This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. (April 2020) |
In population genetics, the Hardy–Weinberg principle, also known as the Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium, model, theorem, or law, states that allele and genotype frequencies in a population will remain constant from generation to generation in the absence of other evolutionary influences. These influences include genetic drift, mate choice, assortative mating, natural selection, sexual selection, mutation, gene flow, meiotic drive, genetic hitchhiking, population bottleneck, founder effect, inbreeding and outbreeding depression.
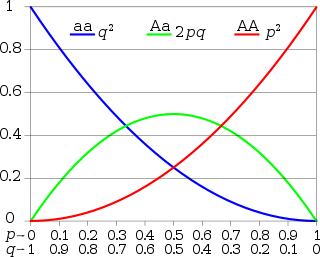
In the simplest case of a single locus with two alleles denoted A and a with frequencies f(A) = p and f(a) = q, respectively, the expected genotype frequencies under random mating are f(AA) = p2 for the AA homozygotes, f(aa) = q2 for the aa homozygotes, and f(Aa) = 2pq for the heterozygotes. In the absence of selection, mutation, genetic drift, or other forces, allele frequencies p and q are constant between generations, so equilibrium is reached.
The principle is named after G. H. Hardy and Wilhelm Weinberg, who first demonstrated it mathematically. Hardy's paper was focused on debunking the view that a dominant allele would automatically tend to increase in frequency (a view possibly based on a misinterpreted question at a lecture[1]). Today, tests for Hardy–Weinberg genotype frequencies are used primarily to test for population stratification and other forms of non-random mating.
Derivation
editConsider a population of monoecious diploids, where each organism produces male and female gametes at equal frequency, and has two alleles at each gene locus. We assume that the population is so large that it can be treated as infinite. Organisms reproduce by random union of gametes (the "gene pool" population model). A locus in this population has two alleles, A and a, that occur with initial frequencies f0(A) = p and f0(a) = q, respectively.[note 1] The allele frequencies at each generation are obtained by pooling together the alleles from each genotype of the same generation according to the expected contribution from the homozygote and heterozygote genotypes, which are 1 and 1/2, respectively:
| (1) |
| (2) |
The different ways to form genotypes for the next generation can be shown in a Punnett square, where the proportion of each genotype is equal to the product of the row and column allele frequencies from the current generation.
| Females | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| A (p) | a (q) | ||
| Males | A (p) | AA (p2) | Aa (pq) |
| a (q) | Aa (qp) | aa (q2) | |
The sum of the entries is p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1, as the genotype frequencies must sum to one.
Note again that as p + q = 1, the binomial expansion of (p + q)2 = p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1 gives the same relationships.
Summing the elements of the Punnett square or the binomial expansion, we obtain the expected genotype proportions among the offspring after a single generation:
| (3) |
| (4) |
| (5) |
These frequencies define the Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium. It should be mentioned that the genotype frequencies after the first generation need not equal the genotype frequencies from the initial generation, e.g. f1(AA) ≠ f0(AA). However, the genotype frequencies for all future times will equal the Hardy–Weinberg frequencies, e.g. ft(AA) = f1(AA) for t > 1. This follows since the genotype frequencies of the next generation depend only on the allele frequencies of the current generation which, as calculated by equations (1) and (2), are preserved from the initial generation:
For the more general case of dioecious diploids [organisms are either male or female] that reproduce by random mating of individuals, it is necessary to calculate the genotype frequencies from the nine possible matings between each parental genotype (AA, Aa, and aa) in either sex, weighted by the expected genotype contributions of each such mating.[2] Equivalently, one considers the six unique diploid-diploid combinations:
and constructs a Punnett square for each, so as to calculate its contribution to the next generation's genotypes. These contributions are weighted according to the probability of each diploid-diploid combination, which follows a multinomial distribution with k = 3. For example, the probability of the mating combination (AA,aa) is 2 ft(AA)ft(aa) and it can only result in the Aa genotype: [0,1,0]. Overall, the resulting genotype frequencies are calculated as:
As before, one can show that the allele frequencies at time t + 1 equal those at time t, and so, are constant in time. Similarly, the genotype frequencies depend only on the allele frequencies, and so, after time t = 1 are also constant in time.
