Metal nitrosyl complexes are complexes that contain nitric oxide, NO, bonded to a transition metal.[2] Many kinds of nitrosyl complexes are known, which vary both in structure and coligand.
Bonding and structure
editMost complexes containing the NO ligand can be viewed as derivatives of the nitrosyl cation, NO+. The nitrosyl cation is isoelectronic with carbon monoxide, thus the bonding between a nitrosyl ligand and a metal follows the same principles as the bonding in carbonyl complexes. The nitrosyl cation serves as a two-electron donor to the metal and accepts electrons from the metal via back-bonding. The compounds Co(NO)(CO)3 and Ni(CO)4 illustrate the analogy between NO+ and CO. In an electron-counting sense, two linear NO ligands are equivalent to three CO groups. This trend is illustrated by the isoelectronic pair Fe(CO)2(NO)2 and [Ni(CO)4].[3] These complexes are isoelectronic and, incidentally, both obey the 18-electron rule. The formal description of nitric oxide as NO+ does not match certain measureable and calculated properties. In an alternative description, nitric oxide serves as a 3-electron donor, and the metal-nitrogen interaction is a triple bond.
Linear vs bent nitrosyl ligands
editThe M-N-O unit in nitrosyl complexes is usually linear, or no more than 15° from linear. In some complexes, however, especially when back-bonding is less important, the M-N-O angle can strongly deviate from 180°. Linear and bent NO ligands can be distinguished using infrared spectroscopy. Linear M-N-O groups absorb in the range 1650–1900 cm−1, whereas bent nitrosyls absorb in the range 1525–1690 cm−1. The differing vibrational frequencies reflect the differing N-O bond orders for linear (triple bond) and bent NO (double bond).
The bent NO ligand is sometimes described as the anion, NO−. Prototypes for such compounds are the organic nitroso compounds, such as nitrosobenzene. A complex with a bent NO ligand is trans-[Co(en)2(NO)Cl]+. The NO− is also common for alkali-metal or alkaline-earth metal-NO molecules. For example. LiNO and BeNO bear Li+NO− and Be+NO− ionic form.[4][5]
The adoption of linear vs bent bonding can be analyzed with the Enemark-Feltham notation.[6] In their framework, the factor that determines the bent vs linear NO ligands is the sum of electrons of pi-symmetry. Complexes with "pi-electrons" in excess of 6 tend to have bent NO ligands. Thus, [Co(en)2(NO)Cl]+, with eight electrons of pi-symmetry (six in t2g orbitals and two on NO, {CoNO}8), adopts a bent NO ligand, whereas [Fe(CN)5(NO)]2−, with six electrons of pi-symmetry, {FeNO}6), adopts a linear nitrosyl. In a further illustration, the {MNO} d-electron count of the [Cr(CN)5NO]3− anion is shown. In this example, the cyanide ligands are "innocent", i.e., they have a charge of −1 each, −5 total. To balance the fragment's overall charge, the charge on {CrNO} is thus +2 (−3 = −5 + 2). Using the neutral electron counting scheme, Cr has 6 d electrons and NO· has one electron for a total of 7. Two electrons are subtracted to take into account that fragment's overall charge of +2, to give 5. Written in the Enemark-Feltham notation, the d electron count is {CrNO}5. The results are the same if the nitrosyl ligand were considered NO+ or NO−.[6]
Bridging nitrosyl ligands
editNitric oxide can also serve as a bridging ligand. In the compound [Mn3(η5C5H5)3 (μ2-NO)3 (μ3-NO)], three NO groups bridge two metal centres and one NO group bridge to all three.[3]
Isonitrosyl ligands
editUsually only of transient existence, complexes of isonitrosyl ligands are known where the NO is coordinated by its oxygen atom. They can be generated by UV-irradiation of nitrosyl complexes.[7]
Representative classes of compounds
editHomoleptic nitrosyl complexes
editMetal complexes containing only nitrosyl ligands are called isoleptic nitrosyls. They are rare, the premier member being Cr(NO)4.[8] Even trinitrosyl complexes are uncommon, whereas polycarbonyl complexes are routine.
Roussin red and black salts
editOne of the earliest examples of a nitrosyl complex to be synthesized is Roussin's red salt, which is a sodium salt of the anion [Fe2(NO)4S2]2−. The structure of the anion can be viewed as consisting of two tetrahedra sharing an edge. Each iron atom is bonded linearly to two NO+ ligands and shares two bridging sulfidi ligands with the other iron atom. Roussin's black salt has a more complex cluster structure. The anion in this species has the formula [Fe4(NO)7S3]−. It has C3v symmetry. It consists of a tetrahedron of iron atoms with sulfide ions on three faces of the tetrahedron. Three iron atoms are bonded to two nitrosyl groups. The iron atom on the threefold symmetry axis has a single nitrosyl group which also lies on that axis.
-
The anion in Roussin's red salt, [Fe2S2(NO)4]2−.
-
The anion in Roussin's black salt, [Fe4S3(NO)7]−.
