The House of Welf (also Guelf or Guelph[1]) is a European dynasty that has included many German and British monarchs from the 11th to 20th century and Emperor Ivan VI of Russia in the 18th century. The originally Franconian family from the Meuse-Moselle area was closely related to the imperial family of the Carolingians.
| House of Welf (Guelf, Guelph) | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Parent house | House of Este (agnatic) Elder House of Welf (cognatic) |
| Country | Germany, Italy, United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland |
| Founded | 8th century |
| Founder | Welf I, Duke of Bavaria |
| Final ruler | Ernest Augustus, Duke of Brunswick |
| Titles |
|
| Estate(s) | Brunswick & Hanover |
| Deposition | 1918 (in Germany) |
| Cadet branches | House of Hanover |
Origins
editThe (Younger) House of Welf is the older branch of the House of Este, a dynasty whose earliest known members lived in Veneto and Lombardy in the late 9th/early 10th century, sometimes called Welf-Este. The first member was Welf I, Duke of Bavaria, also known as Welf IV. He inherited the property of the Elder House of Welf when his maternal uncle Welf III, Duke of Carinthia and Verona, the last male Welf of the Elder House, died in 1055.
Welf IV was the son of Welf III's sister Kunigunde of Altdorf and her husband Albert Azzo II, Margrave of Milan. In 1070, Welf IV became Duke of Bavaria.
Welf II, Duke of Bavaria married Countess Matilda of Tuscany, who died childless and left him her possessions, including Tuscany, Ferrara, Modena, Mantua, and Reggio, which played a role in the Investiture Controversy. Since the Welf dynasty sided with the Pope in this controversy, partisans of the Pope came to be known in Italy as Guelphs (Guelfi).
The first genealogy of the Welfs is the Genealogia Welforum, composed shortly before 1126. A much more detailed history of the dynasty, the Historia Welforum, was composed around 1170. It is the earliest history of a noble house in Germany.
-
Kunigunde of Altdorf, sister of Welf III, wife of Albert Azzo II of Este, Margrave of Milan, parents of Welf IV
-
Welf I, Duke of Bavaria (c. 1030/1040 – 1101)
-
Welf II, Duke of Bavaria (1073–1120)
Bavaria and Saxony
editHenry IX, Duke of Bavaria, from 1120 to 1126, was the first of the three dukes of the Welf dynasty called Henry. His wife Wulfhild was the heiress of the house of Billung, possessing the territory around Lüneburg in Lower Saxony. Their son, Henry the Proud, was the son-in-law and heir of Lothair II, Holy Roman Emperor and became also Duke of Saxony on Lothair's death.
Lothair left his territory around Brunswick, inherited from his mother of the Brunonids, to his daughter Gertrud. Her husband Henry the Proud became then the favoured candidate in the imperial election against Conrad III of the Hohenstaufen. Henry lost the election, as the other princes feared his power and temperament, and was dispossessed of his duchies by Conrad III.
Henry's brother Welf VI (1115–1191), Margrave of Tuscany, later left his Swabian territories around Ravensburg, the original possessions of the Elder House of Welf, to his nephew Emperor Frederick I, and thus to the House of Hohenstaufen.
-
Henry the Black, duke of Bavaria (1075–1126) and his wife Wulfhild of Billung
-
Henry the Proud (1102–1139), Duke of Bavaria and Saxony, and his wife Gertrud of Saxony, daughter of Lothair II, Holy Roman Emperor, Duke of Saxony
-
Welf VI (1115–1191), Margrave of Tuscany
-
Steingaden Abbey, Swabia, place of burial of its founder Welf VI (d. 1191)
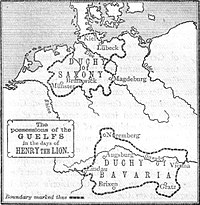
The next duke of the Welf dynasty Henry the Lion (1129/1131–1195) recovered his father's two duchies, Saxony in 1142, Bavaria in 1156 and thus ruled vast parts of Germany. In 1168 he married Matilda (1156–1189), the daughter of Henry II of England and Eleanor of Aquitaine, and sister of Richard I of England, gaining ever more influence. His first cousin, Frederick I, Holy Roman Emperor of the Hohenstaufen dynasty, tried to get along with him, but when Henry refused to assist him once more in an Italian war campaign, conflict became inevitable.
Dispossessed of his duchies after the Battle of Legnano in 1176 by Emperor Frederick I and the other princes of the German Empire eager to claim parts of his vast territories, he was exiled to the court of his father-in-law Henry II in Normandy in 1180. He returned to Germany three years later.
Henry made his peace with the Hohenstaufen Emperor in 1185 and returned to his much diminished lands around Brunswick without recovering his two duchies. Bavaria had been given to Otto I, Duke of Bavaria, and the Duchy of Saxony was divided between the Archbishop of Cologne, the House of Ascania and others. Diminished lands did not prevent him from imprisoning Richard I on his return from the Third Crusade, and demanding a huge ransom in 1193. Henry died at Brunswick in 1195.
-
Henry the Lion (1130–1195), Duke of Bavaria and Saxony
-
Matilda Plantagenet (1156–1189), wife of Henry the Lion, sister of Richard I of England
-
Henry's Dankwarderode Castle in Brunswick
-
Henry's Brunswick Lion
-
Otto IV, Holy Roman Emperor, son of Henry the Lion and Matilda of England
Brunswick and Hanover
editHenry the Lion's son, Otto of Brunswick, was elected King of the Romans and crowned Holy Roman Emperor Otto IV after years of further conflicts with the Hohenstaufen emperors. He incurred the wrath of Pope Innocent III and was excommunicated in 1215. Otto was forced to abdicate the imperial throne by the Hohenstaufen Frederick II.[2] He was the only Welf to become Holy Roman Emperor.
Henry the Lion's grandson Otto the Child became duke of a part of Saxony in 1235, the new Duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg, and died there in 1252. The duchy was divided several times during the High Middle Ages amongst various lines of the House of Welf. The subordinate states had the legal status of principalities within the duchy, which remained as an undivided imperial fief. Each state was generally named after the ruler's residence, e.g., the rulers of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel originally lived in Wolfenbüttel.
Whenever a branch of the family died out in the male line, the territory was given to another line, as the duchy remained enfeoffed to the family as a whole rather than its individual members. All members of the House of Welf, male or female, bore the title Duke/Duchess of Brunswick-Lüneburg in addition to the style of the subordinate principality.[3] By 1705, the subordinate principalities had taken their final form as the Electorate of Hanover and the Principality of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel, and these would become the Kingdom of Hanover and the Duchy of Brunswick after the Congress of Vienna in 1815.