If in either monoecious or dioecious organisms, either the allele or genotype proportions are initially unequal in either sex, it can be shown that constant proportions are obtained after one generation of random mating. If dioecious organisms are heterogametic and the gene locus is located on the X chromosome, it can be shown that if the allele frequencies are initially unequal in the two sexes [e.g., XX females and XY males, as in humans], f′(a) in the heterogametic sex 'chases' f(a) in the homogametic sex of the previous generation, until an equilibrium is reached at the weighted average of the two initial frequencies.
Deviations from Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium
editThe seven assumptions underlying Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium are as follows:[3]
- organisms are diploid
- only sexual reproduction occurs
- generations are nonoverlapping
- mating is random
- population size is infinitely large
- allele frequencies are equal in the sexes
- there is no migration, gene flow, admixture, mutation or selection
Violations of the Hardy–Weinberg assumptions can cause deviations from expectation. How this affects the population depends on the assumptions that are violated.
- Random mating. The HWP states the population will have the given genotypic frequencies (called Hardy–Weinberg proportions) after a single generation of random mating within the population. When the random mating assumption is violated, the population will not have Hardy–Weinberg proportions. A common cause of non-random mating is inbreeding, which causes an increase in homozygosity for all genes.
If a population violates one of the following four assumptions, the population may continue to have Hardy–Weinberg proportions each generation, but the allele frequencies will change over time.
- Selection, in general, causes allele frequencies to change, often quite rapidly. While directional selection eventually leads to the loss of all alleles except the favored one (unless one allele is dominant, in which case recessive alleles can survive at low frequencies), some forms of selection, such as balancing selection, lead to equilibrium without loss of alleles.
- Mutation will have a very subtle effect on allele frequencies through the introduction of new allele into a population. Mutation rates are of the order 10−4 to 10−8, and the change in allele frequency will be, at most, the same order. Recurrent mutation will maintain alleles in the population, even if there is strong selection against them.
- Migration genetically links two or more populations together. In general, allele frequencies will become more homogeneous among the populations. Some models for migration inherently include nonrandom mating (Wahlund effect, for example). For those models, the Hardy–Weinberg proportions will normally not be valid.
- Small population size can cause a random change in allele frequencies. This is due to a sampling effect, and is called genetic drift. Sampling effects are most important when the allele is present in a small number of copies.
In real world genotype data, deviations from Hardy–Weinberg Equilibrium may be a sign of genotyping error.[4][5][6]
Sex linkage
editWhere the A gene is sex linked, the heterogametic sex (e.g., mammalian males; avian females) have only one copy of the gene (and are termed hemizygous), while the homogametic sex (e.g., human females) have two copies. The genotype frequencies at equilibrium are p and q for the heterogametic sex but p2, 2pq and q2 for the homogametic sex.
For example, in humans red–green colorblindness is an X-linked recessive trait. In western European males, the trait affects about 1 in 12, (q = 0.083) whereas it affects about 1 in 200 females (0.005, compared to q2 = 0.007), very close to Hardy–Weinberg proportions.
If a population is brought together with males and females with a different allele frequency in each subpopulation (males or females), the allele frequency of the male population in the next generation will follow that of the female population because each son receives its X chromosome from its mother. The population converges on equilibrium very quickly.
Generalizations
editThe simple derivation above can be generalized for more than two alleles and polyploidy.
Generalization for more than two alleles
editConsider an extra allele frequency, r. The two-allele case is the binomial expansion of (p + q)2, and thus the three-allele case is the trinomial expansion of (p + q + r)2.
More generally, consider the alleles A1, ..., An given by the allele frequencies p1 to pn;
giving for all homozygotes:
and for all heterozygotes:
Generalization for polyploidy
editThe Hardy–Weinberg principle may also be generalized to polyploid systems, that is, for organisms that have more than two copies of each chromosome. Consider again only two alleles. The diploid case is the binomial expansion of:
and therefore the polyploid case is the binomial expansion of:
where c is the ploidy, for example with tetraploid (c = 4):
| Genotype | Frequency |
|---|---|
| AAAA | |
| AAAa | |
| AAaa | |
| Aaaa | |
| aaaa |
Whether the organism is a 'true' tetraploid or an amphidiploid will determine how long it will take for the population to reach Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium.
