The Japanese giant salamander (Andrias japonicus) is a species of fully aquatic giant salamander endemic to Japan, occurring across the western portion of the main island of Honshu, with smaller populations present on Shikoku and in northern Kyushu. With a length of up to 5 feet (1.5 m),[4] it is the third-largest salamander in the world, only being surpassed by the very similar and closely related Chinese giant salamander and the South China giant salamander.
| Japanese giant salamander | |
|---|---|

| |
| Japanese giant salamander in Tottori Prefecture, Japan | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Amphibia |
| Order: | Urodela |
| Family: | Cryptobranchidae |
| Genus: | Andrias |
| Species: | A. japonicus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Andrias japonicus (Temminck, 1836)
 | |
| Synonyms[2] | |
|
List
| |


It is known in Japanese as Ōsanshōuo (オオサンショウウオ/大山椒魚), literally meaning "giant salamander". Other local names include Hanzaki[5], Hanzake[6], and Ankou.[5] This salamander was first catalogued by Europeans when the resident physician of Dejima Island in Nagasaki, Philipp Franz von Siebold, captured an individual and shipped it back to Leiden in the Netherlands, in the 1820s. The species was designated as a special natural monument in 1951, and is protected by the Central Government.[7] It is one of the only six species of giant salamanders in the world.
Description
editThe Japanese giant salamander can grow to a length of 5 feet (1.5 m) and a weight of 55 pounds (25 kg). The largest wild specimen on record weighed 58 lb (26.3 kg) and was 4.46 ft (136 cm) long.[8] It is the third-largest amphibian in the world, only smaller than its close relatives, the South China giant salamander[9] and the Chinese giant salamander. The brown and black mottled skin of A. japonicus provides camouflage against the bottoms of streams and rivers. Its body surface is covered with numerous small warts with distinctive warts concentrating on its head. It has very small eyes with no eyelids and poor eye sight. Its mouth extends across the width of its head, and can open to the width of its body.[10]
A. japonicus possesses large skin folds on its neck that effectively increase its overall body surface area. This assists in epidermal gas exchanges, which in turn regulates carbon dioxide and oxygen exchange with the water. Capillaries in the surface of the skin facilitate this gas exchange.[11] The skin folds along each side of the body are more pronounced in the hellbender than in the Japanese giant salamander.
The Japanese giant salamander can be distinguished from the Chinese giant salamander by the arrangement of tubercles on the head and throat. The tubercles are larger and more numerous compared to the mostly single and irregularly scattered tubercles of the Chinese giant salamander. The snout is also more rounded, and the tail is slightly shorter.[12]
Adult males develop enlarged cloacal glands during the breeding season. Compared to an adult female, an adult male typically possesses a larger and wider head in proportion to its body. It is difficult to distinguish sex outside of the breeding season.
Distribution
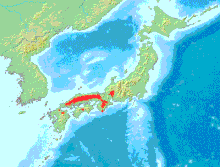
editThe Japanese giant salamander occurs in southwestern Japan (west of Gifu Prefecture in Honshu and parts of Shikoku and Kyushu). In particular, Okayama, Hyogo, Shimane, Tottori, Yamaguchi, Mie, Ehime, Gifu, and Ōita Prefecture are known to harbor its robust populations.[13] They are typically found in fast-flowing mountain streams of these prefectures. It has been speculated that some of the populations in Wakayama Prefecture were introduced by humans and it is unknown whether naturally-distributed populations exist in Wakayama Prefecture.[14]
The Japanese giant salamander occurs in freshwater habitats ranging from relatively large river (20–50 m) to small headwater streams (0.5 - 4 m).[15][16] Smaller breeding adults tend to use small headwater streams presumably in order to avoid intraspecific competition with larger individuals in larger streams.[16] Mark-recapture records suggest that giant salamanders migrate between a mainstem and tributaries of the same river.[16] Environmental DNA surveys and the following physical field surveys suggest that small headwater streams likely serve as important habitats for juveniles and larvae.[16] While habitat degradation threatens the Japanese giant salamander, it can inhabit disturbed streams surrounded by agriculture fields such as rice paddy fields.[15] Adults appear to do well in a stream surrounded by rice paddy fields because rice paddy fields provide habitats for frogs, which serve as primary diet for adult giant salamanders in such a stream.[15] However, streams surrounded by rice paddy fields are typically characterized by agricultural dams and concrete stream banks, which likely imposes a negative impact on their reproduction and thus result in low recruitment.[15]
Behavior
editThe Japanese giant salamander is restricted to streams with clear, cool water. Due to its large size and lack of gills, it is confined to flowing water where oxygen is abundant.[17] It is entirely aquatic and almost entirely nocturnal. Unlike typical pond-breeding salamanders whose juveniles migrate to land after losing their gills through metamorphosis, it stays in the aquatic habitat even after metamorphosis and breaches its head above the surface to obtain air without venturing out of the water and onto land. The salamander also absorbs oxygen through its skin, which has many folds to increase surface area.[10]
When threatened, the Japanese giant salamander can excrete a strong-smelling, milky substance. It has very poor eyesight, and possesses special sensory cells covering its skin, running from head to toe, the lateral line system. These sensory cells' hair-like shapes detect minute vibrations in the environment, and are quite similar to the hair cells of the human inner ear. This feature is essential for hunting prey due to its poor eyesight.
