KN-62 is a derivative of isoquinolinesulfonamide, it is a selective, specific and cell permeable inhibitor of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase type II (CaMK II) with IC50 of 900nM,[1] charactered by hydrophobicity. KN-62 also potently inhibits the purinergic receptor P2X7.[2]
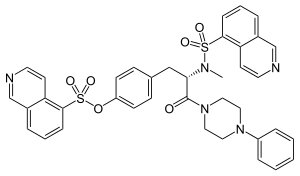
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
4-[(2S)-2-(N-Methylisoquinoline-5-sulfonamido)-3-oxo-3-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)propyl]phenyl isoquinoline-5-sulfonate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | C063302 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C38H35N5O6S2 | |
| Molar mass | 721.84 g/mol |
| Boiling point | 964.7±75.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 537.3±37.1 °C |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Inhibitory mechanism on CaMK II
editKN-62 blocks the combination of CaM and CaMK II by binding directly to the calmodulin binding site of the enzyme, disenables CaMK II's autophosphorylation, consequently leading inactivation. Kinetic analysis exhibits that this inhibitory effect of KN-62 is competitive with respect to calmodulin.[3] Since KN-62 binds to the calmodulin binding site of CaMK II, KN-62 doesn't inhibit activity of autophosphorylated CaMK II.
Besides, KN-62 also acts as a potent non-competitive antagonist at the purinergic receptor P2RX7 with IC50 of 15nM.
References
edit- ^ "avtivity in vitro and in vivo of KN-62". selleck chemicals.
- ^ Humphreys, BD; Virginio, C; Surprenant, A; Rice, J; Dubyak, GR (July 1998). "Isoquinolines as antagonists of the P2X7 nucleotide receptor: high selectivity for the human versus rat receptor homologues". Molecular Pharmacology. 54 (1): 22–32. doi:10.1124/mol.54.1.22. PMID 9658186.
- ^ Okazaki K, et al. (Sep 1994). "KN-62, a specific Ca++/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase inhibitor, reversibly depresses the rate of beating of cultured fetal mouse cardiac myocytes". J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 270 (3): 1319–24. PMID 7932185.