Complete generalization
editFor distinct alleles in -ploids, the genotype frequencies in the Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium are given by individual terms in the multinomial expansion of :
Significance tests for deviation
editTesting deviation from the HWP is generally performed using Pearson's chi-squared test, using the observed genotype frequencies obtained from the data and the expected genotype frequencies obtained using the HWP. For systems where there are large numbers of alleles, this may result in data with many empty possible genotypes and low genotype counts, because there are often not enough individuals present in the sample to adequately represent all genotype classes. If this is the case, then the asymptotic assumption of the chi-squared distribution, will no longer hold, and it may be necessary to use a form of Fisher's exact test, which requires a computer to solve. More recently a number of MCMC methods of testing for deviations from HWP have been proposed (Guo & Thompson, 1992; Wigginton et al. 2005)
Example chi-squared test for deviation
editThis data is from E. B. Ford (1971) on the scarlet tiger moth, for which the phenotypes of a sample of the population were recorded. Genotype–phenotype distinction is assumed to be negligibly small. The null hypothesis is that the population is in Hardy–Weinberg proportions, and the alternative hypothesis is that the population is not in Hardy–Weinberg proportions.
| Phenotype | White-spotted (AA) | Intermediate (Aa) | Little spotting (aa) | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | 1469 | 138 | 5 | 1612 |
From this, allele frequencies can be calculated:
and
So the Hardy–Weinberg expectation is:
Pearson's chi-squared test states:
There is 1 degree of freedom (degrees of freedom for test for Hardy–Weinberg proportions are # genotypes − # alleles). The 5% significance level for 1 degree of freedom is 3.84, and since the χ2 value is less than this, the null hypothesis that the population is in Hardy–Weinberg frequencies is not rejected.
Fisher's exact test (probability test)
editFisher's exact test can be applied to testing for Hardy–Weinberg proportions. Since the test is conditional on the allele frequencies, p and q, the problem can be viewed as testing for the proper number of heterozygotes. In this way, the hypothesis of Hardy–Weinberg proportions is rejected if the number of heterozygotes is too large or too small. The conditional probabilities for the heterozygote, given the allele frequencies are given in Emigh (1980) as
where n11, n12, n22 are the observed numbers of the three genotypes, AA, Aa, and aa, respectively, and n1 is the number of A alleles, where .
An example Using one of the examples from Emigh (1980),[7] we can consider the case where n = 100, and p = 0.34. The possible observed heterozygotes and their exact significance level is given in Table 4.
| Number of heterozygotes | Significance level |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0.000 |
| 2 | 0.000 |
| 4 | 0.000 |
| 6 | 0.000 |
| 8 | 0.000 |
| 10 | 0.000 |
| 12 | 0.000 |
| 14 | 0.000 |
| 16 | 0.000 |
| 18 | 0.001 |
| 20 | 0.007 |
| 22 | 0.034 |
| 34 | 0.067 |
| 24 | 0.151 |
| 32 | 0.291 |
| 26 | 0.474 |
| 30 | 0.730 |
| 28 | 1.000 |
Using this table, one must look up the significance level of the test based on the observed number of heterozygotes. For example, if one observed 20 heterozygotes, the significance level for the test is 0.007. As is typical for Fisher's exact test for small samples, the gradation of significance levels is quite coarse.
However, a table like this has to be created for every experiment, since the tables are dependent on both n and p.
Equivalence tests
editThe equivalence tests are developed in order to establish sufficiently good agreement of the observed genotype frequencies and Hardy Weinberg equilibrium. Let denote the family of the genotype distributions under the assumption of Hardy Weinberg equilibrium. The distance between a genotype distribution and Hardy Weinberg equilibrium is defined by , where is some distance. The equivalence test problem is given by and , where is a tolerance parameter. If the hypothesis can be rejected then the population is close to Hardy Weinberg equilibrium with a high probability. The equivalence tests for the biallelic case are developed among others in Wellek (2004).[8] The equivalence tests for the case of multiple alleles are proposed in Ostrovski (2020).[9]
Inbreeding coefficient
editThe inbreeding coefficient, (see also F-statistics), is one minus the observed frequency of heterozygotes over that expected from Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium.
where the expected value from Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium is given by
For example, for Ford's data above:
For two alleles, the chi-squared goodness of fit test for Hardy–Weinberg proportions is equivalent to the test for inbreeding, .