Principality of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel
editIn 1269 the Principality of Brunswick was formed following the first division of the Duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg. In 1432, as a result of increasing tensions with the townsfolk of Brunswick, the Brunswick Line moved their residence to Wolfenbüttel Castle, thus the name Wolfenbüttel became the unofficial name of this principality. With Ivan VI of Russia the Brunswick line even had a short intermezzo on the Russian imperial throne in 1740. Not until 1754 was the residence moved back to Brunswick, into the new Brunswick Palace. In 1814 the principality became the Duchy of Brunswick, ruled by the senior branch of the House of Welf.
Principality of Calenberg – later Electorate of Brunswick-Lüneburg
editIn 1432 the estates gained by the Principality of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel between the Deister and Leine split away as the Principality of Calenberg. In 1495 it was expanded around Göttingen and in 1584 went back to the Wolfenbüttel Line. In 1634, as a result of inheritance distributions, it went to the House of Luneburg residing at Celle Castle. In 1635 it was given to George, younger brother of Prince Ernest II of Lüneburg, who chose Hanover as his residence.
New territory was added in 1665, and in 1705 the Principality of Luneburg was taken over by the Hanoverians. In 1692 Duke Ernest Augustus from the Calenberg-Hanover Line acquired the right to be a prince-elector of the Holy Roman Empire as the Prince-Elector of Brunswick-Lüneburg. Colloquially the Electorate was known as the Electorate of Hanover. In 1814 it was succeeded by the Kingdom of Hanover.
British succession
editReligion-driven politics placed Ernest Augustus's wife Sophia of the Palatinate in the line of succession to the British crown by the Act of Settlement 1701, written to ensure a Protestant succession to the thrones of Scotland and England at a time when anti-Catholic sentiment ran high in much of Northern Europe and Great Britain. Sophia died shortly before her first cousin once removed, Anne, Queen of Great Britain, the last sovereign of the House of Stuart.
Sophia's son George I succeeded Queen Anne and formed a personal union from 1714 between the British crown and the Electorate of Hanover, which lasted until well after the end of the Napoleonic Wars more than a century later, through the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire and the rise of a new successor kingdom. The British royal family became known as the House of Hanover.
-
Coat of arms of the Hanoverian Kings of Great Britain (1714–1801)
-
George I (1714–1727)
-
George II (1727–1760)
-
Frederick, Prince of Wales (b. 1707 d. 1751)
-
George III (1760–1820)
-
George IV (1820–1830)
-
William IV (1830–1837)
-
Victoria (1837–1901)
Kingdom of Hanover
editThe "Electorate of Hanover" (the core duchy) was enlarged with the addition of other lands and became the Kingdom of Hanover in 1814 at the Congress of Vienna. During the first half of the nineteenth century, the Kingdom was ruled as personal union by the British crown from its creation under George III of the United Kingdom, the last elector of Hanover until the death of William IV in 1837.
At that point, the crown of Hanover went to William's younger brother, Ernest Augustus, Duke of Cumberland and Teviotdale under the Salic law requiring the next male heir to inherit, whereas the British throne was inherited by an elder brother's only daughter, Queen Victoria. Her offspring belong to the House of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha: in 1917 the name was changed to the House of Windsor.
The Kingdom of Hanover was lost in 1866 by Ernest Augustus's son George V of Hanover, Austria's ally during the Austro-Prussian War, when it was annexed by Prussia after Austria's defeat and became the Prussian province of Hanover. The Welfs went into exile at Gmunden, Austria, where they built Cumberland Castle.
-
Coat of arms of the kingdom of Hanover 1837
-
King George V of Hanover
Brunswick succession
editThe senior line of the dynasty had ruled the much smaller principality of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel, created the sovereign Duchy of Brunswick in 1814. This line became extinct in 1884. Although the Duchy should have been inherited by the Duke of Cumberland, son of the last king of Hanover, Prussian suspicions of his loyalty led the duchy's throne to remain vacant until 1913, when the Duke of Cumberland's son, Ernst August, married the daughter of Kaiser Wilhelm II and was allowed to inherit it. His rule there was short-lived, as the monarchy came to an end following the First World War in 1918.
The Welf dynasty continues to exist. The last member sitting on a European throne was Frederica of Hanover, Queen of Greece († 1981), mother of Queen Sofia of Spain and King Constantine II of Greece. Frederica's brother Prince George William of Hanover married Princess Sophie of Greece and Denmark, sister of Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh. The House's head is Queen Frederica's nephew Ernst August, the third and present husband of Princess Caroline of Monaco.
-
The Leine Palace in Hanover
-
Herrenhausen Palace and Herrenhausen Gardens in Hanover
Rulers of the House of Welf
editHouse of Welf
editPartitions under Welf rule
edit| County of Altdorf (820–1191) |
County of Auxerre (866–888) Raised to: Kingdom of Upper Burgundy (888–1032) | ||||||||||
| Annexed to the Holy Roman Empire |
County Palatine of the Rhine (1195–1214) |
Lordship of Lüneburg (1126–1235) Raised to: Duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg (1235–1269) | |||||||||
| Annexed to House of Wittelsbach | |||||||||||
| Brunswick (1269–1291) |
Lüneburg (1st creation) (1269–1369) | ||||||||||