Adults feed mainly on freshwater crabs, other crustaceans, worms, insects,[18] frogs, and fish. It has a very slow metabolism and can sometimes go for weeks without eating.[10] It lacks natural competitors. It is a long-lived species, with the captive record being an individual that lived in the Natura Artis Magistra, the Netherlands, for 52 years.[4] In the wild, it may live for nearly 80 years.[citation needed]
Lifecycle
editThe Japanese giant salamander remains in bodies of water its entire life. During the mating season, typically in late August and early September, sexually mature males start actively finding suitable nesting sites and often migrate upstream into smaller sections of the river or its tributaries.[19] Because of the limited availability of suitable nesting sites, only large and competitive males are able to occupy nesting sites and become den masters. A den master diligently cleans his den[20] guards his den against intruders including other males who try to steal the den while allowing a sexually active female enter the den. Mating begins as the female starts laying eggs and the den master starts releasing sperm, which often stimulate other subordinate males hiding around the den to enter the den and join the mating. As a result, a single female often mates with multiple males. The den master stays in the den with the fertilized eggs while the other males and the female leave the den. He provides parental care for the embryos by guarding the eggs and fanning water over them with his tail to increase oxygen flow.[21] As the den-master kicks his back legs and fans with his tail, organic debris is swept out of the nest and carried away from the nest from the water current. If this behavior were not performed, organic material would build up in the nest and lead to water mold infection. Therefore, the behavior is classified as pre-ovipositional parental care.[22] The den-master continues providing parental care for the hatchlings until the following spring when the larvae start dispersing from the nest.[23] Researchers also observed that den masters consumed eggs and larvae that showed the sign of failed fertilization, death, or water mold infection.[21][23] The researchers termed the behavior of selectively eating his own eggs or larvae "hygienic filial cannibalism" and hypothesize that this behavior importantly increases the survivorship of the remaining offspring by preventing water mold infection on the dead offspring from spreading over the healthy offspring.
Conservation
editThreats
editThe Japanese giant salamander is threatened by pollution, habitat loss (among other changes, by the silting up of the rivers where it lives), dams and concrete banks, and invasive species.[15][16][24][1] In particular, it is important to note that the construction of concrete streambanks and agricultural dams throughout the distribution range has imposed a significant negative impact on giant salamanders. Concrete banks have deprived of habitats suited for nesting sites, and dams block migration paths and have caused habitat fragmentation. With the ongoing climate change, it is predicted that frequency and intensity of rainstorms in Japan will increase.[25] These rainstorms will likely destroy stream banks more frequently, which could result in the construction of more flood-control dams and concrete banks.
Introgressive hybridization between the native Japanese giant salamander and the introduced Chinese giant salamander (A. davidianus) is one of the major conservation challenges.[24] It has been suggested that although the details are not known, the Chinese giant salamanders imported for food to Japan in 1972 were the sources of the ongoing introgressive hybridization.[26][27] In Kamo River in Kyoto Prefecture, the study conducted from 2011 to 2013 found that 95% of the captured giant salamanders were hybrids.[24] The introgressive hybridization appears to be spreading across several watersheds.[24] Although the Chinese giant salamander has recently been split up into multiple species, recent genetic studies have confirmed that the Chinese giant salamander introduced to Japan is the initially described Chinese species, A. davidianus.[27]
In some regions, giant salamanders used to be hunted as a source of food, but hunting has ceased because of the protection acts established after World War II.