The inbreeding coefficient is unstable as the expected value approaches zero, and thus not useful for rare and very common alleles. For: ; is undefined.
History
editMendelian genetics were rediscovered in 1900. However, it remained somewhat controversial for several years as it was not then known how it could cause continuous characteristics. Udny Yule (1902) argued against Mendelism because he thought that dominant alleles would increase in the population.[10] The American William E. Castle (1903) showed that without selection, the genotype frequencies would remain stable.[11] Karl Pearson (1903) found one equilibrium position with values of p = q = 0.5.[12] Reginald Punnett, unable to counter Yule's point, introduced the problem to G. H. Hardy, a British mathematician, with whom he played cricket. Hardy was a pure mathematician and held applied mathematics in some contempt; his view of biologists' use of mathematics comes across in his 1908 paper where he describes this as "very simple":[13]
- To the Editor of Science: I am reluctant to intrude in a discussion concerning matters of which I have no expert knowledge, and I should have expected the very simple point which I wish to make to have been familiar to biologists. However, some remarks of Mr. Udny Yule, to which Mr. R. C. Punnett has called my attention, suggest that it may still be worth making...
- Suppose that Aa is a pair of Mendelian characters, A being dominant, and that in any given generation the number of pure dominants (AA), heterozygotes (Aa), and pure recessives (aa) are as p:2q:r. Finally, suppose that the numbers are fairly large, so that mating may be regarded as random, that the sexes are evenly distributed among the three varieties, and that all are equally fertile. A little mathematics of the multiplication-table type is enough to show that in the next generation the numbers will be as (p + q)2:2(p + q)(q + r):(q + r)2, or as p1:2q1:r1, say.
- The interesting question is: in what circumstances will this distribution be the same as that in the generation before? It is easy to see that the condition for this is q2 = pr. And since q12 = p1r1, whatever the values of p, q, and r may be, the distribution will in any case continue unchanged after the second generation
The principle was thus known as Hardy's law in the English-speaking world until 1943, when Curt Stern pointed out that it had first been formulated independently in 1908 by the German physician Wilhelm Weinberg.[14][15] William Castle in 1903 also derived the ratios for the special case of equal allele frequencies, and it is sometimes (but rarely) called the Hardy–Weinberg–Castle Law.
Derivation of Hardy's equations
editHardy's statement begins with a recurrence relation for the frequencies p, 2q, and r. These recurrence relations follow from fundamental concepts in probability, specifically independence, and conditional probability. For example, consider the probability of an offspring from the generation being homozygous dominant. Alleles are inherited independently from each parent. A dominant allele can be inherited from a homozygous dominant parent with probability 1, or from a heterozygous parent with probability 0.5. To represent this reasoning in an equation, let represent inheritance of a dominant allele from a parent. Furthermore, let and represent potential parental genotypes in the preceding generation.
The same reasoning, applied to the other genotypes yields the two remaining recurrence relations. Equilibrium occurs when each proportion is constant between subsequent generations. More formally, a population is at equilibrium at generation when
- , , and
By solving these equations necessary and sufficient conditions for equilibrium to occur can be determined. Again, consider the frequency of homozygous dominant animals. Equilibrium implies
First consider the case, where , and note that it implies that and . Now consider the remaining case, where :
where the final equality holds because the allele proportions must sum to one. In both cases, . It can be shown that the other two equilibrium conditions imply the same equation. Together, the solutions of the three equilibrium equations imply sufficiency of Hardy's condition for equilibrium. Since the condition always holds for the second generation, all succeeding generations have the same proportions.
Numerical example
editEstimation of genotype distribution
editAn example computation of the genotype distribution given by Hardy's original equations is instructive. The phenotype distribution from Table 3 above will be used to compute Hardy's initial genotype distribution. Note that the p and q values used by Hardy are not the same as those used above.
As checks on the distribution, compute
and
For the next generation, Hardy's equations give
Again as checks on the distribution, compute
and
which are the expected values. The reader may demonstrate that subsequent use of the second-generation values for a third generation will yield identical results.
