The black-throated loon (Gavia arctica), also known as the Arctic loon and the black-throated diver, is a migratory aquatic bird found in the northern hemisphere, primarily breeding in freshwater lakes in northern Europe and Asia. It winters along sheltered, ice-free coasts of the north-east Atlantic Ocean and the eastern and western Pacific Ocean. This loon was first described by Carl Linnaeus in 1758 and has two subspecies. It was previously considered to be the same species as the Pacific loon, of which it is traditionally considered to be a sister species, although this is debated. In a study that used mitochondrial and nuclear intron DNA, the black-throated loon was found to be sister to a clade consisting of the Pacific loon and two sister species, the common loon and the yellow-billed loon.
| Black-throated loon | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Gaviiformes |
| Family: | Gaviidae |
| Genus: | Gavia |
| Species: | G. arctica
|
| Binomial name | |
| Gavia arctica | |
| Subspecies | |
| |
| |
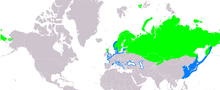
| Range of the black-throated loon Breeding Non-breeding
| |
| Synonyms | |
|
Colymbus arcticus Linnaeus, 1758 | |
The black-throated loon measures about 70 cm (28 in) in length and can weigh anywhere from 1.3 to 3.4 kilograms (2.9 to 7.5 lb). In breeding plumage, the adult of the nominate subspecies has mostly black upperparts, with the exception of some of the mantle and scapulars, which have white squares. The head and hindneck are grey, and the sides white and striped black. Most of the throat is also black, giving this bird the name "black-throated loon". The colour of the throat patch can be used to distinguish the two subspecies; the throat patch of the other subspecies, G. a. viridigularis, is green. The underparts are mostly white, including the bottom of the throat. The flanks are also white, a feature which can be used to separate this bird from the Pacific loon. When the bird is not breeding, the black patch on the throat is absent, replaced with white; most of the black lines on the throat are also missing, except those on the bottom sides, and the upperparts are unpatterned with the exception of a few white spots on the upperwing. The juvenile is similar to the non-breeding adult, except more brown overall.
The timing of the breeding season is variable; in the southern part of its range, this loon starts breeding in April, whereas in the northern portion, it waits until after the spring thaw. It builds an oval nest about 23 centimetres (9.1 in) across, either near the breeding lake or on vegetation emerging from it. The black-throated loon usually lays a clutch of two, rarely one or three, brown-green eggs with dark splotches. After an incubation period of 27 to 29 days, the chick hatches, and is fed a diet of small fish and invertebrates. The adult mostly eats fish. To catch this food, it forages by itself or in pairs, very rarely foraging in groups. It dives from the water, going no deeper than 5 metres (16 ft). Most dives are successful. Whether or not at least one chick will hatch from a nest is variable, ranging from 30% to 90%. Most failures come from predators and flooding. Overall, the population of this loon is declining, although the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) still rates it as least concern, because the population decline is not rapid enough. The black-throated loon is protected under both the Migratory Bird Treaty Act of 1918 and the Agreement on the Conservation of African-Eurasian Migratory Waterbirds.