- Preserved specimen kept at Naturalis Biodiversity Center (NL)
Status
editAs of 2022 the Japanese giant salamander is considered Vulnerable by IUCN,[1] and is included on CITES Appendix I.[28] It is considered Vulnerable by the Japanese Ministry of the Environment.[29] Additionally, it has been given the highest protection as a "Special Natural Monument" by the Japanese Agency for Cultural Affairs since 1952 due to its cultural and educational significance.[30]
Efforts
editDespite the national protection and conservation status, there have been no conservation programs or actions initiated by the government agencies. Instead, nonprofit organizations such as the Japanese Giant Salamander Society[31] and the Hanzaki Research Institute of Japan[32] have organized volunteers to conduct population assessments in some areas. The Japanese Giant Salamander Society also organizes annual meetings to promote the conservation education and information sharing about the species. There is no range-wide conservation or recovery program, which is essential to the conservation of the species whose populations have been declining throughout its range.[1]
The Hiroshima City Asa Zoological Park of Japan was the first domestic organization to successfully breed Japanese giant salamanders in captivity.[33] Several of their offspring were given to the National Zoo of the United States to establish a breeding program.[34] Although Asa Zoological Park has not released any offspring to streams, it has a capacity to carry out a headstarting program if needed.
Cultural references
editThe Japanese giant salamander has been the subject of legend and artwork in Japan, for example, in the ukiyo-e work by Utagawa Kuniyoshi. The well-known Japanese mythological creature known as the kappa may be inspired by the Japanese giant salamander.[35][better source needed]
There is a giant salamander festival every year on August 8 in Yubara, Maniwa City, Okayama prefecture to honour the animal and celebrate its life. The giant salamanders are called "Hanzaki" in Yubara, due to the belief that even if they are ripped in half (han) they continue to survive. There are two giant salamander floats: a dark male and a red female.[36]
As of 2017, a picture book entitled "Zakihan" was also published in both Japanese and English wherein the main character is a "hanzaki" called "Zakihan".
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ a b c d IUCN SSC Amphibian Specialist Group (2022). "Japanese Giant Salamander". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2022. Retrieved 9 December 2022.
- ^ "Amphibian Species of the World - Andrias japonicus (Temminck, 1836)". Research.amnh.org. Archived from the original on 2009-03-26. Retrieved 2010-02-04.
- ^ "Appendices | CITES". cites.org. Retrieved 2022-01-14.
- ^ a b Andrias japonicus - Amphibiaweb
- ^ a b "What is the Hanzaki Research Institute of Japan?". 日本ハンザキ研究所 (in Japanese). Retrieved 2021-11-17.
- ^ "ハンザケ資料展示室". よりみちにちなん (in Japanese). 2020-02-29. Retrieved 2021-11-17.
- ^ オオサンショウウオ (in Japanese). The Agency for Cultural Affairs. Retrieved 2011-09-24.
- ^ Tochimoto, pers. com>
- ^ "Newly described Chinese giant salamander may be world's largest amphibian". 17 September 2019.
- ^ a b c "Japanese Giant Salamander". Smithsonian National Zoological Park. Archived from the original on 2016-06-24. Retrieved 2016-06-13.
- ^ "Andrias japonicus". Animal Diversity Web. Retrieved 2018-03-28.
- ^ "AmphibiaWeb - Andrias japonicus".
- ^ "Natural Monuments in Japan (Animals and Plants)".
- ^ Shimizu, Zenkichi; Tamai, Sumio (2016). "Records of Japanese giant salamander Andrias japonicus from Wakayama Prefecture, Japan". The Nanki Seibutsu. 58: 99–106.
- ^ a b c d e Okada, Sumio; Utsunomiya, Taeko; Okada, Tamami; Felix, Zachary; Ito, Fumihiko (2008). "Characteristics of Japanese Giant Salamander (Andronias japonicus) populations in two small tributary streams in Hiroshima Prefecture, Western Honshu, Japan". Herpetological Conservation and Biology. 3: 192–202.
- ^ a b c d e Bjordahl, Brianna; Okada, Sumio; Takahashi, Mizuki (2020). "Assessment of small tributaries as possible habitats for larvae and juveniles of Japanese giant salamanders, Andrias japonicus, by coupling environmental DNA with traditional field surveys". Salamandra. 56: 148–158.
- ^ The Encyclopedia of Reptiles and Amphibians. Facts on File Inc. 1986. ISBN 0-8160-1359-4.
- ^ "Andrias japonicus". Animal Diversity Web.
- ^ Kuwabara, K.; Ashikaga, K.; Minamigawa, N.; Nakanishi, M.; Shimada, H.; Kamata, H.; Fukumoto, Y. (2005). "The breeding ecology and conservation of the Japanese giant salamander, Andrias japonicus, at Shijihara and Kamiishi in Tokyohira-cho, Hiroshima Prefecture". Natural History of Nishi-Chugoku Mountains. 10: 101-133 (in Japanese with English abstract).