| Grubenhagen (1291–1596) |
Wolfenbüttel (1st creation) (1291–1292) | ||||||||||
| Göttingen (1291–1463) |
|||||||||||
| Wolfenbüttel (2nd creation) (1344–1400) |
Lüneburg under Ascanian rule (1373–1388) | ||||||||||
| Lüneburg (2nd creation) (1388–1705) | |||||||||||
| Calenberg (1st creation) (1432–1584) |
Wolfenbüttel (3rd creation) (1409–1485) | ||||||||||
| Wolfenbüttel (4th creation) (1494–1807) | |||||||||||
| (annexed Grubenhagen 1617) | |||||||||||
| Calenberg (2nd creation) (1634–1692) Recalled Hanover in 1692 | |||||||||||
| Electorate of Hanover (1692–1866) | |||||||||||
| Annexed by France | |||||||||||
| Brunswick (1813–1918) | |||||||||||
| Annexed by Prussia | |||||||||||
Table of rulers
edit| Ruler | Born | Reign | Death | Ruling part | Consort | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elder House of Welf | |||||||
| Welf (I) | 760 | c. 800-825 | 825 | County of Altdorf | Hedwig of Bavaria four children |
Eponymous founder of the family | |
| Conrad I the Elder | ? | 825–864 | 864 | County of Altdorf | Adelaide of Tours three children |
||
| Welf I | ? | 864–876 | 876 | County of Altdorf | Unknown at least one child |
||
| Conrad II the Younger | ? | 864–876 | 876 | County of Auxerre | Waldrada of Worms one child |
||
| Eticho | c. 850 | 876–911 | c. 911 | County of Altdorf | Egila three children |
||
| Rudolf I | 859 | 876–911 | 25 October 911 | County of Auxerre (until 888) Kingdom of Upper Burgundy (from 888) |
Guilla of Provence c. 880 four children |
First King of Burgundy, from 888. | |
| Henry (I) of the Golden Chariot |
c. 880 | 911–935 | c. 935 | County of Altdorf | Atha of Hohenwart three children |
||
| Rudolf II | 11 July 880 | 911–937 | 11 July 937 | Kingdom of Upper Burgundy | Bertha of Swabia 922 two children |
Also King of Italy (922–926). | |
| Rudolf I | c. 910 | 935–950 | c. 950 | County of Altdorf | Siburgis at least one child |
||
| Conrad III the Peaceful | 925 | 937–993 | 19 October 993 | Kingdom of Upper Burgundy | Adelaide of Bellay one child Matilda of France 866 four children |
||
| Rudolf II | c. 940 | 950–990 | c. 990 | County of Altdorf | Ita of Öhningen three children |
||
| Henry (II) | c. 960 | 990–1000 | 15 November 1000 | County of Altdorf | Unmarried | Left no descendants. He was succeeded by his brother. | |
| Rudolf III the Pious | 970 | 993–1032 | 6 September 1032 | Kingdom of Upper Burgundy | Agiltrude (d.1011) no children Ermengarde of Burgundy 28 June 1011 no children |
After his childless death, the Kingdom was annexed by the Holy Roman Empire. | |
| Welf II | c. 960 | 1000–1030 | 10 March 1030 | County of Altdorf | Imiza of Luxembourg 1017 two children |
||
| Welf III | 1007 | 1030–1055 | 13 November 1055 | County of Altdorf | Unmarried | Also Duke of Carinthia. Left no descendants, and the lands passed to his nephews, sons of his sister Kunigunde. | |
| Younger House of Welf | |||||||
| Welf IV | c. 1035/40 | 1055–1101 | 6 November 1101 | County of Altdorf | Ethelinde of Northeim 1062 no children Judith of Flanders 1071 three children |
Son of Kunigunde of Altdorf and Albert Azzo II, Margrave of Milan, inherited his maternal family's possessions. Also Duke of Bavaria (1070–1077 and 1096–1101). | |
| Welf V the Fat | 1072 | 1101–1120 | 24 September 1120 | County of Altdorf | Matilda of Tuscany 1088/89 no children |
Left no children, and the county went to his brother. Also Duke of Bavaria. | |
| Henry (III) the Black | 1075 | 1120–1126 | 13 December 1126 | County of Altdorf | Wulfhilde of Saxony 1095 eight children |
Inherited by marriage possessions in the Luneburg, to the north. | |
| Welf VI | 1115 | 1126–1191 | 15 December 1191 | County of Altdorf | Uta of Schauenburg c. 1130 two children |
Children of Henry the Black, Welf VI and Henry the Proud divided their inheritance: Welf VI kept the original possessions to the south, and Henry the northern ones, besides inheriting his father's title of Duke of Bavaria (1136–38), and conquering also the title of Duke of Saxony (1137–1139) inherited from their mother. Welf VI would also go on to become Margrave of Tuscany and Duke of Spoleto (1152–1160 and 1167–1173).
In 1129, after Henry the Proud's defeat against Lothair III, Holy Roman Emperor, his sister Sophia was given a seat at Regensburg.[4] From c. 1150 until his death in 1167, Welf VI's son, Welf VII, was associated to his father, but predeceased him. After Welf VI's death, Altdorf was annexed to the Holy Roman Empire. | |
| Henry (I) the Proud | 1108 | 1126–1139 | 20 October 1139 | Lordship of Lüneburg | Gertrude of Süpplingenburg 1202 one child | ||
| Sophia | 1105 | 1129–1145 | 1145 | County of Altdorf (at Regensburg) |
Berthold III, Duke of Zähringen c. 1120 no children Leopold, Margrave of Styria c. 1122 four children | ||
| Welf VII | 1135 | c. 1150-1167 | 12 September 1167 | County of Altdorf | Unmarried | ||
| Regency of Gertrude of Süpplingenburg (1139–1142) | Inherited Brunswick from his mother after her death in 1143. Also Duke of Saxony (1142–1180) and Duke of Bavaria (1156–1180). When Frederick I, Holy Roman Emperor, became king of Germany, he restored Bavaria to the Welf line. | ||||||
| Henry (II) the Lion | 1129/31 | 1139–1195 | 6 August 1195 | Lordship of Lüneburg | Clementia of Zähringen 1147 three children Matilda of England 1168 five children | ||
| Henry (III) the Elder | 1173 | 1195–1213 1195–1212 |
28 April 1227 | Lordship of Lüneburg County Palatine of the Rhine |
Agnes of Hohenstaufen 1193 three children Agnes of Landsberg 1209 no children |
Inherited the land jointly until 1213, when after William's death, they resigned this possessions in favor that William's son, the inheritor of the Luneburg property. Henry was Count Palatine of the Rhine (1195–1213), and Otto was Holy Roman Emperor (1212–1218). | |
| Otto | 1175 | 1195–1213 | 19 May 1218 | Lordship of Lüneburg |