-
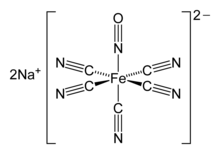
The nitroprusside anion, [Fe(CN)5NO]2−, an octahedral complex containing a "linear NO" ligand.
-
trans-[Co(en)2(NO)Cl]+, an octahedral complex containing a "bent NO" ligand.
Preparation
editMany nitrosyl complexes are quite stable, thus many methods can be used for their synthesis.[9]
From NO
editNitrosyl complexes are traditionally prepared by treating metal complexes with nitric oxide. The method is mainly used with reduced precursors. Illustrative is the nitrosylation of cobalt carbonyl to give cobalt tricarbonyl nitrosyl:[10]
- Co2(CO)8 + 2 NO → 2 CoNO(CO)3 + 2 CO
From NO+ and NOCl
editReplacement of ligands by the nitrosyl cation may be accomplished using nitrosyl tetrafluoroborate. This reagent has been applied to the hexacarbonyls of molybdenum and tungsten:[11][12]
- M(CO)6 + 4 MeCN + 2 NOBF4 → [M(NO)2(MeCN)4](BF4)2
Nitrosyl chloride and molybdenum hexacarbonyl react to give [Mo(NO)2Cl2]n.[13] Diazald is also used as an NO source.[14]
From hydroxylamine
editHydroxylamine is a source of nitric oxide anion via a disproportionation:[15]
- K2[Ni(CN)4] + 2 NH2OH + KOH → K2[Ni(CN)3)NO] + NH3 + 2 H2O + KCN
From nitric acid
editNitric acid is a source of nitric oxide complexes, although the details are obscure. Probably relevant is the conventional self-dehydration of nitric acid:
- 2 HNO3 → NO2+NO3− + H2O
Nitric acid is used in some preparations of nitroprusside from ferrocyanide:
- HNO3 + [Fe(CN)6]4- → [Fe(CN)5(NO)]2- + OH− + OCN−
From nitrous acid
editSome anionic nitrito complexes undergo acid-induced deoxygenation to give the linear nitrosyl complex.
- [LnMNO2]− + H+ → [LnMNO] + OH−
The reaction is reversible in some cases.
Oxidation of ammine complexes
editIn some metal-ammine complexes, the ammonia ligand can be oxidized to nitrosyl:[16]
- H2O + [Ru(terpy)(bipy)(NH3)]+ → [Ru(terpy)(bipy)(NO)]2+ + 5 H+ + 6 e−
Reactions
editAn important reaction is the acid/base equilibrium, yielding transition metal nitrite complexes:
- [LnMNO]2+ + 2OH− ⇌ LnMNO2 + H2O
This equilibrium serves to confirm that the linear nitrosyl ligand is, formally, NO+, with nitrogen in the oxidation state +3
- NO+ + 2 OH− ⇌ NO2− + H2O
Since nitrogen is more electronegative than carbon, metal-nitrosyl complexes tend to be more electrophilic than related metal carbonyl complexes. Nucleophiles often add to the nitrogen.[2] The nitrogen atom in bent metal nitrosyls is basic, thus can be oxidized, alkylated, and protonated, e.g.:
- (Ph3P)2(CO)ClOsNO + HCl → (Ph3P)2(CO)ClOsN(H)O
In rare cases, NO is cleaved by metal centers:
- Cp2NbMe2 + NO → Cp2(Me)Nb(O)NMe
- 2 Cp2(Me)Nb(O)NMe → 2 Cp2Nb(O)Me + ½MeN=NMe
Applications
editMetal-nitrosyls are assumed to be intermediates in catalytic converters, which reduce the emission of NOx from internal combustion engines. This application has been described as "one of the most successful stories in the development of catalysts."[18]
Metal-catalyzed reactions of NO are not often useful in organic chemistry. In biology and medicine, nitric oxide is however an important signalling molecule in nature and this fact is the basis of the most important applications of metal nitrosyls. The nitroprusside anion, [Fe(CN)5NO]2−, a mixed nitrosyl cyano complex, has pharmaceutical applications as a slow release agent for NO. The signalling function of NO is effected via its complexation to haem proteins, where it binds in the bent geometry. Nitric oxide also attacks iron-sulfur proteins giving dinitrosyl iron complexes.
Thionitrosyls
editSeveral complexes are known with NS ligands. Like nitrosyls, thionitrosyls exist as both linear and bent geometries.[20]
References
edit- ^ "Sodium Nitroprusside". www.drugs.com. The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Retrieved 21 October 2022.
- ^ a b Hayton, T. W.; Legzdins, P.; Sharp, W. B. (2002). "Coordination and Organometallic Chemistry of Metal-NO Complexes". Chem. Rev. 102 (1): 935–991. doi:10.1021/cr000074t. PMID 11942784.
