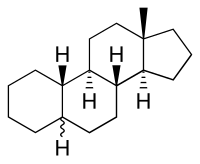
Estrane is a C18 steroid derivative, with a gonane core.
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
5ξ-Estrane[1]
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(3aS,3bR,5aΞ,9aS,9bR,11aS)-11a-Methylhexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 3125721 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H30 | |
| Molar mass | 246.438 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Estrenes are estrane derivatives that contain a double bond, with an example being nandrolone.[2] Estratrienes (estrins) are estrane derivatives that contain three double bonds, for instance estrin (estra-1,3,5(10)-triene). A class of female sex hormones, estrogens, such as estradiol, estrone, and estriol are estratrienes.
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (2014). Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013. The Royal Society of Chemistry. p. 1529. doi:10.1039/9781849733069. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ Estrenes at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)