Estimation of carrier frequency
editThe Hardy–Weinberg principle can also be used to estimate the frequency of carriers of an autosomal recessive condition in a population based on the frequency of suffers.
Let us assume an estimated babies are born with cystic fibrosis, this is about the frequency of homozygous individuals observed in Northern European populations. We can use the Hardy–Weinberg equations to estimate the carrier frequency, the frequency of heterozygous individuals, .
As is small we can take p, , to be 1.
We therefore estimate the carrier rate to be , which is about the frequency observed in Northern European populations.
This can be simplified to the carrier frequency being about twice the square root of the birth frequency.
Graphical representation
editIt is possible to represent the distribution of genotype frequencies for a bi-allelic locus within a population graphically using a de Finetti diagram. This uses a triangular plot (also known as trilinear, triaxial or ternary plot) to represent the distribution of the three genotype frequencies in relation to each other. It differs from many other such plots in that the direction of one of the axes has been reversed.[16] The curved line in the diagram is the Hardy–Weinberg parabola and represents the state where alleles are in Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium. It is possible to represent the effects of natural selection and its effect on allele frequency on such graphs.[17] The de Finetti diagram was developed and used extensively by A. W. F. Edwards in his book Foundations of Mathematical Genetics.[18]
See also
edit- F-statistics
- Fixation index
- QST_(genetics)
- Wahlund effect
- Regression toward the mean
- Multinomial distribution (Hardy–Weinberg is a trinomial distribution with probabilities )
- Additive disequilibrium and z statistic
- Population genetics
- Genetic diversity
- Founder effect
- Population bottleneck
- Genetic drift
- Inbreeding depression
- Coefficient of inbreeding
- Coefficient of relationship
- Natural selection
- Fitness
- Genetic load
Notes
edit- ^ The term frequency usually refers to a number or count, but in this context, it is synonymous with probability.
References
editCitations
edit- ^ Edwards, A. W. F. (2008). "G. H. Hardy (1908) and Hardy–Weinberg Equilibrium". Genetics. 179 (3): 1143–1150. doi:10.1534/genetics.104.92940. ISSN 0016-6731. PMC 2475721. PMID 18645201.
- ^ Carr, Dr. Steven M. "Hardy–Weinberg in dioecious organisms". www.mun.ca.
- ^ Hartl DL, Clarke AG (2007) Principles of population genetics. Sunderland, MA: Sinauer
- ^ Hosking, Louise; Lumsden, Sheena; Lewis, Karen; Yeo, Astrid; McCarthy, Linda; Bansal, Aruna; Riley, John; Purvis, Ian; Xu, Chun-Fang (May 2004). "Detection of genotyping errors by Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium testing". European Journal of Human Genetics. 12 (5): 395–399. doi:10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201164. ISSN 1018-4813. PMID 14872201.
- ^ Pompanon, François; Bonin, Aurélie; Bellemain, Eva; Taberlet, Pierre (November 2005). "Genotyping errors: causes, consequences and solutions". Nature Reviews Genetics. 6 (11): 847–859. doi:10.1038/nrg1707. ISSN 1471-0064. PMID 16304600. S2CID 14031116.
- ^ Cox, David G.; Kraft, Peter (2006). "Quantification of the Power of Hardy–Weinberg Equilibrium Testing to Detect Genotyping Error". Human Heredity. 61 (1): 10–14. doi:10.1159/000091787. ISSN 0001-5652. PMID 16514241. S2CID 37599930.
- ^ a b Emigh, Ted H. (1980). "A Comparison of Tests for Hardy–Weinberg Equilibrium". Biometrics. 36 (4): 627–642. doi:10.2307/2556115. JSTOR 2556115. PMID 25856832.
- ^ Wellek, Stefan (September 2004). "Tests for establishing compatibility of an observed genotype distribution with Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium in the case of a biallelic locus". Biometrics. 60 (3): 694–703. doi:10.1111/j.0006-341X.2004.00219.x. PMID 15339292. S2CID 12028776.Official web link (subscription required)
- ^ Ostrovski, Vladimir (February 2020). "New equivalence tests for Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium and multiple alleles". Stats. 3: 34–39. doi:10.3390/stats3010004.Official web link
- ^ Yule, 1902
- ^ Castle, 1903
- ^ Pearson, 1903
- ^ Hardy, 1908
- ^ Crow, James F. (1999). "Hardy, Weinberg and language impediments". Genetics. 152 (3): 821–825. doi:10.1093/genetics/152.3.821. PMC 1460671. PMID 10388804.