Taxonomy and etymology
editThe black-throated loon was formally described in 1758 by the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus in the tenth edition of his Systema Naturae under the binomial name Colymbus arcticus.[2] Linnaeus specified the type locality as Europe and America but in 1761 he restricted it to Sweden.[3][4] In 1897 the American ornithologist Joel Asaph Allen suggested that the black-throated loon should be moved to the genus Gavia that had been introduced by Johann Forster in 1788. This proposal was adopted by the American Ornithologists' Union (AOU) in 1899.[5][6] The genus name Gavia comes from the Latin for 'sea mew', as used by the ancient Roman naturalist Pliny the Elder.[7] The specific arctica is Latin for 'northern' or 'Arctic'.[8] The name of the subspecies viridigularis stems from the Latin viridis, meaning 'green', and the Latin gularis, meaning 'throated', in reference to the green throat of this subspecies.[9] The common name, black-throated loon, stems from its black throat patch. This loon is also called the Arctic loon and the black-throated diver.[10]
There are two subspecies:[11]
- Gavia arctica arctica (Linnaeus, 1758) – This subspecies is found in northern Europe, east to the center of northern Asia, and from that to the Lena River and Transbaikal. It migrates to the coasts of northwestern Europe and the coasts of the Mediterranean, Black, and Caspian Seas.[10]
- G. a. viridigularis Dwight, 1918 – This subspecies is found in eastern Russia from the Lena River and Transbaikal east to the peninsulas of Chukotka and Kamchatka and the northern portion of Sakhalin. It migrates to the northwestern Pacific coasts.[10]
G. a. viridigularis was considered to be a separate species when described by Jonathan Dwight in 1918,[12] but in 1919 Arthur Cleveland Bent suggested that it be moved to its current placement as a subspecies.[13] The black-throated loon was previously considered conspecific with the North American Pacific loon, which was its subspecies,[14] but they have now been split into two species;[10] there was no evidence of the two interbreeding in areas where they occurred together.[15] Furthermore, the architecture of the air sacs in the lungs of the two species are significantly different.[16] This split was done by the AOU in 1985.[14] The phylogeny of this species is debated, the black-throated loon and the Pacific loon traditionally being considered sister species, whereas a study using mitochondrial and nuclear intron DNA supported placing the black-throated loon sister to a clade consisting of the Pacific loon and the two sister species that are the common loon and the yellow-billed loon. This latter study is criticised on the basis that it may form a phylogeny on incomplete lineage sorting. In the former phylogeny, the split between the Pacific loon and the black-throated loon is proposed to have happened about 6.5 million years ago.[15]
Description
editThe adult black-throated loon is 58 to 73 cm (23 to 29 in) in length with a 100 to 130 cm (39 to 51 in) wingspan and a weight of 1.3 to 3.4 kilograms (2.9 to 7.5 lb). The nominate subspecies in its breeding plumage has a grey head and hindneck, with a black throat and a large black patch on the foreneck, both of which have a soft purple gloss. The lower throat has a necklace-shaped patch of short parallel white lines. The sides of the throat have about five long parallel white lines that start at the side of the patch on the lower throat and run down to the chest, which also has a pattern of parallel white and black lines. The rest of the underparts, including the centre of the chest, are pure white. The upperparts are blackish down to the base of the wing, where there are a few rows of high contrast white squares that cover the mantle and scapulars. There are small white spots on both the lesser and median coverts. The rest of the upperwing is a blackish colour. The underwing is paler than the upperwing, and the underwing coverts are white. The tail is blackish. The bill and legs are black, with a pale grey colour on the inner half of the legs. The toes and the webs are grey, the latter also being flesh coloured. The irides are a deep brown-red. The sexes are alike, and the subspecies viridigularis is very similar to the nominate except that the former has a green throat patch, instead of black.[10] The subspecies viridigularis retains a purplish gloss, although less than the nominate.[13]
The non-breeding adult differs from the breeding adult in that the cap and the back of the neck are more brownish. The non-breeding adult also lacks the patterned upperparts of the breeding adult, although some of the upperwing coverts do not lose their white spots. This results in the upperparts being an almost unpatterned black from above. The sides of the throat are usually darker at the white border separating the sides of the throat and the front of the throat; most of the time a thin dark necklace between these two areas can be seen. There is white on the sides of the head that are below the eye. The bill is a steel-grey with, similar to the breeding adult, a blackish tip.[10]
