[56][57] | LC IUCN | |||
| 32 | Pale-faced bulbul | Pycnonotus leucops | Upper montane forest[54][58] | LC IUCN | Sometimes considered to be a subspecies of the flavescent bulbul.[59] | ||
| 33 | Bornean stubtail | Urosphena whiteheadi | Hill dipterocarp forest; lower and upper montane forest[30] | LC IUCN | 157 | ||
| 34 | Friendly bush-warbler | Locustella accentor | Upper montane forest[30] | LC IUCN | 157 | ||
| 35 | Chestnut-crested yuhina | Staphida everetti | Hill dipterocarp forest; lower and upper montane forest[30] | LC IUCN | 157 | ||
| 36 | Pygmy white-eye | Heleia squamifrons | Hill dipterocarp forest and lower montane forest[30] | LC IUCN | 157 | ||
| 37 | Mountain blackeye | Zosterops emiliae | Upper montane forest[30] | LC IUCN | 157 | ||
| 38 | Meratus white-eye | Zosterops meratusensis | Montane forest | LC IUCN | |||
| 39 | Bare-headed laughingthrush | Melanocichla calva | Lower and upper montane forest[30] | LC IUCN | 157 | ||
| 40 | Black-throated wren-babbler | Turdinus atrigularis | Lowland dipterocarp forest[60][61] | NT IUCN | |||
| 41 | Black-browed babbler | Malacocincla perspicillata | Probably lowland forest[62][63] | DD IUCN | Rediscovered in 2020, more than 170 years after the only specimen was collected.[23] | s099 | |
| 42 | Mountain wren-babbler | Gypsophila crassa | Lower and upper montane forest[30] | LC IUCN | 157 | ||
| 43 | Bornean wren-babbler | Ptilocichla leucogrammica | Lowland dipterocarp and peat swamp forests; kerangas forest[60][64] | VU IUCN | |||
| 44 | Chestnut-hooded laughingthrush | Pterorhinus treacheri | Hill dipterocarp forest; lower and upper montane forests[65][66] | LC IUCN | |||
| 45 | Everett's thrush | Zoothera everetti | Lower and upper montane forest[30] | NT IUCN | 157 | ||
| 46 | Fruithunter | Chlamydochaera jefferyi | Lower and upper montane forest[30] | LC IUCN | 157 | ||
| 47 | White-crowned shama | Copsychus stricklandii | Lowland and hill dipterocarp and peat swamp forests; lower montane forest[67][68] | LC IUCN | Sometimes considered to be a subspecies of the white-rumped shama.[69] | ||
| 48 | Dayak blue flycatcher | Cyornis montanus | Montane forest | LC IUCN | Sometimes considered to be a subspecies of the hill blue flycatcher (aka Javan blue flycatcher). | 157 | |
| 49 | Meratus blue flycatcher | Cyornis kadayangensis | Montane forest | NT IUCN | 157 | ||
| 50 | Bornean blue flycatcher | Cyornis superbus | Lowland and hill dipterocarp forest[70][71] | LC IUCN | |||
| 51 | Crocker jungle flycatcher | Cyornis ruficrissa | Montane forest | Not recognised by IUCN | Sometimes considered to be a subspecies of the Philippine jungle flycatcher. | 157 | |
| 52 | Eyebrowed jungle flycatcher | Vauriella gularis | Lower and upper montane forest[30] | LC IUCN | 157 | ||
| 53 | Bornean forktail | Enicurus borneensis | Streams in lower to upper montane forest[72][73] | Not recognised by IUCN | Sometimes considered to be a subspecies of the white-crowned forktail.[74] | ||
| 54 | Bornean whistling thrush | Myophonus borneensis | Lower and upper montane forest[75][73] | LC IUCN | |||
