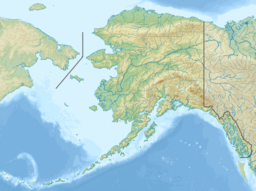
The Imuruk Basin (Imaġruk or Narvaġruk in Iñupiaq) is an approximately 90 sq mi (230 km2), 17-mile (27 km) long shallow estuary located on the Seward Peninsula in the U.S. state of Alaska. The estuary's drainage basin covers about one quarter of the peninsula. The basin is fed by the Kuzitrin, Kruzgamepa, Agiapuk, and Cobblestone Rivers and is drained by the Tuksuk Channel, which empties into Grantley Harbor (Pacific Ocean).
| Imuruk Basin | |
|---|---|
 View of the Imuruk Basin from the north. | |
| Location | Nome Census Area, Alaska, United States |
| Coordinates | 65°07′14″N 165°42′00″W / 65.12056°N 165.70000°W |
| Primary inflows | |
| Primary outflows | Tuksuk Channel |
| Basin countries | United States |
| Surface area | ~90 sq mi (230 km2)[1] |
| Max. depth | 20 feet (6 m)[2] |
| Surface elevation | 3 feet (1 m)[3] |
The Imuruk Basin was a strategic waterway for early Iñupiat by providing accessibility to the Bering Sea from the Seward Peninsula's interior.
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ "Water Power Aspects of the National Conservation System Study Areas Under Section 17(d)(2) of the Alaska Native Claims Settlement Act" (PDF). United States Department of the Interior; Alaska Power Administration. Retrieved September 8, 2019.
- ^ "Norton Sound/Bering Strait Regional Comprehensive Salmon Plan 1996–2010" (PDF). Alaska Department of Fish and Game. Retrieved September 8, 2019.
- ^ "Feature Detail Report for: Imuruk Basin". United States Geological Survey. Retrieved September 8, 2019.