The juvenile is similar to the non-breeding adult, but has a browner appearance. It has a buffy scaling on the upperparts that is especially pronounced on the scapulars. The lower face and front of the neck has a diffused brownish tinge. The juvenile does not have the white spots on the wing coverts, and its irides are darker and more dull in colour. The chick hatches with down feathers that range from sooty-brown to brownish-grey, usually with a slightly paler head. The abdomen is pale.[10]
The black-throated loon can be distinguished from the Pacific loon by the white on the flanks of the former.[17]
Vocalizations
editThe male, when breeding, vocalizes a loud and rhythmic "oooéé-cu-cloooéé-cu-cloooéé-cu-cluuéé" whistling song. A "áááh-oo" wail can also be heard, and a growling or croaking "knarr-knor", a sound given especially at night. The alarm call at the nest is a rising "uweek".[10]
Distribution and habitat
editThe black-throated loon has a large range, breeding taking place across northern Europe, Asia,[1] and the Seward Peninsula in Alaska.[17] When breeding, it is found in the area around isolated, deep freshwater lakes[18] larger than 0.1 square kilometres (0.039 sq mi),[19] especially those with inlets,[10] as it prefers to face only small stretches of open water.[20] When it is not breeding, this loon moves in a general southward direction and towards ice-free sea,[10] usually wintering in coasts on north-east Atlantic Ocean and those on the eastern and western Pacific Ocean, such as the coasts of Japan.[1] During this time, its habitat is usually inshore waters along sheltered coasts, although it will sometimes be found inland, in places such as the Mediterranean and Black seas.[10]
Behaviour
editLike other loons, this bird does not take flight well; it takes off by pattering on a "runway" of water.[21] While flying, it makes a barking "kwow" flight call.[22]
Breeding
editThis species usually nests on the ground[23] within about 1 metre (3.3 ft) of the lake it breeds at.[19] This loon also sometimes nests on vegetation, like Arctophila fulva, that has emerged from lakes. The nest site is often reused the next year.[24] The nest itself is oval-shaped[23] and built mostly by the female[25] out of heaped plant material like leaves and sticks.[18] The nest is about 23 centimetres (9.1 in) across. Families of black-throated loons often move their nest site from the original nest ponds they inhabited to wetlands nearby after the chicks reach two weeks of age. The journey is generally less than 150 metres (490 ft).[24]
In the southern portion of its range, this loon starts to breed in April, whereas in the northern parts of its range, it waits until the spring thaw,[10] when there is adequate water for it to take off.[23] It usually arrives before the lake thaws, in the latter case.[25]
Before copulation, the female hunches its neck and swims close to the shore until it finds a suitable place and then lies down on the shore. The male sometimes adopts the same posture as the female. During this time, the only vocalization made is a one note "hum". During copulation, the male, coming ashore, mounts the female and occasionally flaps its wings loudly. After this, the male returns to the water and preens itself. The female stays ashore for a maximum of about 23 minutes and usually starts to build the nest.[25]
The black-throated loon lays a clutch of two, very rarely one or three,[10] 76 by 47 millimetres (3.0 by 1.9 in) eggs that are brown-green with darker speckles. These eggs are incubated by both parents for a period of 27 to 29 days,[18] with the female spending the most time incubating. During incubation, this bird turns its eggs. The interval between when they are turned is very irregular, ranging from one minute to about six hours.[25] After they hatch, the mobile young are fed by both parents for a period of weeks.[18] The chicks fledge about 60 to 65 days after hatching, and achieve sexual maturity after two to three years.[10]
Nesting success, whether or not at least one chick will hatch from any given nest, is variable year to year, ranging from under 30% to over 90%.[24] For clutches of two eggs, the average nesting success is about 50%, whereas in clutches with only one egg, this rate is about 60%.[20] The nesting success is influenced most by predation,[23] and flooding.[20] Some of the adults that lose their clutch early in the incubation period renest. Most of the time, only one chick survives to fledge, the other dying within seven days of hatching.[24] In Scotland, a study concluded that a single pair usually fledges a chick, on average, 25% of the time per year.[10] This can be increased by artificial means, such as constructing rafts for loons to nest on.[26] Whether or not there is at least one chick fledged is influenced by the density of fish in the breeding lake; a lake with a higher density of fish usually reduces the chance that a pair will fledge a chick, even though this loon feeds mainly on fish. There are two factors that might contribute to this; the first being that aquatic insects, an alternative food source for chicks, are more dense when there are less fish, and the second being that a higher density of fish means more northern pike, a predator of small chicks.[27]