Beatrice of Swabia Maria of Brabant | ||
| William Longsword | 11 April 1184 | 1195–1213 | 12 December 1213 | Lordship of Lüneburg | Helena of Denmark 1202 Hamburg one child | ||
| Henry (IV) the Younger | 1196 | 1212–1214 | 26 April 1214 | County Palatine of the Rhine | Unmarried | After his death the Palatinate was inherited by the House of Wittelsbach, to which his sister Agnes had married. | |
| Regency of Otto IV, Holy Roman Emperor (1213–1218) | He was raised to Duke and recognised as such in 1235, by Frederick II, Holy Roman Emperor | ||||||
| Otto I the Child | 1204 | 1213–1252 | 9 June 1252 | Brunswick-Lüneburg | Matilda of Brandenburg 1228 ten children | ||
| Albert I the Tall | 1236 | 1252–1279 | 15 August 1279 | Brunswick (in Brunswick-Lüneburg until 1269) |
Elisabeth of Brabant 1254 no children Alexia of Montferrat 1263 seven children |
Children of Otto I, they shared rule of the land until 1269. Albert became Prince of Brunswick and John a Prince of Luneburg. | |
| John | 1242 | 1252–1277 | 13 December 1277 | Lüneburg (in Brunswick-Lüneburg until 1269) |
Liutgard of Holstein-Itzehoe 1265 five children | ||
| All Welf lines continued to bear the title "Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg" between the division of 1269 and the end of the Holy Roman Empire in 1806. This was an additional title to the representation of their actual territorial lordship. However, as this is a list of rulers, the list goes beyond the use of the title, going through all generations until the end of the noble family representation in the land, in 1918. | |||||||
| Regencies of Albert I, Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg (1277–1279) and Conrad of Brunswick-Lüneburg, Prince-Bishop of Verden (1277–1282) | His rule was marked by several feuds, financed by pledges (Verpfändungen), involving border and property disputes with his neighbours. Otto restricted the rights of the knights and safeguarded public order. | ||||||
| Otto II the Strict | 1266 | 1277–1330 | 10 April 1330 | Lüneburg | Matilda of Bavaria 1288 five children | ||
| Henry I the Admirable | August 1267 | 1279–1322 | 7 September 1322 | Grubenhagen (until 1291 in Brunswick) |
Agnes of Meissen 1282 sixteen children |
Children of Albert I, ruled jointly. In 1291 divided the land: Henry received Grubenhagen, William Wolfenbüttel and Albert Göttingen. William died without descendants, and Albert reunited his land with his brother's. Wolfenbüttel became part of Göttingen. | |
| William I | 1270 | 1279–1292 | 30 September 1292 | Wolfenbüttel (until 1291 in Brunswick) |
Elisabeth of Hesse 190 no children | ||
| Albert II the Fat | 1268 | 1279–1318 | 22 September 1318 | Göttingen (until 1291 in Brunswick) |
Rixa of Werle 1284 ten children | ||
| Otto (I) the Mild | 24 June 1292 | 1318–1344 | 30 August 1344 | Göttingen | Judith of Hesse 1311 no children Agnes of Brandenburg-Salzwedel 1319 no children |
Sons of Albert II, ruled jointly. After Otto's death Magnus and Ernest divided the land: Magnus received Wolfenbüttel and Ernest Göttingen. | |
| Ernest I | 1305 | 1318–1367 | 24 April 1367 | Göttingen | Elizabeth of Hesse 1337 three children | ||
| Magnus I the Pious | 1304 | 1318–1344 | 1369 | Göttingen | Sophia of Brandenburg-Stendal 1327 eight children | ||
| 1344–1369 | Wolfenbüttel | ||||||
| Henry II | Before 1296 | 1322–1351 | After 1351 | Grubenhagen | Jutta of Brandenburg-Stendal 1318 four children Helvis of Ibelin 1324 six children |
Sons of Henry I, ruled jointly. | |
| Ernest I | 1297 | 1322–1361 | 9 March 1361 | Grubenhagen | Adelheid of Everstein-Polle June 1335 nine children | ||
| William | 1298 | 1322–1360 | 1360 | Grubenhagen | Unmarried | ||
| John I | Before 1296 | 1322–1325 | After 1367 | Grubenhagen | Unmarried | ||
| Otto III | 1296 | 1330–1352 | 19 August 1352 | Lüneburg | Matilda of Mecklenburg 1311 three children |
Sons of Otto II, ruled jointly. After Otto's death in 1352, William ruled alone. His death without descendants precipitated the Lüneburg War of Succession in 1370. | |
| William II the Elder | c. 1300 | 1330–1369 | 23 November 1369 | Lüneburg | Hedwig of Ravensberg 7 April 1328 one child Maria After 1387 one child Sophia of Anhalt-Bernburg 12 March 1346 no children Agnes of Saxe-Lauenburg 1363 no children | ||
| Albert I | c. 1339 | 1361–1383 | 1383 | Grubenhagen | Agnes of Brunswick-Lüneburg c. 1380? one child |
Sons of Ernest I, ruled jointly. John II abdicated 1364 to join the clergy and Albert became sole ruler. | |
| John II | c. 1339 | 1361–1364 | 18 January 1401 | Grubenhagen | Adelheid of Everstein-Polle June 1335 nine children | ||
| Frederick I | 1350 | 1361–1421 | 1421 | Grubenhagen (at Osterode) |
Adelaide of Anhalt-Zerbst (d. before 1421) one child | ||
| Otto (II) the Evil | 1330 | 1367–1394 | 13 November 1394 | Göttingen | Margarethe of Jülich-Berg 1379 two children |
||
| Magnus II of the Necklace (Torquatus) | 1304 | 1369–1373 | 25 July 1373 | Wolfenbüttel (with Lüneburg) |
Katherine of Anhalt-Bernburg 1327 eight children |
Inherited Wolfenbüttel from his father. However, the Lüneburg War of Succession allowed his succession also in this duchy. However, the War of Succession brought, after his death, the dukes of Saxe-Wittenberg to the government. | |
| After the death of Magnus II with the Necklace, a treaty (the Reconciliation of Hanover) was agreed between the widow of Magnus II and her sons and the claimers, Albert of Saxe-Wittenberg and his uncle Duke Wenceslaus I of Saxe-Wittenberg: the estates of the Principality were to pay homage both to the Welfs and to the Ascanians, and the two noble houses would govern the state alternately. Initially, the land would be given to the two Ascanians from Wittenberg, and after their death it would go to the sons of the fallen Duke Magnus II.
