The Iceland gull (Larus glaucoides) is a medium-sized gull that breeds in the Arctic regions of Canada and Greenland, but not in Iceland (as its name suggests), where it is only seen during winter. The genus name is from Latin larus, which appears to have referred to a gull or other large seabird. The specific name glaucoides denotes its resemblance to Larus glaucus, a synonym of Larus hyperboreus, the glaucous gull; -oides is Ancient Greek and means "resembling".[2]
| Iceland gull | |
|---|---|

| |
| Adult, Ithaca, NY | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Charadriiformes |
| Family: | Laridae |
| Genus: | Larus |
| Species: | L. glaucoides
|
| Binomial name | |
| Larus glaucoides Meyer, B, 1822
| |
| Subspecies | |
| |
| |
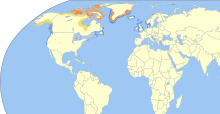
| Distribution
Breeding Migration Nonbreeding Nonbreeding (scarce)
| |

Description
editThe Iceland gull is a medium-sized gull, although relatively slender and light in weight. In length, it can measure from 50 to 64 cm (20 to 25 in), wingspan is from 115 to 150 cm (45 to 59 in), and weight is from 480 to 1,100 g (1.06 to 2.43 lb). Among standard measurements, the wing chord is 37.9 to 44.3 cm (14.9 to 17.4 in), the bill is 3.6 to 5.4 cm (1.4 to 2.1 in), and the tarsus is 4.9 to 6.7 cm (1.9 to 2.6 in).[3][4][5] It is smaller and thinner-billed than the very large glaucous gull, and is usually smaller than the herring gull. It takes four years to reach maturity.
Call
editThe call is a "laughing" cry like the herring gull, but higher pitched.
Ecology
editIt is migratory, wintering from in the North Atlantic as far south as the British Isles and northernmost states of the eastern United States, as well as in the interior of North America as far west as the western Great Lakes. It is much scarcer in Europe than the similar glaucous gull.
This species breeds colonially or singly on coasts and cliffs, making a nest lined with grass, moss, or seaweed on the ground or cliff. Normally, two or three light brown eggs are laid. They breed in Canada and Greenland, but not in Iceland.
Like most Larus gulls, these are omnivores, eating fish, molluscs, offal, scraps, and eggs. They forage while flying, picking up food at or just below the water's surface, and they also feed while walking or swimming. Their scavenging habits lead them to frequent garbage dumps, sewage outlets, and places where fish are cleaned.
Taxonomy and systematics
editThe American taxon of Iceland gull by the American Ornithological Society as of 2017 considers the following as subspecies:[6]
- Kumlien's gull, L. g. kumlieni
- Thayer's gull, L. g. thayeri
The nominate subspecies, L. g. glaucoides, is very pale in all plumage, with absolutely no melanin in the tips of the primaries in adult plumage. Adults are pale grey above, with a yellowish-green bill. Immatures are very pale grey; the bill is more extensively dark than with glaucous gull, and lacks pink.
References
edit- ^ BirdLife International. (2019) [amended version of 2018 assessment]. "Larus glaucoides". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T22729877A155595584. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22729877A155595584.en. Retrieved 13 April 2021.
- ^ Jobling, James A (2010). The Helm Dictionary of Scientific Bird Names. London: Christopher Helm. pp. 174, 219. ISBN 978-1-4081-2501-4.
- ^ Olsen, Klaus Malling; Larsson, Hans (2004). Gulls of North America, Europe, and Asia. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0691119977.
- ^ Harrison, Peter (1991). Seabirds: An Identification Guide. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. ISBN 978-0-395-60291-1.
- ^ Dunning, John B. Jr., ed. (1992). CRC Handbook of Avian Body Masses. CRC Press. ISBN 978-0-8493-4258-5.
- ^ Chesser, R. Terry; Burns, Kevin J.; Cicero, Carla; Dunn, John L.; Kratter, Andrew W; Lovette, Irby J; Rasmussen, Pamela C.; Remsen, J.V. Jr; Rising, James D.; Stotz, Douglas F.; Winker, Kevin (2017). "Fifty-eighth supplement to the American Ornithological Society's Check-list of North American Birds". The Auk. 134 (3): 751–773. doi:10.1642/AUK-17-72.1.
External links
edit- BirdLife species factsheet for Larus glaucoides
- "Larus glaucoides". Avibase.
- "Iceland gull media". Internet Bird Collection.
- Iceland gull photo gallery at VIREO (Drexel University)
- Interactive range map of Larus glaucoides at IUCN Red List maps
- Audio recordings of Iceland gull on Xeno-canto.
- Larus glaucoides in Field Guide: Birds of the World on Flickr
