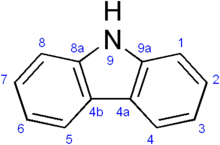
Carbazole is an aromatic heterocyclic organic compound. It has a tricyclic structure, consisting of two six-membered benzene rings fused on either side of a five-membered nitrogen-containing ring. The compound's structure is based on the indole structure, but in which a second benzene ring is fused onto the five-membered ring at the 2–3 position of indole (equivalent to the 9a–4a double bond in carbazole, respectively).
| |

| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
9H-Carbazole[1] | |
| Other names
9-azafluorene
dibenzopyrrole diphenylenimine diphenyleneimide USAF EK-600 | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 3956 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.542 |
| EC Number |
|
| 102490 | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H9N | |
| Molar mass | 167.211 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.301 g cm−3 |
| Melting point | 246.3 °C (475.3 °F; 519.5 K)[2] |
| Boiling point | 354.69 °C (670.44 °F; 627.84 K)[2] |
| −117.4 × 10−6 cm3 mol−1 | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 
| |
| Warning | |
| H341, H351, H400, H411, H413 | |
| P201, P202, P273, P281, P308+P313, P391, P405, P501 | |
| Flash point | 220 °C (428 °F; 493 K)[2] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Carbazole is a constituent of tobacco smoke.[3]
History
editCarl Graebe and Carl Glaser first isolated the compound from coal tar in 1872.[4]
Production
editFew carbazole production methods are economically viable, due to limited demand. During coal tar distillation, carbazole concentrates in the anthracene distillate and must be removed before anthraquinone production; that waste product is the major industrial carbazole source.[4][5] Polar compounds (e.g., ketones) selectively precipitate it from the anthracene; a more modern technique is simply selective crystallization from molten coal tar at high temperature[4] or low pressure (70 mmHg).[6]
A classic laboratory organic synthesis for carbazole is the Borsche–Drechsel cyclization.[7][8]
In the first step, phenylhydrazine is condensed with cyclohexanone to the corresponding imine. The second step is a hydrochloric acid-catalyzed rearrangement reaction and ring-closing reaction to tetrahydrocarbazole. In one modification, both steps are rolled into one by carrying out the reaction in acetic acid.[9] In the third step, this compound is oxidized by red lead to carbazole itself.
Another classic is the Bucherer carbazole synthesis, which uses a naphthol and an aryl hydrazine.[10]
A third method for the synthesis of carbazole is the Graebe–Ullmann reaction.
In the first step, an N-phenyl-1,2-diaminobenzene (N-phenyl-o-phenylenediamine) is converted into a diazonium salt which instantaneously forms a 1,2,3-triazole. The triazole is unstable and at elevated temperatures, nitrogen is released and the carbazole is formed.[11][12]
Diphenylamine derivatives, being electron rich, naturally oxidize to carbazoles when heated in air.[13] A similar reaction is the Mallory reaction:
Substituted carbazoles are most easily synthesized with transition metal coupling reactions. For applications that transition-metal impurities in the final product might inhibit, an alternative is nucleophilic aromatic substitution on dibenzothiophene dioxide.[14]
Natural Occurrence
editCarbazoles occur naturally in carbazole alkaloids. Carbazole alkaloids with unsubstituted benzene rings occur rarely. Olivacin has been found in the bark of Aspidosperma olivaceum and ellipticin in Ochrosia elliptica.[15] Some carbazole alkaloids, especially glybomin B, have been isolated from Glycosmis pentaphylla.[16]
-
Glycozoline
-
Olivacine
-
Ellipticin
-
Glybomine B
Applications
editAs carbazoles have a relatively rich UV-visible light spectrum, they see application as pigments[4] and photocatalysts.[17] The parent carbazole is used in Hydron Blue production[4] and aminoethylcarbazole is used in pigment violet 23 production.[18]
Carbazoles stabilize triplet emitters in certain light-emitting diodes;[4] in general, they are electron photodonors (hole acceptors).[19]
Carbazole electrochemically oxidizes to a conductive polymer, which has not achieved substantial industrial use.[20] Polyvinylcarbazole is useful in the electrical and electronic industries, and certain carbazole novolaks are extremely heat resistant.[4]
In organic chemistry, carbazole proper is also an ingredient for several bioactive molecules. The insecticide Nirosan,[4] the cocaine overdose antidote Rimcazole, and the veterinary NSAID Carprofen are all made from carbazole. The topoisomerase II inhibitor ellipticine fuses carbazole to a pyridine ring.