- ^ a b Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. pp. 447–453. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ^ Ariyarathna, Isuru R.; Miliordos, Evangelos (15 July 2019). "Electronic and geometric structure analysis of neutral and anionic metal nitric chalcogens: The case of MNX series (M=Li, Na, Be and X=O, S, Se, Te)". Journal of Computational Chemistry. 40 (19): 1740–1751. doi:10.1002/jcc.25829. PMID 30920017. S2CID 85546245.
- ^ Ariyarathna, Isuru (1 March 2021). "First Principle Studies on Ground and Excited Electronic States: Chemical Bonding in Main-Group Molecules, Molecular Systems with Diffuse Electrons, and Water Activation using Transition Metal Monoxides".
- ^ a b Enemark, J. H.; Feltham, R. D. (1974). "Principles of structure, bonding, and reactivity for metal nitrosyl complexes". Coord. Chem. Rev. 1974 (13): 339–406. doi:10.1016/S0010-8545(00)80259-3.
- ^ Mikhailov, Artem A.; Wenger, Emmanuel; Kostin, Gennadiy A.; Schaniel, Dominik (2019). "Room‐Temperature Photogeneration of Nitrosyl Linkage Isomers in Ruthenium Nitrosyl Complexes" (PDF). Chemistry – A European Journal. 25 (31): 7569–7574. doi:10.1002/chem.201901205. PMID 30957917. S2CID 102349334.
- ^ Herberhold Max (1972). "Tetranitrosylchromium [Cr(NO)4]". Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English. 11 (12): 1092–1094. doi:10.1002/anie.197210921.
- ^ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 449. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ^ Paul Gilmont; Arthur A. Blanchard (1946). "Dicobalt Octacarbonyl, Cobalt Nitrosyl Tricarbonyl, and Cobalt Tetracarbomyl Hydride". Inorganic Syntheses. Vol. 2. p. 238. doi:10.1002/9780470132333.ch76. ISBN 978-0-470-13233-3.
- ^ Richard R. Thomas; Ayusman Sen (1990). "Acetonitrile Complexes of Selected Transition Metal Cations". Inorganic Syntheses. Vol. 28. pp. 63–67. doi:10.1002/9780470132593.ch14. ISBN 978-0-470-13259-3.
- ^ Francine Agbossou; Edward J. O'Connor; Charles M. Garner; N. Quirós Méndez; Jesús M. Fernández; Alan T. Patton; James A. Ramsden; J. A. Gladysz; Joseph M. O'Connor; Tracy Tajima; Kevin P. Gable (1992). "Cyclopentadienyl Rhenium Complexes". Inorganic Syntheses. Vol. 29. pp. 211–225. doi:10.1002/9780470132609.ch51. ISBN 978-0-470-13260-9.
- ^ B. F. G. Johnson; K. H. Al‐Obadi (1970). "Dihalogenodinitrosylmolybdenum and Dihalogenodinitrosyltungsten". Inorganic Syntheses. Vol. 12. pp. 264–266. doi:10.1002/9780470132432.ch47. ISBN 978-0-470-13243-2.
- ^ James K. Hoyano; Peter Legzdins; John T. Malito (1978). "(η 5 ‐Cyclopentadienydnitrosyl Complexes of Chromium, Molybdenum, and Jungsten". Inorganic Syntheses. Vol. 13. pp. 126–131. doi:10.1002/9780470132494.ch21. ISBN 978-0-470-13249-4.
- ^ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1984). Chemistry of the Elements. Oxford: Pergamon Press. p. 516. ISBN 978-0-08-022057-4.
- ^ Dunn, Peter L.; Cook, Brian J.; Johnson, Samantha I.; Appel, Aaron M.; Bullock, R. Morris (2020). "Oxidation of Ammonia with Molecular Complexes". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 142 (42): 17845–17858. doi:10.1021/jacs.0c08269. OSTI 1706682. PMID 32977718. S2CID 221938378.
- ^ Walker, F. A. (2005). "Nitric Oxide Interaction with Insect Nitrophorins and Thoughts on the Electron Configuration of the FeNO6 Complex". J. Inorg. Biochem. 99 (1): 216–236. doi:10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2004.10.009. PMID 15598503.
- ^ Kaspar, Jan; Fornasiero, Paolo; Hickey, Neal (2003). "Automotive Catalytic Converters: Current Status and Some Perspectives". Catalysis Today. 77 (4): 419–449. doi:10.1016/S0920-5861(02)00384-X.
- ^ Jessica Fitzpatrick; Eunsuk Kim (2015). "Synthetic Modeling Chemistry of Iron–Sulfur Clusters in Nitric Oxide Signaling". Acc. Chem. Res. 48 (8): 2453–2461. doi:10.1021/acs.accounts.5b00246. PMID 26197209.
- ^ Ng, Ho-Yuen; Cheung, Wai-Man; Kwan Huang, Enrique; Wong, Kang-Long; Sung, Herman H.-Y.; Williams, Ian D.; Leung, Wa-Hung (2015). "Ruthenium chalcogenonitrosyl and bridged nitrido complexes containing chelating sulfur and oxygen ligands". Dalton Transactions. 44 (42): 18459–18468. doi:10.1039/C5DT02513C. PMID 26442594.