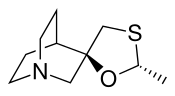
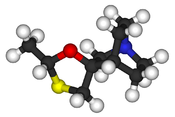
Cevimeline (trade name Evoxac) is a synthetic analog of the natural alkaloid muscarine with a particular agonistic effect on M1 and M3 receptors. It is used in the treatment of dry mouth and Sjögren's syndrome.
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Evoxac |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a608025 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth (capsules) |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | <20% |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C10H17NOS |
| Molar mass | 199.31 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Medical uses
editCevimeline is used in the treatment of xerostomia (dry mouth)[1][2] and Sjögren's syndrome.[1] It increases the production of saliva.[2]
Side effects
editKnown side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, excessive sweating, rash, headache, runny nose, cough, drowsiness, hot flashes, blurred vision, and difficulty sleeping.[3]
Contraindications include asthma and angle closure glaucoma.[citation needed]
Mechanism of action
editCevimeline is a cholinergic agonist.[2] It has a particular effect on M1 and M3 receptors.[2] By activating the M3 receptors of the parasympathetic nervous system, cevimeline stimulates secretion by the salivary glands, thereby alleviating dry mouth.
See also
edit- Pilocarpine — a similar parasympathomimetic medication for dry mouth (xerostomia)
- Bethanechol — a similar muscarinic parasympathomimetic with longer-lasting effect
References
edit- ^ a b Ono M, Takamura E, Shinozaki K, Tsumura T, Hamano T, Yagi Y, Tsubota K (July 2004). "Therapeutic effect of cevimeline on dry eye in patients with Sjögren's syndrome: a randomized, double-blind clinical study". American Journal of Ophthalmology. 138 (1): 6–17. doi:10.1016/j.ajo.2004.02.010. PMID 15234277.
- ^ a b c d Fox RI, Fox CM (2019). "Management of Sjögren's". Dubois' Lupus Erythematosus and Related Syndromes (9th ed.). Elsevier. pp. 745–758. doi:10.1016/B978-0-323-47927-1.00060-8. ISBN 978-0-323-47927-1.
- ^ "Cevimeline". MedicineNet. Retrieved 12 October 2007.