Feeding
editA top predator in the pelagic zone of some subarctic lakes,[28] this bird feeds on fish and sometimes insects, molluscs, crustaceans, and plant matter.[10] The black-throated loon usually forages by itself or in pairs, rarely feeding in groups with multiple species.[29] It dives from the water,[30] at depths of no more than 5 metres (16 ft).[31] Just before diving, this loon stretches and holds up its neck until it is erect and at full length. It usually jumps slightly upwards before diving.[32] These dives are frequent, with an average of about 1.6 dives per minute. Most dives, about 80% of them, are successful, and those that are successful are usually shorter than those that are unsuccessful, with an average of 17 seconds for each successful dive, and 27 seconds for each unsuccessful dive. These dives usually only result in small items, and those that yield larger pieces of food are usually more than 40 seconds, where this bird catches quick-swimming fish.[31]
When it is breeding, the adult usually feeds away from the nest, foraging either at the opposite end of the breeding or at lakes near the breeding lake. When foraging for newly hatched chicks, the adult forages in the lake where the nest is or in nearby lakes, returning after a prey item has been caught. When the chicks are older, they usually accompany both of the parents, swimming a few metres behind them. The strategy that predominates immediately after hatching is generally still employed when the chicks are older, but at a reduced rate.[33] The chicks are fed only one item of prey at a time. The young are also able to capture food themselves at least 36 days after hatching, although they are still fed daily up until about 70 days of age.[25]
The diet of black-throated loon chicks varies, the prey in the breeding lake being a major factor. For the first eight days, chicks are usually fed three-spined sticklebacks and common minnows if they are found in the breeding lake. If they are not present, then the chicks are brought up mainly on small invertebrates until about eight days, when they are able to take trout of about 100 millimetres (3.9 in) in length. Although in these chicks trout makes up the majority of their diet, they are still fed invertebrates in large numbers. In all lakes, salmonids make up an important part of the chicks' diet after eight days. Salmonids, especially those between 100 and 240 millimetres (3.9 and 9.4 in), are important in the diets of older chicks. Eels are also an important food for older chicks.[33]
Predators and parasites
editThe black-throated loon is sometimes parasitized by Eustrongylides tubifex, a species of nematode that can cause Eustrongylidosis.[34] Mammalian predators, such as red foxes and pine martens,[19] are likely the cause of about 40% of clutch losses. Avian predators, such as hooded crows, also take the eggs of this loon.[20]
Status
editConservation
editDespite the fact that its population is declining, the black-throated loon is listed as a species of least concern by the IUCN. This is because the species has a large population and an extremely large range, and its decline does not appear to be rapid.[1] In the United States, it is protected under the Migratory Bird Treaty Act of 1918,[35] while in Europe and Africa, it is protected under the Agreement on the Conservation of African-Eurasian Migratory Waterbirds.[36]
Threats
editAcidification and heavy-metal pollution of the breeding lake possibly threatens this bird. It is also vulnerable to oil pollution, especially when near fishing grounds. Fishing nets are also a cause of mortality. This loon is sensitive to windfarms near the coast. Overall, the annual mortality rate of the adult black-throated loon is 10%.[10]
References
editCitations
edit- ^ a b c d BirdLife International (2018). "Gavia arctica". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2018: e.T22697834A132606505. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22697834A132606505.en. Retrieved 13 November 2021.
- ^ Linnaeus, Carl (1758). Systema Naturae per regna tria naturae, secundum classes, ordines, genera, species, cum characteribus, differentiis, synonymis, locis (in Latin). Vol. 1 (10th ed.). Holmiae (Stockholm): Laurentii Salvii. p. 135.
- ^ Linnaeus, Carl (1761). Fauna svecica, sistens animalia sveciae regni mammalia, aves amphibia, pisces, insecta, vermes (in Latin) (2nd ed.). Stockholmiae: Sumtu & Literis Direct. Laurentii Salvii. p. 52.
- ^ Mayr, Ernst; Cottrell, G. William, eds. (1979). Check-List of Birds of the World. Vol. 1 (2nd ed.). Cambridge, Massachusetts: Museum of Comparative Zoology. p. 138.
- ^ Allen, J. A. (1897). "The proper generic name of the loons". General Notes. The Auk. 14 (3): 312. doi:10.2307/4068646. JSTOR 4068646.
- ^ Committee of the American Ornithologists' Union (1899). "Ninth supplement to the American Ornithologists' Union Check-List of North American Birds". The Auk. 16: 97–133 [98].
- ^ Johnsgard, Paul A. (1987). Diving Birds of North America. University of Nevada–Lincoln. ISBN 978-0-8032-2566-4.