After their death, rule of the Principality was to revert to the Ascanians. In order to underpin the agreement, in 1374 Albert of Saxe-Lüneburg married Catharina, the widow of Magnus II. The treaty also envisaged the creation of a statutory body representing the estates, which was to supervise the treaty. However, 1373–1388 would be the only period in which a Brunswick-Luneburg land was not ruled by a Welf:
In the wake of his death, Elector Wenceslas appointed Bernard, his brother-in-law, as co-regent involved him in the government. But his younger brother Henry did not agree with this ruling, and after vain attempts to reach an agreement, the fight flared up again in the spring of 1388. Elector Wenceslas had to assemble an army without the help of Bernard, supported by the town of Lüneburg. From Winsen an der Aller, he wanted to attack Celle, which was held by Henry and his mother. During the preparations Elector Wenceslas fell seriously ill and died shortly thereafter. According to legend, he was poisoned. Lüneburg continued the preparations, formed an alliance with the Bishop of Minden and Count of Schaumburg and set up his own army. On 28 May 1388, battle was joined at Winsen an der Aller; it ended in victory for Henry. According to the provisions of the Treaty of Hanover from the year 1373, after the death of Wensceslas, the Principality passed to the House of Welf. In 1389, an inheritance agreement between the Welfs and the Ascanians was concluded, the treaty of 1374 was abolished, and the Principality was secured for the Welfs. | |||||||
| Frederick I | 1357 | 1373–1400 | 5 June 1400 | Wolfenbüttel | Anna of Saxe-Wittenberg 1386 two children |
Children of Magnus II. As the eldest, Frederick inherited Wolfenbuttel alone, while his younger brothers held Luneburg sinceits recovery in 1388. After Frederick I's childless death in 1400, the remaining brothers exchanged feuds until 1428. | |
| Henry (I) the Mild | 1355 | 1388–1416 | 14 October 1416 | Lüneburg | Sophia of Pomerania 11 November 1388 two children Margaret of Hesse 30 January 1409 one child | ||
| 1400–1409 | Wolfenbüttel | ||||||
| Bernard I | between 1358 and 1364 | 1388–1409 1428–1434 |
11 June 1434 | Lüneburg | Margaret of Saxe-Wittenberg 1386 three children | ||
| 1409–1428 | Wolfenbüttel | ||||||
| Regency of Frederick I, Duke of Brunswick-Osterode (1383–1401) | |||||||
| Eric I the Winner | c. 1383 | 1383–1427 | 28 May 1427 | Grubenhagen | Elisabeth of Brunswick-Göttingen six children | ||
| Otto (III) the One-Eyed | 1380 | 1394–1463 | 6 February 1463 | Göttingen | Agnes of Hesse 1408 one child |
With no male heirs, after his death Göttingen is absorbed by Calenberg. | |
| William (III & I) the Victorious | 1392 | 1416–1428 | 25 July 1482 | Lüneburg | Cecilia of Brandenburg 30 May/6 June 1423 Berlin two children Matilda of Holstein-Pinneberg 1466 one child |
Sons of Henry the Mild, ruled jointly. In 1428 they exchanged, with their uncle Bernard I, Lüneburg for Wolfenbüttel. In 1432 founded the Principality of Calenberg, a split-off from Lüneburg, and left the remaining Wolfenbüttel to his brother Henry IV. After the latter's death William took his lands. In 1463, attached the Principality of Göttingen to Calenberg. In 1473, William also annexed Wolfenbüttel. | |
| 1428–1432 | Wolfenbüttel | ||||||
| 1432–1482 | Calenberg (with Göttingen from 1463, and Wolfenbüttel from 1473) | ||||||
| Henry (II) the Peaceful | 1411 | 1416–1428 | 7 December 1473 | Lüneburg | Helena of Clèves 1436 one child | ||
| 1428–1473 | Wolfenbüttel | ||||||
| Otto II | 1396 | 1421–1452 | 1452 | Grubenhagen (at Osterode) |
Schonetta of Nassau-Weilburg (d.1436) 1414 one child |
After his death, Osterode returned to Grubenhagen. | |
| Regency of Otto II, Duke of Brunswick-Osterode (1427–1440) | Sons of Eric I, were under regency until 1440, when they divided Grubenhagen. Henry kept Heldenburg Castle, and Albert Herzberg Castle, but kept the joint rule at Osterode am Harz and Einbeck. Ernest didn't participate in the division, and abdicated in 1464, to become a canon in Halberstadt. | ||||||
| Henry III | 1416 | 1427–1464 | 20 December 1464 | Grubenhagen (at Heldenburg from 1440) |
Margaret of Żagań before 27 June 1457 two children | ||
| Albert II | 1 November 1419 | 1427–1485 | 15 August 1485 | Grubenhagen (at Herzberg) |
Elisabeth of Waldeck 15 October 1471 two children | ||
| Ernest II | 1418 | 1427–1466 | 1466 | Grubenhagen | Unmarried | ||
| Otto IV the Lame | ? | 1434–1446 | 1446 | Lüneburg | Elisabeth of Eberstein 1425 one child |
Ruled jointly. Their rule was marked by major building work to Celle Castle and also by numerous reforms which improved the legal situation of farmers vis-a-vis their local lords. Frederick abdicated to his sons and went to a monastery, but after the death of his son Otto, he left the monastery and resumed his rule. | |
| Frederick II the Pious | 1418 | 1434–1457 1471–1478 |
19 March 1478 | Lüneburg | Magdalene of Brandenburg 3 July 1429 Tangermünde three children | ||
| Otto V the Magnanimous | 1439 | 1457–1471 | 9 January 1471 | Lüneburg | Anne of Nassau-Siegen 25 September 1467 Celle two children |
Children of Frederick II, ruled jointly. Bernard was also Prince-Bishop of Hildesheim. | |
| Bernard II | 1437 | 1457–1464 | 1464 | Lüneburg | Matilda of Holstein-Pinneberg 1463 no children | ||
| Regency of Albert II, Duke of Brunswick-Grubenhagen (1464–1479) | With his uncle Albert, officialized the division of Grubenhagen. However, his death without descendants allowed his cousins (sons of Albert) to reunite Grubenhagen. | ||||||
| Henry IV | 1460 | 1464–1526 | 6 December 1526 | Grubenhagen (at Heldenburg) |
Elisabeth of Saxe-Lauenburg 26 August 1494 Einbeck no children | ||
| Regency of Anne of Nassau-Siegen (1478–1486) | Son of Otto V. As he opposed to the newly elected Emperor Charles V, the latter deposed him from the duchy and gave it to his sons. | ||||||
| Henry (III) the Middle | 15 September 1468 | 1478–1520 | 19 February 1532 | Lüneburg | Margaret of Saxony 27 February 1487 Celle seven children Anna von Camp c. 1528? no children | ||
| Frederick III the Turbulent | 1424 | 1482–1485 | 7 July 1503 | Calenberg | Anna of Brunswick-Grubenhagen-Einbeck After 1460 no children Margaret of Rietberg 10 May 1483 no children |
Imprisoned by his brother William, who took his place. | |
