Bejel, or endemic syphilis, is a chronic skin and tissue disease caused by infection by the endemicum subspecies of the spirochete Treponema pallidum. Bejel is one of the "endemic treponematoses" (endemic infections caused by spiral-shaped bacteria called treponemes), a group that also includes yaws and pinta. Typically, endemic trepanematoses begin with localized lesions on the skin or mucous membranes. Pinta is limited to affecting the skin, whereas bejel and yaws are considered to be invasive because they can also cause disease in bone and other internal tissues.[1]
| Nonvenereal endemic syphilis | |
|---|---|
| Other names | nonvenereal syphilis, endemic syphilis, bejel |
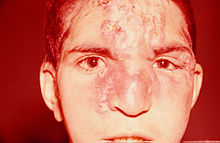 | |
| Disfiguring infiltration of the nose, glabella, and forehead with clustered nodules in left interciliary region of boy with endemic syphilis, Iran, 2010. | |
| Pronunciation | |
| Specialty | Infectious disease |
Signs and symptoms
editBejel usually begins in childhood as a small patch on the mucosa, often on the interior of the mouth, followed by the appearance of raised, eroding lesions on the limbs and trunk. Periostitis (inflammation) of the leg bones is commonly seen, and gummas of the nose and soft palate develop in later stages.[2]
Causes
editAlthough the organism that causes bejel, Treponema pallidum endemicum,[3] is morphologically and serologically indistinguishable from Treponema pallidum pallidum, which causes venereal syphilis, transmission of bejel is not venereal in nature.[4] However, recent epidemiological evidence suggests that Treponema pallidum endemicum may also cause venereal syphilis.[5]
Diagnosis
editThe diagnosis of bejel is based on the geographic history of the patient as well as laboratory testing of material from the lesions (dark-field microscopy). The responsible spirochaete is readily identifiable on sight in a microscope as a treponema.[2]
Epidemiology
editBejel has been known to be endemic in the Sahel region spanning from Mauritania and Senegal to Sudan, the other African countries of Côte d'Ivoire, Benin, and Somalia, the Kalahari Desert spanning from Namibia to Zimbabwe, West Asia spanning from Syria to Pakistan, and the Arabian Peninsula countries of Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and Oman.[6] It is unclear if it remains endemic in these countries, but a recent study suggested that the causative bacteria circulates outside of this range as venereal syphilis.[5]
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ Mitjà O, Šmajs D, Bassat Q (2013). "Advances in the diagnosis of endemic treponematoses: yaws, bejel, and pinta". PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases. 7 (10): e2283. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0002283. PMC 3812090. PMID 24205410.
- ^ a b Marks M, Solomon AW, Mabey DC (October 2014). "Endemic treponemal diseases". Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene. 108 (10): 601–7. doi:10.1093/trstmh/tru128. PMC 4162659. PMID 25157125.
- ^ Antal GM, Lukehart SA, Meheus AZ (January 2002). "The endemic treponematoses". Microbes and Infection. 4 (1): 83–94. doi:10.1016/S1286-4579(01)01513-1. PMID 11825779.
- ^ Pace JL, Csonka GW (October 1984). "Endemic non-venereal syphilis (bejel) in Saudi Arabia". The British Journal of Venereal Diseases. 60 (5): 293–7. doi:10.1136/sti.60.5.293. PMC 1046341. PMID 6487985.
- ^ a b Deresinski, Stan (2022-03-09). "Bejel: Sometimes a Venereal Nonvenereal Treponematosis—and in Places You Might Not Expect". Clinical Infectious Diseases | Oxford Academic. Retrieved 2024-06-10.
- ^ "Status of bejel endemicity". www.who.int. Retrieved 2024-06-10.