- ^ Jobling, James A (2010). The Helm Dictionary of Scientific Bird Names. London: Christopher Helm. p. 53. ISBN 978-1-4081-2501-4.
- ^ Jobling, James A. del Hoyo, Josep; Elliott, Andrew; Sargatal, Jordi; Christie, David A.; de Juana, Eduardo (eds.). "Key to Scientific Names in Ornithology". Handbook of the Birds of the World Alive. Barcelona: Lynx Edicions. Retrieved 2 August 2017.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q Carboneras, C.; Garcia, E. F. J. (2017). del Hoyo, Josep; Elliott, Andrew; Sargatal, Jordi; Christie, David A.; de Juana, Eduardo (eds.). "Arctic Loon (Gavia arctica)". Handbook of the Birds of the World Alive. Barcelona: Lynx Edicions. doi:10.2173/bow.arcloo.01. Retrieved 28 May 2017.
- ^ Gill, Frank; Donsker, David; Rasmussen, Pamela, eds. (December 2023). "Kagu, Sunbittern, tropicbirds, loons, penguins". IOC World Bird List Version 14.1. International Ornithologists' Union. Retrieved 25 June 2024.
- ^ Dwight, Jonathan (1918). "A new species of loon (Gavia viridigularis) from northeastern Siberia". The Auk. 35 (2): 196–199. doi:10.2307/4072850. ISSN 0004-8038. JSTOR 4072850.
- ^ a b Bent, A. C. (1919). "Geographical variation in black-throated loons". The Auk. 36 (2): 238–242. doi:10.2307/4073044. ISSN 0004-8038. JSTOR 4073044.
- ^ a b Monroe, Jr., Burt L.; Banks, Richard C.; Fitzpatrick, John W.; Howell, Thomas R.; Johnson, Ned K.; Ouellet, Henri; Remsen, James V.; Storer, Robert W. (1985). "Thirty-fifth supplement to the American Ornithologists' Union check-list of North American birds". The Auk. 102 (3): 680–686. doi:10.1093/auk/102.3.680.
- ^ a b Sprengelmeyer, Quentin D. (2014). A phylogenetic reevaluation of the genus Gavia (Aves: Gaviiformes) using next-generation sequencing (Master of Science). Northern Michigan University.
- ^ Kadosaki, Masaaki (1975). "A preliminary study on the structure of lung-air sac system of loons". Japanese Journal of Ornithology. 23 (95–96): 1–6. doi:10.3838/jjo1915.23.1.
- ^ a b Ted Floyd (27 May 2008). Smithsonian Field Guide to the Birds of North America. HarperCollins. p. 74. ISBN 978-0-06-112040-4.
- ^ a b c d Hauber, Mark E. (1 August 2014). The Book of Eggs: A Life-Size Guide to the Eggs of Six Hundred of the World's Bird Species. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. p. 53. ISBN 978-0-226-05781-1.
- ^ a b c Hake, Mikael; Dahlgren, Tomas; Åhlund, Matti; Lindberg, Peter; Eriksson, Mats O. G. "The impact of water level fluctuation on the breeding success of the black-throated diver Gavia arctica in south-west Sweden". Ornis Fennica. 82 (1): 1–12. ISSN 0030-5685.
- ^ a b c d Mudge, G. P.; Talbot, T. R. (1992). "The breeding biology and causes of nest failure of Scottish black-throated divers Gavia arctica". Ibis. 135 (2): 113–120. doi:10.1111/j.1474-919X.1993.tb02822.x. ISSN 0019-1019.
- ^ Pielou, E. C. (31 July 2012). A Naturalist's Guide to the Arctic. University of Chicago Press. p. 203. ISBN 978-0-226-14867-0.
- ^ Peterson, Roger Tory; Mountfort, Guy; Hollom, P. A. D. (15 December 2001). A Field Guide to the Birds of Britain and Europe. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. p. 12. ISBN 978-0-618-16675-6.
- ^ a b c d Petersen, Margaret R. (1979). "Nesting ecology of arctic loons". The Wilson Bulletin. 91 (4): 608–617.
- ^ a b c d Bergman, Robert D.; Derksen, Dirk V. (1977). "Observations on arctic and red-throated loons at Storkersen Point, Alaska". Arctic. 30 (1): 41–51. doi:10.14430/arctic2682.