| William (IV & II) the Younger | 1425 | 1482–1485 | 7 July 1503 | Wolfenbüttel | Elizabeth of Stolberg-Wernigerode 1444 three children |
Inherited Wolfenbüttel from his father. Joined Calenberg to his domains in 1485, when he imprisoned his brother. Abdicated to his sons in 1491. | |
| 1485–1491 | Calenberg (with Wolfenbüttel) | ||||||
| Philip I | 1476 | 1485–1551 | 4 September 1551 | Grubenhagen (at Herzberg; from 1526 all Grubenhagen) |
Unknown before 1509 one child Catherine of Mansfeld-Vorderort c. 1510? nine children |
Son of Albert V, in 1526 reunited Grubenhagen under his hands. | |
| Eric I the Elder | 16 February 1470 | 1491–1540 | 30 July 1540 | Calenberg | Katharina of Saxony 1496/97 no children Elisabeth of Brandenburg 7 July 1525 Stettin four children |
Sons of William V, ruled jointly. In 1494, they divided their lands. Henry retained Wolfenbüttel and Eric retained Calenberg. | |
| Henry (IV) the Elder | 14 June 1463 | 1491–1494 | 23 June 1514 | Calenberg | Catherine of Pomerania-Wolgast 1486 nine children | ||
| 1494–1514 | Wolfenbüttel | ||||||
| Henry (V) the Younger | 10 November 1489 | 1514–1568 | 11 June 1568 | Wolfenbüttel | Maria of Württemberg 1515 eight children Sophia of Poland 22/25 February 1556 no children |
He was the last Catholic of his family. Under him the medieval fortress (Burg) was rebuilt into a castle (Schloss); he was a passionate opponent of the Lutherans, and driving force behind the Catholic alliance established against the Schmalkaldic League; the disinheritance of a third son could not be carried out. | |
| Otto (VI & I) | 24 August 1495 | 1520–1549 | 11 August 1549 | Lüneburg (from 1527 in Harburg) |
Meta von Camp 1527 no children |
Sons of Henry VII, ruled jointly. Otto abdicated in 1527 and founded his own estate, the Lordship of Harburg, which passed to his own descendants. Ernest was a champion of the Protestant cause during the early years of the Protestant Reformation. Francis started his co-rulership in 1536, and abdicated three years later to rule in his own estate, the Principality of Gifhorn, which was reannexed to Lüneburg after his death as he left no descendants. | |
| Ernest I the Confessor | 27 June 1497 | 1520–1546 | 11 January 1546 | Lüneburg | Sophia of Mecklenburg-Schwerin 2 June 1528 Schwerin seven children | ||
| Francis | 23 November 1508 | 1536–1539 | 23 November 1549 | Lüneburg | Clara of Saxe-Lauenburg 29 September 1547 Amt Neuhaus seven children | ||
| Regencies of Elisabeth of Brandenburg and Philip I, Landgrave of Hesse (1540–1545) | During his regency, his mother implemented the Reformation in Calenberg. She also wrote a "government manual" for Eric, with important advice that should serve him as a guide. Left no descendants, and Calenberg was annexed to Wolfenbüttel. | ||||||
| Eric II | 10 August 1528 | 1540–1584 | 17 November 1584 | Calenberg | Sidonie of Saxony 17 May 1545 Hann. Münden no children Dorothea of Lorraine 26 November 1575 Nancy no children | ||
| Council of Regency (1546–1555) | Left no descendants. The land passed to his brothers. | ||||||
| Francis Otto | 20 June 1530 | 1546–1559 | 29 April 1559 | Lüneburg | Elizabeth Magdalene of Brandenburg 1559 no children | ||
| Otto II | 25 September 1528 | 1549–1603 | 26 October 1603 | Lüneburg (in Harburg) |
Margaret of Schwarzburg-Leutenberg 8 September 1551 four children Hedwig of East Frisia 8 October 1562 twelve children |
||
| Ernest III | 17 December 1518 | 1551–1567 | 2 April 1567 | Grubenhagen | Margaret of Pomerania-Wolgast 9 October 1547 Wolgast one child |
Left no male descendants. The land passed to his brother Wolfgang. | |
| Henry (VI) | 1533 | 1559–1598 | 19 January 1598 | Lüneburg (from 1569 in Dannenberg) |
Ursula of Saxe-Lauenburg 1569 seven children |
Brothers of Francis Otto, ruled jointly. In 1569 Henry founded the duchy of Dannenberg, which left to his own descendants. William ruled alone from 1569. | |
| William V the Younger | 4 July 1535 | 1559–1592 | 20 August 1592 | Lüneburg | Dorothea of Denmark 12 October 1561 fifteen children | ||
| Wolfgang | 6 April 1531 | 1567–1595 | 14 May 1595 | Grubenhagen | Dorothea of Saxe-Lauenburg 10 December 1570 Osterode am Harz no children |
Like most of his predecessors, he had financial problems, so he was often forced to sell or pledge major parts of his possession and he had to demand high taxes. As he left no male descendants, the land passed to his brother Philip. | |
| Julius | 29 June 1528 | 1568–1589 | 3 May 1589 | Wolfenbüttel | Hedwig of Brandenburg 25 February 1560 Cölln eleven children |
In 1584 absorbes the Principality of Calenberg. By embracing the Protestant Reformation, establishing the University of Helmstedt, and introducing a series of administrative reforms, Julius was one of the most important Brunswick dukes in the early modern era. | |
| Ernest II | 31 December 1564 | 1592–1611 | 2 March 1611 | Lüneburg | Unmarried | Left no descendants. The land passed to his brother, Christian. | |
| Henry Julius | 15 October 1564 | 1589–1613 | 30 July 1613 | Wolfenbüttel | Dorothea of Saxony 26 September 1585 Wolfenbüttel one child Elizabeth of Denmark 19 April 1590 Cölln ten children |
In 1596 occupied Grubenhagen. | |
| Philip II | 2 May 1533 | 1595–1596 | 4 April 1596 | Grubenhagen | Clara of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel 1 July 1560 Wolfenbüttel no children |
As he left no male descendants, the land had no heir and was occupied by the Principality of Wolfenbüttel. | |
| Grubenhagen annexed to Wolfenbüttel, and then definitely to Lüneburg | |||||||
| Julius Ernest | 11 March 1571 | 1598–1636 | 26 October 1636 | Lüneburg (at Dannenberg) |
Maria of East Frisia 1 September 1614 two children Sybille of Brunswick-Lüneburg 1616 two children |
Left no descendants. The short-lived Dannenberg principality reverted to Lüneburg. | |
| William Augustus | 15 March 1564 | 1603–1642 | 30 March 1642 | Lüneburg (in Harburg) |
Unmarried | Sons of Otto II, ruled together in Harburg. After William Augustus' death, the lordship reunited with Lüneburg. | |
| Otto III | 20 March 1572 | 1603–1641 | 4 August 1641 | Lüneburg (in Harburg) |
Hedwig of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel 14 April 1621 Wolfenbüttel no children | ||
| Christopher | 21 August 1570 | 1603–1606 | 7 July 1606 | Lüneburg (in Harburg) |
Elisabeth of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel 28 October 1604 Harburg no children | ||
