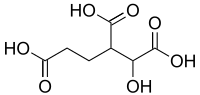
Homoisocitric acid is an isomer of homocitric acid in which the hydroxyl is on the 2 position.[1] It is an intermediate in the α-aminoadipate pathway of lysine biosynthesis where it is produced by homocitrate synthase and is a substrate for homoaconitase.
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1-Hydroxybutane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid | |
| Other names
3-Carboxy-2-hydroxyadipic acid
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H10O7 | |
| Molar mass | 206.150 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Homoisocitrate is an anion, salt, or ester of homoisocitric acid.
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ "Homoisocitric Acid". U.S. National Library of Medicine; National Center for Biotechnology Information.