- ^ Stern, Curt (1962). "Wilhelm Weinberg". Genetics. 47: 1–5.
- ^ Cannings, C.; Edwards, A.W.F. (1968). "Natural selection and the de Finetti diagram". Annals of Human Genetics. 31 (4): 421–428. doi:10.1111/j.1469-1809.1968.tb00575.x. PMID 5673165. S2CID 8863631.
- ^ See e.g. Ineichen & Batschelet 1975
- ^ Edwards, 1977
Sources
edit- Castle, W. E. (1903). "The laws of Galton and Mendel and some laws governing race improvement by selection". Proceedings of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences. 35: 233–242.
- Crow, Jf (July 1999). "Hardy, Weinberg and language impediments". Genetics. 152 (3): 821–5. doi:10.1093/genetics/152.3.821. ISSN 0016-6731. PMC 1460671. PMID 10388804.
- Edwards, A.W.F. 1977. Foundations of Mathematical Genetics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2nd ed., 2000). ISBN 0-521-77544-2
- Emigh, T.H. (1980). "A comparison of tests for Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium". Biometrics. 36 (4): 627–642. doi:10.2307/2556115. JSTOR 2556115. PMID 25856832.
- Ford, E.B. (1971). Ecological Genetics, London.
- Guo, Sw; Thompson, Elizabeth A. (June 1992). "Performing the exact test of Hardy–Weinberg proportion for multiple alleles". Biometrics. 48 (2): 361–72. doi:10.2307/2532296. ISSN 0006-341X. JSTOR 2532296. PMID 1637966.
- Hardy, G. H. (July 1908). "Mendelian Proportions in a Mixed Population" (PDF). Science. 28 (706): 49–50. Bibcode:1908Sci....28...49H. doi:10.1126/science.28.706.49. ISSN 0036-8075. PMC 2582692. PMID 17779291.
- Ineichen, Robert; Batschelet, Eduard (1975). "Genetic selection and de Finetti diagrams". Journal of Mathematical Biology. 2: 33–39. doi:10.1007/BF00276014. S2CID 123415153.
- Masel, Joanna (2012). "Rethinking Hardy–Weinberg and genetic drift in undergraduate biology". BioEssays. 34 (8): 701–10. doi:10.1002/bies.201100178. PMID 22576789. S2CID 28513167.
- Pearson, K. (1903). "Mathematical contributions to the theory of evolution. XI. On the influence of natural selection on the variability and correlation of organs". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A. 200 (321–330): 1–66. Bibcode:1903RSPTA.200....1P. doi:10.1098/rsta.1903.0001.
- Stern, C. (1943). "The Hardy–Weinberg law". Science. 97 (2510): 137–138. Bibcode:1943Sci....97..137S. doi:10.1126/science.97.2510.137. JSTOR 1670409. PMID 17788516.
- Weinberg, W. (1908). "Über den Nachweis der Vererbung beim Menschen". Jahreshefte des Vereins für vaterländische Naturkunde in Württemberg. 64: 368–382.
- Wigginton, Je; Cutler, Dj; Abecasis, Gr (May 2005). "A Note on Exact Tests of Hardy–Weinberg Equilibrium". American Journal of Human Genetics. 76 (5): 887–93. doi:10.1086/429864. ISSN 0002-9297. PMC 1199378. PMID 15789306.
- Yule, G. U. (1902). "Mendel's laws and their probable relation to intra-racial heredity". New Phytol. 1 (193–207): 222–238. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.1902.tb07336.x.
External links
edit- EvolutionSolution (at bottom of page)
- Hardy–Weinberg Equilibrium Calculator
- genetics Population Genetics Simulator[permanent dead link]
- HARDY C implementation of Guo & Thompson 1992
- Source code (C/C++/Fortran/R) for Wigginton et al. 2005
- Online de Finetti Diagram Generator and Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium tests
- Online Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium tests and drawing of de Finetti diagrams Archived 26 May 2015 at the Wayback Machine
- Hardy–Weinberg Equilibrium Calculator