- ^ a b c d e Sjolander, Sverre (1978). "Reproductive behaviour of the black-throated diver Gavia arctica". Ornis Scandinavica. 9 (1): 51–65. doi:10.2307/3676139. ISSN 0030-5693. JSTOR 3676139.
- ^ Hancock, Mark (2000). "Artificial floating islands for nesting Black-throated Divers Gavia arctica in Scotland: construction, use and effect on breeding success". Bird Study. 47 (2): 165–175. Bibcode:2000BirdS..47..165H. doi:10.1080/00063650009461172.
- ^ Eriksson, Mats O. G. (1986). "Reproduction of black-throated diver Gavia arctica in relation to fish density in oligotrophic lakes in southwestern Sweden". Ornis Scandinavica. 17 (3): 245–248. doi:10.2307/3676833. ISSN 0030-5693. JSTOR 3676833.
- ^ Amundsen, Per-Arne; Lafferty, Kevin D.; Knudsen, Rune; Primicerio, Raul; Klemetsen, Anders; Kuris, Armand M. (2009). "Food web topology and parasites in the pelagic zone of a subarctic lake". Journal of Animal Ecology. 78 (3): 563–572. Bibcode:2009JAnEc..78..563A. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2656.2008.01518.x. ISSN 0021-8790. PMID 19175443.
- ^ Baltz, D. M.; Morejohn, G. Victor (1977). "Food habits and niche overlap of seabirds wintering on Monterey Bay, California". The Auk. 94 (3): 526–543.
- ^ De Graaf, Richard M.; Tilghman, Nancy G.; Anderson, Stanley H. (1985). "Foraging guilds of North American birds". Environmental Management. 9 (6): 493–536. Bibcode:1985EnMan...9..493D. doi:10.1007/BF01867324. ISSN 0364-152X. S2CID 85418857.
- ^ a b Bundy, Graham (2009). "Breeding and feeding observations on the black-throated diver". Bird Study. 26 (1): 33–36. doi:10.1080/00063657909476614. ISSN 0006-3657.
- ^ Russell, Robert W. (2002). Rodewald, P. G. (ed.). "Arctic Loon (Gavia arctica)". The Birds of North America. doi:10.2173/bow.arcloo.01. Retrieved 11 July 2017.
- ^ a b Jackson, Digger B. (2002). "Between-lake differences in the diet and provisioning behaviour of black-throated divers Gavia arctica breeding in Scotland". Ibis. 145 (1): 30–44. doi:10.1046/j.1474-919X.2003.00119.x. ISSN 0019-1019.
- ^ Fastzkie, Jean Sprinkle; Crites, John L. (1977). "A redescription of Eustrongylides tubifex (Nitzsch 1819) Jagerskiold 1909 (Nematoda: Dioctophymatidae) from mallards (Anas platyrhynchos)". The Journal of Parasitology. 63 (4): 707–12. doi:10.2307/3279578. ISSN 0022-3395. JSTOR 3279578. PMID 886407.
- ^ "Migratory Bird Treaty Act Protected Species (10.13 List)". US Fish & Wildlife Service. Retrieved 13 July 2017.
- ^ "Species". aewa.org. Agreement on the Conservation of African-Eurasian Migratory Waterbirds.
Bibliography
edit- Harrison, Peter (1988). Seabirds: An Identification Guide (2nd ed.). London: Christopher Helm. pp. 34, plate 6, 209. ISBN 978-0-7470-1410-2. OCLC 813599822.
- Field Guide to the Birds of North America. Washington, DC: National Geographic Society. 2002. ISBN 978-0-7922-6877-2.
External links
edit- Flicker Field Guide Birds of the World Photographs
- Black-throated Diver Gavia arctica at BTO BirdFacts
- Profile Arctic Loon at avibirds.com
- Arctic Loon – A Field Guide to Birds of Armenia
- BirdLife species factsheet for Gavia arctica
- "Gavia arctica". Avibase.
- Explore Species: Arctic Loon at eBird (Cornell Lab of Ornithology)
- Arctic Loon photo gallery at VIREO (Drexel University)
- Audio recordings of Black-throated loon on Xeno-canto.