| Regency of Elizabeth of Denmark (1616–1622) | Children of Henry Julius. Frederick Ulirch inheriteed the major duchy, and Sophie Hedwig a seat at Spiegelberg. Because of his alcoholism, Frederick Ulrich was deposed by his own mother, with the help of her brother, Christian IV of Denmark. She took the regency in his name. During her regency, Elizabeth lost in 1617 the Principality of Grubenhagen and left the government business for Anton von Streithorst, who nearly ruined the state by minting coins from cheap metals and thus causing inflation. Because of the bad situation of the state, the king of Denmark had Frederick take control of the government again. Frederick didn't leave descendants, and his lands passed to collateral lines of the Lüneburg Welfs. | ||||||
| Frederick Ulrich | 5 April 1591 | 1613–1634 | 11 August 1634 | Wolfenbüttel | Anna Sophia of Brandenburg 4 September 1614 Wolfenbüttel no children | ||
| Sophia Hedwig | 13 June 1592 | 1613–1642 | 13 January 1642 | Wolfenbüttel (at Spiegelberg) |
Ernest Casimir I, Count of Nassau-Dietz 8 June 1607 Dillenburg two children | ||
| Christian the Elder | 9 November 1566 | 1611–1633 | 8 November 1633 | Lüneburg (with Grubenhagen from 1617) |
Unmarried | Absorbed Grubenhagen from Wolfenbüttel. As he left no descendants, the land passed to his brother, Augustus. Grubenhagen is definitively annexed to Lüneburg. | |
| Augustus the Elder | 18 November 1568 | 1633–1636 | 1 October 1636 | Lüneburg (and Grubenhagen) | Unmarried | No legitimate issue. The land passed to his brother, Frederick IV. | |
| George | 17 February 1582 | 1634–1641 | 2 April 1641 | Calenberg | Anne Eleonore of Hesse-Darmstadt 14 December 1617 Darmstadt eight children |
Younger son of William VI. Inherited Calenberg from his cousin Frederick Ulrich, who had left no descendants. Abdicated to his son in 1641. | |
| Augustus the Younger | 10 April 1579 | 1634–1666 | 17 September 1666 | Wolfenbüttel | Clara Maria of Pomerania-Barth 13 December 1607 Strelitz two children Dorothea of Anhalt-Zerbst 26 October 1623 Zerbst five children Elisabeth Sophie of Mecklenburg 1635 two children |
Younger son of Henry (VI). Inherited Wolfenbüttel from his cousin Frederick Ulrich, who had left no descendants. In 1643 he moved into the Residence at Wolfenbüttel, was the founder of a barock theatre and the Bibliotheca Augusta. | |
| Frederick IV | 28 August 1574 | 1636–1648 | 10 December 1648 | Lüneburg | Unmarried | As he left no descendants, the land passed to a nephew, Christian Louis, son of Frederick's brother George. | |
| Christian Louis | 25 February 1622 | 1641–1648 | 15 March 1665 | Calenberg | Sophia Dorothea of Schleswig-Holstein-Sonderburg-Glücksburg 9 October 1653 no children |
In 1648 inherited the Principality of Lüneburg from his uncle Frederick IV, he gave Calenberg to his younger brother George William, and instead ruled the larger territory of Lüneburg. | |
| 1648–1665 | Lüneburg | ||||||
| George William | 26 January 1624 | 1648–1665 | 28 August 1705 | Calenberg | Éléonore Desmier d'Olbreuse 1676 one child |
When his brother, Christian Louis died childless in 1665, George William inherited Luneburg. He then gave Calenberg to his next brother, John Frederick. At his death without male descendants, the land passed to his son-in-law, the Elector of Hanover. Lüneburg is annexed to Hanover. | |
| 1665–1705 | Lüneburg | ||||||
| Lüneburg definitely annexed to Hanôver | |||||||
| Rudolf Augustus | 16 May 1627 | 1666–1704 | 26 January 1704 | Wolfenbüttel | Christiane Elizabeth of Barby-Mühlingen 1650 three children Rosine Elisabeth Menthe 1681 (morganatic) no children |
Sons of Augustus II, the eldest two ruled jointly from 1685 to 1702. The youngest, Ferdinand Albert, ruled from the town of Bevern. According to reports dating to 1677, Rudolf Augustus slashed a way through the Lechlum Forest, the Alten Weg ("Old Way"), later the "Barock Road" between the Lustschloss of Antoinettenruh via the little barock castle [later the Sternhaus] to the Großes Weghaus at Stöckheim; in 1671 captured the town and fortress of Brunswick. After the death of Rudolf Augustus, Anthony Ulrich returned to the throne and ruled alone. A politician, art lover and poet, he founded a museum named after him in Brunswick; he had also Salzdahlum Castle built. | |
| Anthony Ulrich | 4 October 1633 | 1685–1702 1704–1714 |
27 March 1714 | Wolfenbüttel | Elizabeth Juliana of Schleswig-Holstein-Sønderburg-Nordborg 17 August 1656 thirteen children | ||
| Ferdinand Albert I | 22 May 1636 | 1666–1687 | 23 April 1687 | Wolfenbüttel (at Bevern) |
Christine of Hesse-Eschwege 25 November 1667 Eschwege six children | ||
| John Frederick | 25 April 1625 | 1665–1679 | 18 December 1679 | Calenberg | Benedicta Henrietta of the Palatinate 30 November 1668 Hanover three children |
Brother of Christian Louis and George William. As he left no male heirs, the land passed to his younger brother, Ernest Augustus. | |
| Ernest Augustus I | 20 November 1629 | 1679–1692 | 23 January 1698 | Calenberg | Sophia of the Palatinate 30 September 1658 Heidelberg seven children |
Youngest son of George. Brother of Christian Louis, George William and John Frederick. In 1692, he was appointed Prince-elector by Leopold I, Holy Roman Emperor, thus raising the House of Welf to electoral dignity. The old Principality of Calenberg thus adopted the new name of Electorate of Hanover. | |
| 1692–1698 | Electorate of Hanover | ||||||
| George I Louis | 28 May 1660 | 1698–1705 | 11 June 1727 | Electorate of Hanover | Sophia Dorothea of Brunswick-Lüneburg 22 November 1682 Celle (annulled 1694) two children |
The electorship became effective under his rule. In 1705 reunited his father-in-law's princedom of Lüneburg to the Electorate. In 1714 was chosen for King of Great Britain, starting a personal union between Hanover and this new country. Lüneburg was definitely annexed to the Electorate. Thus the Wolfenbüttel was the remaining old land of Brunswick-Lüneburg that remained separate. | |
| Augustus William | 8 March 1662 | 1714–1731 | 23 March 1731 | Wolfenbüttel | Christine Sophie of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel 1681 no children Sophie Amalie of Holstein-Gottorp 1695 no children Elisabeth Sophie Marie of Schleswig-Holstein-Sonderborg-Norburg 1710 no children |
Son of Anthony Ulrich. Ruler of the only land that was still not in Hanoverian lands, to which it would never belong. | |