| 55 | Bornean leafbird | Chloropsis kinabaluensis | Lower and upper montane forest[76][77] | LC IUCN | |||
| 56 | Yellow-rumped flowerpecker | Prionochilus xanthopygius | Lowland, hill and lower montane forest[78][79] | LC IUCN | |||
| 57 | Spectacled flowerpecker | Dicaeum dayakorum | Lowland and hill dipterocarp forest[80][79] | DD IUCN | Described to science in 2019.[81] | ||
| 58 | Black-sided flowerpecker | Dicaeum monticolum | Hill dipterocarp forest; lower and upper montane forest[30] | LC IUCN | 157 | ||
| 59 | Bornean spiderhunter | Arachnothera everetti | Lowland, hill, and lower montane forest[82][83] | LC IUCN | Sometimes considered to be a subspecies of streaky-breasted spiderhunter.[84] | ||
| 60 | Whitehead's spiderhunter | Arachnothera juliae | Lower and upper montane forest[30] | LC IUCN | 157 | ||
| 61 | Dusky munia | Lonchura fuscans | Scrub, gardens, grasslands, and rice paddies[85][86] | LC IUCN |
See also
editNotes
edit- ^ This list uses the taxonomy proposed by the International Ornithologists' Union.[9] Avian checklists and field guides typically list species in taxonomic order to show the evolutionary relationships between species; those which are more closely related are physically listed nearer each other.[27]
- ^ This column sorts by threat level, as outlined in the key above.
Citations
edit- ^ a b Myers 2016, p. 9.
- ^ Phillipps & Phillipps 2014, p. 30.
- ^ a b Myers 2016, p. 11.
- ^ Phillipps & Phillipps 2014, p. 22.
- ^ Gawin et al. 2014, p. 87.
- ^ a b Myers 2016, p. 22.
- ^ Moyle et al. 2009, p. 1864.
- ^ Lim et al. 2018.
- ^ a b c Gill, Donsker & Rasmussen 2021.
- ^ Davison 2016, p. 8.
- ^ a b Myers 2016, p. 27.
- ^ a b Myers 2016, p. 28.
- ^ Phillipps & Phillipps 2014, p. 31.
- ^ Curran et al. 2004, p. 1001.
- ^ Borneo Today 2017.
- ^ Phillipps & Phillipps 2014, p. 330.
- ^ BirdLife International 2004.
- ^ BirdLife International 2021b.
- ^ Stattersfield et al. 1998, p. 24.
- ^ a b BirdLife International 2021e.
- ^ BirdLife International 2021f.
- ^ a b BirdLife International 2021c.
- ^ a b Akbar et al. 2020, p. 13.
- ^ BirdLife International 2021a.
- ^ BirdLife International 2021h.
- ^ a b BirdLife International 2021d.
- ^ Cornell Lab of Ornithology 2015.
- ^ Myers 2016, p. 44.
- ^ Birdlife International 2016a.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y Stattersfield et al. 1998, p. 486.
- ^ BirdLife International 2016b.
- ^ Phillipps & Phillipps 2014, p. 44.
- ^ a b Myers 2016, p. 48.
- ^ Phillipps & Phillipps 2014, p. 46.
- ^ Phillipps & Phillipps 2014, p. 182.
- ^ Myers 2016, p. 170.
- ^ Moyle et al. 2008, pp. 94–95.
- ^ Phillipps & Phillipps 2014, p. 168.
- ^ Myers 2016, p. 148.
- ^ Phillipps & Phillipps 2014, p. 204.
- ^ Myers 2016, p. 194.
- ^ BirdLife International 2016c.
- ^ Phillipps & Phillipps 2014, p. 96.
- ^ Myers 2016, p. 88.
- ^ a b c d Phillipps & Phillipps 2014, p. 216.
- ^ a b Myers 2016, p. 206.
- ^ a b Myers 2016, p. 208.
- ^ a b c Phillipps & Phillipps 2014, p. 236.
- ^ Myers 2016, p. 214.
- ^ a b Myers 2016, p. 232.
- ^ Phillipps & Phillipps 2014, p. 246.
- ^ Myers 2016, p. 244.
- ^ ITIS 2012a.