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (2014). Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013. The Royal Society of Chemistry. p. 212. doi:10.1039/9781849733069. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ a b c Lide, David R. (2007). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 88th Edition. CRC Press. pp. 3–86. ISBN 978-0-8493-0488-0.
- ^ Talhout, Reinskje; Schulz, Thomas; Florek, Ewa; Van Benthem, Jan; Wester, Piet; Opperhuizen, Antoon (2011). "Hazardous Compounds in Tobacco Smoke". Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 8 (12): 613–628. doi:10.3390/ijerph8020613. PMC 3084482. PMID 21556207.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Collin, Gerd; Höke, Hartmut; Talbiersky, Jörg. "Carbazole". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a05_059.pub2. ISBN 978-3527306732.
{{cite encyclopedia}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Cofrancesco, A. J., "Anthraquinone", Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology, New York: John Wiley, p. 5, doi:10.1002/0471238961.0114200803150618.a01, ISBN 9780471238966
- ^ Betts, W. D., "Tar and Pitch", Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology, New York: John Wiley, p. 5, doi:10.1002/0471238961.20011802052020.a01, ISBN 9780471238966
- ^ W. Borsche (1908). "Ueber Tetra- und Hexahydrocarbazolverbindungen und eine neue Carbazolsynthese. (Mitbearbeitet von. A. Witte und W. Bothe.)". Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem. (in German). 359 (1–2): 49–80. doi:10.1002/jlac.19083590103.
- ^ E. Drechsel (1888). "Ueber Elektrolyse des Phenols mit Wechselströmen". J. Prakt. Chem. (in German). 38 (1): 65–74. doi:10.1002/prac.18880380105.
- ^ Rogers, Crosby U.; Corson, B. B. (1950). "1,2,3,4-Tetrahydrocarbazole (Carbazole, 1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-)". Organic Syntheses. 30: 90. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.030.0090; Collected Volumes, vol. 4, p. 884.
- ^ Wang, Zerong (2010). "Bucherer Carbazole Synthesis". Comprehensive Organic Name Reactions and Reagents. pp. 549–552. doi:10.1002/9780470638859.conrr120. ISBN 9780470638859.
- ^ Carl Graebe; Fritz Ullmann (1896). "Ueber eine neue Carbazolsynthese". Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem. (in German). 291 (1): 16–17. doi:10.1002/jlac.18962910104.
- ^ O. Bremer (1934). "Über die Bedeutung der Graebe-Ullmannschen Carbazolsynthese und deren Übertragung auf N-substituierte Pyridino-triazole". Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem. (in German). 514 (1): 279–291. doi:10.1002/jlac.19345140116.
- ^ Vogt, Peter F.; Gerulis, John J. "Amines, Aromatic". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Vol. 2. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. p. 703. doi:10.1002/14356007.a02_037. ISBN 978-3527306732.
- ^ Bhanuchandra, M.; Yorimitsu Hideki. "Dibenzothiophene 5,5-dioxide". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rn02046.
- ^ Eberhard Breitmaier (1997), Alkaloide, Wiesbaden: Springer Fachmedien, p. 49, ISBN 978-3-519-03542-8
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Awas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Rizzo, Carmelo J. (2005). "N-Methylcarbazole". N -Methylcarbazole. Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rn00578. ISBN 0-471-93623-5.
- ^ U.S. patent 4,345,074
- ^ Ying Wang, "Photoconductive polymers", Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology, New York: John Wiley, p. 15, doi:10.1002/0471238961.1608152023011407.a01, ISBN 9780471238966
- ^ Naarmann, Herbert. "Polymers, Electrically conducting". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Vol. 29. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. p. 309. doi:10.1002/14356007.a21_429. ISBN 978-3527306732.