- ^ Terry, J.; Taguchi, Y.; Dixon, J.; Kuwabara, K.; Takahashi, M. K. (2019). "Preoviposition paternal care in a fully aquatic giant salamander: nest cleaning by a den master". Journal of Zoology. 307 (1): 36–42. doi:10.1111/jzo.12615. ISSN 1469-7998. S2CID 92209611.
- ^ a b Okada, Sumio; Fukuda, Yukihiro; Takahashi, Mizuki (2015). "Paternal care behaviors of Japanese giant salamander Andrias japonicus in natural populations". Journal of Ethology. 33: 1–7. doi:10.1007/s10164-014-0413-5.
- ^ Terry, J., Taguchi, Y., Dixon, J., Kuwabara, K., & Takahashi, M. K. (2019). Preoviposition paternal care in a fully aquatic giant salamander: nest cleaning by a den master. Journal of Zoology, 307(1), 36–42. https://doi.org/10.1111/jzo.12615
- ^ a b Takahashi, M. K.; Okada, S.; Fukuda, Y. (2017). "From embryos to larvae: seven-month-long paternal care by male Japanese giant salamander". Journal of Zoology. 302 (1): 24–31. doi:10.1111/jzo.12433. ISSN 1469-7998.
- ^ a b c d Matsui, Masafumi (2014). "Confirmation of genetic pollution of alien Chinese giant salamander on native Japanese species (In Japanese)" (PDF).
- ^ Ministry of the Environment, Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism, & Japan Meteorological Agency (2018): Climate change in Japan and its impacts. – Synthesis Report on Observations, Projections and Impact Assessments of Climate Change, 2018.
- ^ "Chinese Giant Salamander / National Institute for Environmental Studies Invasive Species Database (In Japanese)". www.nies.go.jp. Retrieved 2021-11-17.
- ^ a b Nishikawa, Kanto; Matsui, Masafumi; Yoshikawa, Natsuhiko; Tominaga, Atsushi; Eto, Koshiro; Fukuyama, Ibuki; Fukutani, Kazumi; Matsubara, Kohei; Hattori, Yasunari; Iwato, Shohei; Sato, Tsukasa; Shimizu, Zenkichi; Onuma, Hirokazu; Hara, Sotaro (2024-01-31). "Discovery of ex situ individuals of Andrias sligoi, an extremely endangered species and one of the largest amphibians worldwide". Scientific Reports. 14 (1): 2575. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-52907-6. hdl:2433/286948. ISSN 2045-2322.
- ^ "Appendices | CITES". cites.org. Retrieved 2021-11-18.
- ^ Ministry of the Environment (2006): Japan Ministry of the Environment Red List.
- ^ Agency for Cultural Affairs (1952): Nationally Designated Important Cultural Properties.
- ^ "HOME | oosan-kai". www.giantsalamander.net (in Japanese). Retrieved 2024-05-01.
- ^ "What is the Hanzaki Research Institute of Japan? - 日本ハンザキ研究所". www.hanzaki.net (in Japanese). Retrieved 2024-05-01.
- ^ Kuwabara, K.; Suzuki, N.; Wakabayashi, F.; Ashikaga, H.; Inoue, T.; Kobara, J. (1989). "Breeding the Japanese Giant Salamander at Asa Zoological Park". International Zoo Yearbook. 1989: 22–31.
- ^ "Japanese Giant Salamanders at the Zoo". Smithsonian National Zoological Park. Archived from the original on 2016-06-29. Retrieved 2016-06-13.
- ^ "River Monsters" programme 6 Series 3 directed by Duncan Chard, screened in UK on ITV1 14.02.2012 at 19.30
- ^ "AltJapan: Hanzaki Matsuri Dakara". altjapan.typepad.com. Retrieved 2017-04-25.
Further reading
edit- Stejneger L (1907). Herpetology of Japan and Adjacent Territory. United States National Museum Bulletin 58. Washington, District of Columbia: Smithsonian Institution. xx + 577 pp. (Megalobatrachus japonicus, pp. 6–11).
- Temminck CJ (1836). Coup-d'oeil sur la Faune des Iles de la Sonde et de l'Empire du Japon. Discours préliminaire destiné à servir d'introduction à la Faune du Japon. Amsterdam: Müller. 30 pp. (Triton japonicus, new species). (in French).
External links
edit- Media related to Andrias japonicus at Wikimedia Commons
- Andrias japonicus at CalPhotos
- Discovery Channel Video on the giant salamander
- BBC report