- ^ a b Phillipps & Phillipps 2014, p. 248.
- ^ Myers 2016, p. 238.
- ^ Phillipps & Phillipps 2014, p. 244.
- ^ Myers 2016, p. 242.
- ^ Myers 2016, p. 240.
- ^ ITIS 2012b.
- ^ a b Phillipps & Phillipps 2014, p. 262.
- ^ Myers 2016, p. 260.
- ^ Phillipps & Phillipps 2014, p. 258.
- ^ Myers 2016, p. 262.
- ^ Myers 2016, p. 258.
- ^ Phillipps & Phillipps 2014, p. 270.
- ^ Myers 2016, p. 266.
- ^ Phillipps & Phillipps 2014, p. 284.
- ^ Myers 2016, p. 280.
- ^ CABI 2021.
- ^ Phillipps & Phillipps 2014, p. 294.
- ^ Myers 2016, p. 284.
- ^ Phillipps & Phillipps 2014, p. 286.
- ^ a b Myers 2016, p. 292.
- ^ ITIS 2012c.
- ^ Phillipps & Phillipps 2014, p. 280.
- ^ Phillipps & Phillipps 2014, p. 220.
- ^ Myers 2016, p. 300.
- ^ Phillipps & Phillipps 2014, p. 304.
- ^ a b Myers 2016, p. 302.
- ^ Phillipps & Phillipps 2014, p. 306.
- ^ Saucier et al. 2019.
- ^ Phillipps & Phillipps 2014, p. 314.
- ^ Myers 2016, p. 314.
- ^ BirdLife International 2021g.
- ^ Phillipps & Phillipps 2014, p. 318.
- ^ Myers 2016, p. 318.
References
edit- Akbar, Panji Gusti; Nugroho, Teguh Willy; Suranto, Muhammad; Fauzan, Muhammad Rizky; Ferdiansyah, Doddy; Trisiyanto, Joko Said & Yong, Ding Li (December 2020). "Missing for 170 years—the rediscovery of black-browed babbler Malacocincla perspicillata on Borneo". BirdingASIA. 34: 13–14.
- BirdLife International (2004). "Most Endemic Bird Areas are in the tropics and important for other biodiversity too". birdlife.org. Retrieved 31 December 2020.
- BirdLife International (2016a). "Dulit Partridge: Rhizothera dulitensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016a: e.T22728242A94976330. Retrieved 7 February 2021.
- BirdLife International (2016b). "Bornean Partridge: Arborophila hyperthra". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016b: e.T22679047A92800839. Retrieved 7 February 2021.
- BirdLife International (2016c). "Bornean Brown Barbet: Caloramphus fuliginosus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016c: e.T22727049A94939526. Retrieved 7 February 2021.
- BirdLife International (2021a). "Data Zone: Bornean coastal zone". Retrieved 18 January 2021.
- BirdLife International (2021b). "Data Zone: Bornean mountains". Retrieved 18 January 2021.
- BirdLife International (2021c). "Data Zone: Kalimantan lowlands". Retrieved 18 January 2021.
- BirdLife International (2021d). "Data Zone: Natuna Islands". Retrieved 18 January 2021.
- BirdLife International (2021e). "Data Zone: North-east Bornean islands". Retrieved 18 January 2021.
- BirdLife International (2021f). "Data Zone: Sabah lowlands". Retrieved 18 January 2021.
- BirdLife International (2021g). "Streaky-breasted Spiderhunter (Arachnothera affinis)". Retrieved 7 February 2021.
- BirdLife International (2021h). "Data Zone: Silvery Pigeon Columba argentina". Retrieved 16 March 2021.
- Borneo Today (18 May 2017). "Priceworth gets green light To log 'controversial' Sabah Forest Reserve". Retrieved 2 February 2021.
- "Copsychus malabaricus (white-rumped shama): notes on taxonomy and nomenclature". CABI. 2021. Retrieved 7 February 2021.