| George II Augustus | 30 October / 9 November 1683O.S./N.S. | 1727–1760 | 25 October 1760 | Electorate of Hanover | Wilhelmina Charlotte Caroline of Brandenburg-Ansbach 22 August / 2 September 1705O.S./N.S. Hanover ten children |
In personal union with Great Britain. | |
| Louis Rudolph | 22 July 1671 | 1731–1735 | 1 March 1735 | Wolfenbüttel | Christine Louise of Oettingen-Oettingen 22 April 1690 Aurich three children |
Left no male heirs, and his land passed to a collateral line. | |
| Ferdinand Albert II | 29 May 1680 | 1687–1735 1735 |
2 September 1735 | Wolfenbüttel (in Bevern) Wolfenbüttel |
Antoinette Amalie of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel 15 October 1712 Brunswick thirteen children |
From the line of Brunswick-Bevern. Grandson of Augustus II. | |
| Charles I | 1 August 1713 | 1735–1773 | 26 March 1780 | Wolfenbüttel | Philippine Charlotte of Prussia 2 June 1733 Berlin thirteen children |
Founder of the Collegium Carolinum in Brunswick, the porcelain makers of Fürstenberg, the fire office; in 1753 the Residence was moved to Brunswick. | |
| George III William Frederick | 4 June 1738 | 1760–1811 | 29 January 1820 | Electorate of Hanover | Charlotte of Mecklenburg-Strelitz 8 September 1761 London fifteen children |
In personal union with Great Britain. | |
| Charles II William Ferdinand | 9 October 1735 | 1773–1806 | 10 November 1806 | Wolfenbüttel | Augusta of Great Britain 16 January 1764 London seven children |
Due to financial problems, was obliged to replace his father. He was the head of the Prussian Army; died in the Battle of Jena; because his son and heir died young, and two other sons were not eligible, rule passed to his youngest son. | |
| With the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire in 1806, the title of Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg ceased to exist. However, its successor states continued. | |||||||
| Frederick William the Black Duke | 9 October 1771 | 1806–1807 1813–1815 |
16 June 1815 | Wolfenbüttel (1813–15) Brunswick (1806–07) |
Marie Elisabeth Wilhelmine of Baden 1 November 1802 Karlsruhe three children |
Duke of Oels/Silesia, the "Black Duke"; recruited a Freikorps (volunteer corps), the Black Brunswickers, at the outbreak of the War of the Fifth Coalition in Bohemia in 1809, and made his way via Brunswick to the North Sea and then on to Great Britain. | |
| On the Eve of Napoleonic era, in 1807 the Duchy was briefly annexed to the Kingdom of France, to appear again in 1813 as Duchy of Brunswick. | |||||||
| George IV Augustus Frederick | 12 August 1762 | 1811–1830 | 26 June 1830 | Electorate of Hanover (until 1814) Kingdom of Hanover (from 1814) |
Caroline Amelia Elizabeth of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel 8 April 1795 London one child |
In personal union with the United Kingdom. Named regent of his father due to his illness, succeeding him after his death in 1820. Left no male descendants. The land passed to his brother. | |
| Regency of George IV of the United Kingdom (1815–1823) | On the eve of the July Revolution of 1830, Charles was in Paris, and did not manage to keep the duchy for himself; his brother William took over with the agreement of the people and his international neighbours. | ||||||
| Charles II | 30 October 1804 | 1815–1830 | 18 August 1873 | Brunswick | Unmarried | ||
| William Henry | 21 August 1765 | 1830–1837 | 20 June 1837 | Kingdom of Hanover | Adelaide of Saxe-Meiningen 13 July 1818 London four children |
In personal union with the United Kingdom. Usually numbered IV as King of Hanover and the United Kingdom. As he left only illegitimate descendants, the land passed to his brother. | |
| William | 25 April 1806 | 1830–1884 | 18 October 1884 | Brunswick | Unmarried | Brother of Charles II. | |
| Victoria | 24 May 1819 | 1837–1901 | 22 January 1901 | United Kingdom | Albert of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha 10 February 1840 St James's Palace nine children |
End of personal union with the United Kingdom, as in this country the successor in 1837 was Queen Victoria (in Hanover the Salic Law was still active). | |
| Ernest Augustus | 5 June 1771 | 1837–1851 | 18 November 1851 | Kingdom of Hanover | Frederica of Mecklenburg-Strelitz 29 May 1815 Neustrelitz three children | ||
| George V Frederick | 27 May 1819 | 1851–1866 | 12 June 1878 | Kingdom of Hanover | Marie of Saxe-Altenburg (I) 18 February 1843 Hanover three children |
He was the last king of Hanover, as his reign ended with the Unification of Germany. | |
| Hanôver annexed to the German Empire | |||||||
| Regencies of Prince Albert of Prussia (1885–1906) and Duke John Albert of Mecklenburg-Schwerin (1906–1913) | His regency came to an end on 1 November 1913 when Ernest Augustus, Crown Prince of Hanover's son, was permitted to ascend to Duchy following his marriage to Princess Victoria Louise of Prussia. In 1918, with the abolition of the monarchy, all nobles titles were equally abolished. | ||||||
| Ernest Augustus | 17 November 1887 | 1913–1918 | 30 January 1953 | Brunswick | Victoria Louise of Prussia 24 May 1913 Berlin five children | ||
Family trees
editWelf family tree 12th century
editWelf family tree 18th century to present
editSome direct ancestors (fathers and sons) of the present generation are:
- Ernest Augustus, King of Hanover (1771–1851), Duke of Cumberland and Teviotdale from 1799, king from 1837
- George V of Hanover (1819–1878)
- Ernest Augustus, Crown Prince of Hanover (1845–1923)
- Ernest Augustus, Duke of Brunswick (1887–1953)
- Ernest Augustus, Prince of Hanover (1914–1987)
- Ernest Augustus, Prince of Hanover (born 1954)
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ Jones, B. (2013). Dictionary of World Biography. Canberra, Australia: Australian National University Press. p. 356. ISBN 9781922144492.
- ^ Canduci, pg. 294
- ^ Riedesel, Friedrich Adolf (1868). von Eelking, Max (ed.). Memoirs, and Letters and Journals, of Major General Riedesel During His Residence in America. Vol. 1. Translated by Stone, William L. Albany: J. Munsell. p. 29.
I remain ever, Your affectionate Charles, Duke of Brunswick and Lüneburg. Brunswick, February 14, 1776. To Colonel Riedesel.
- ^ "Sophia von Bayern. In: Genealogie Mittelalter: Mittelalterliche Genealogie im Deutschen Reich bis zum Ende der Staufer". Retrieved 2016-04-27.