- Cornell Lab of Ornithology (16 November 2015). "What is taxonomic order and why is it used for the sequence of birds in my field guide?". All About Birds. Retrieved 24 March 2021.
- Curran, L.M.; Trigg, S.N.; McDonald, A.K.; Astiani, D.; Hardiono, Y.M.; Siregar, P.; Caniago, I.; Kasischke, E. (2004). "Lowland forest loss in protected areas of Indonesian Borneo" (PDF). Science. 303 (5660): 1000–1003. Bibcode:2004Sci...303.1000C. doi:10.1126/science.1091714. PMID 14963327. S2CID 45484999.
- Davison, G. W. H. (2016). Birds of Borneo: Sabah, Sarawak, Brunei and Kalimantan. London, UK: Bloomsbury Publishing. ISBN 978-1-4729-3287-7.
- "Enicurus leschenaulti". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. 2012c. Retrieved 7 February 2021.
- Gawin, Dency F.; Rahman, Mustafa Abdul; Ramji, Mohamad Fizl Sidq; Smith, Brian Tilston; Lim, Haw Chuan; Moyle, Robert G. & Sheldon, Frederick H. (January 2014). "Patterns of avian diversification in Borneo: the case of the endemic mountain black-eye (Chlorocharis emiliae)". The Auk. 131 (1): 86–99. doi:10.1642/AUK-13-190.1. hdl:1808/16597. JSTOR 90008069. S2CID 13787326.
- Gill, Frank; Donsker, David & Rasmussen, Pamela, eds. (2021). "IOC World Bird List". IOC. Retrieved 16 January 2021.
- "Iole olivacea". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. 2012a. Retrieved 7 February 2021.
- Lim, B.T.M.; Sadanandan, K.R.; Dingle, C.; Leung, Y.Y.; Prawiradilaga, D.M.; Irham, M.; Ashari, H.; Lee, J.G.H. & Rheindt, F.E. (2018). "Molecular evidence suggests radical revision of species limits in the great speciator white‑eye genus Zosterops". Journal of Ornithology. 160: 1–16. doi:10.1007/s10336-018-1583-7. S2CID 51890116.
- Moyle, Robert G.; Filardi, Christopher F.; Smith, Catherine E. & Diamond, Jared (10 February 2009). "Explosive Pleistocene diversification and hemispheric expansion of a "great speciator"" (PDF). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 106 (6): 1863–1868. Bibcode:2009PNAS..106.1863M. doi:10.1073/pnas.0809861105. JSTOR 40421688. PMC 2644129. PMID 19181851.
- Moyle, Robert G.; Hosner, Peter A.; Nais, Jamili; Lakim, Maklarin & Sheldon, Frederick H. (March 2008). "Taxonomic status of the Kinabalu 'linchi' swiftlet". Bulletin of the British Ornithologists' Club. 128 (2): 94–100.
- Myers, Susan (2016). Birds of Borneo (2nd ed.). London, UK: Christopher Helm. ISBN 978-1-4729-2444-5.
- Phillipps, Quentin & Phillipps, Karen (2014). Phillipps' Field Guide to the Birds of Borneo: Sabah, Sarawak, Brunei, and Kalimantan (3rd ed.). Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-16167-9.
- "Pycnonotus flavescens". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. 2012b. Retrieved 7 February 2021.
- Saucier, Jacob R.; Milensky, Christopher M.; Caraballo-Ortiz, Marcos A.; Ragai, Roslina; Dahlan, N. Faridah & Edwards, David P. (2019). "A distinctive new species of flowerpecker (Passeriformes: Dicaeidae) from Borneo" (PDF). Zootaxa. 4686 (4): 451–464. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.4686.4.1. PMID 31719467. S2CID 207962716.
- Stattersfield, Alison J.; Crosby, Michael J.; Long, Adrian J. & Wege, David C. (1998). Endemic Bird Areas of the World: Priorities for Biodiversity Conservation. Cambridge, UK: BirdLife International. ISBN 978-0-946888-33-7.