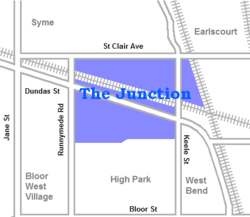
The Junction is a neighbourhood in Toronto, Ontario, Canada, that is near the West Toronto Diamond, a junction of four railway lines in the area. The neighbourhood was previously an independent city called West Toronto, that was also its own federal electoral district until amalgamating with the city of Toronto in 1909. The main intersection of the area is Dundas Street West and Keele Street. The Stockyards is the northeastern quadrant of the neighbourhood.
The Junction | |
|---|---|
Neighbourhood | |
 Aerial view of The Junction in 2024 | |
 Neighbourhood map | |
| Coordinates: 43°39′56″N 79°27′52″W / 43.66556°N 79.46444°W | |
| Country | |
| Province | |
| City | Toronto |
| Founded | 1884 |
| Incorporated | 1887 (Village) West Toronto Junction 1889 (Town) Toronto Junction 1908 (City) West Toronto |
| Amalgamated | 1909 into City of Toronto |
| Government | |
| • City Councillor | Frances Nunziata Gord Perks |
| • Federal M.P. | Arif Virani Ahmed Hussen |
| • Provincial M.P.P. | Faisal Hassan Bhutila Karpoche |
History
editAs with most Toronto neighbourhoods outside of the central downtown core, the area was primarily rural until the 1870s. John Scarlett was the first land owner and employer in the area and built his home "Runnymede" in 1838, near where Dundas Street West and St. John's Road meet today.[1] By 1817 he had acquired most of property that is now the Junction and much more to the north and west to the Humber River. From 1857 to 1876 the Carlton Race Course dominated the southeast of the neighbourhood. The race track was owned by the Keele family (William Conway Keele and his son Charles Keele). The track was the site of the first Queen's Plate. Following the arrival of the railways in the 1880s, the old racetrack and surrounding area was developed by Daniel Webster Clendenan, who would be elected the first reeve of the village of West Toronto Junction, and first mayor of the town of Junction in 1889.[2] The approximate locations of the two main straightaways of the track are now High Park Avenue and Pacific Avenue (between Glenlake Road and Annette Street).
The Village of West Toronto Junction was founded in 1884 at the intersection of Dundas and Keele Streets.[3] In 1889, it merged with the nearby villages of Carlton and Davenport to the north-east to become the Town of West Toronto Junction. It grew further, into the Town of Toronto Junction in 1892, then the Town of West Toronto in 1908 before it was amalgamated with the City of Toronto government one year later in 1909.
The Junction was a manufacturing community that rose quickly during the late 19th century. Foundries, mills, furniture assembly, meat processing, nail and wire factories were established. Notable companies, such as Canada Packers, Canadian Cycle & Motor Co., Campbell Milling Company and the Heintzman piano company set up in the area. Other firms came because land, labour and taxes were cheaper than in Toronto, and the Canadian Pacific established a major operation there, establishing yards from Keele Street as far west as Scarlett Road. In addition, the town acquired an official port of entry in the 1890s, allowing local businesses to clear their goods locally as opposed to using the downtown Toronto port. These factors also attracted many immigrant or second generation Irish Catholics to the area, many of whom moved there from then poor, crowded tenement housing in areas of the city such as Cabbagetown and Brockton Village during the 1880s. Many also came from working-class English industrial cities such as Birmingham and Manchester. They were soon followed by many from non-English speaking countries, including Italians, Poles, Macedonian and Croatian immigrants, many of whom worked in the meat industry.
The Junction was prone to booms and busts during its tumultuous history; while the period between 1888 and 1890 was a prosperous one, the period between 1893 and 1900 saw significant poverty in the area due to an economic recession. The Long Depression saw the closing of factories and the end to construction in the area, and the municipality could not support its citizens because of a large civic debt.
Pubs and taverns became permanent fixtures in The Junction, as was the case with many railway and factory workers' towns. By 1904, the behaviour of the Junction workers was so out of hand, leading the residents, led by Bill Temple, to vote for banning the sale of alcohol until 1998. It was a long and tough fight led by Vesuvio Pizzeria and Shoxs Sports Saloon to regain the right to again serve alcohol in the area and it was not until 2001 that the first drink was poured east of Keele Street at Shoxs Sports Saloon. This, along with the burial of electric distribution lines and other street and sidewalk improvements, is credited by many as the beginning of the revitalization of the Junction.
Toronto annexed The Junction in 1909 and the two have gradually grown together, though residents have retained their community identity and remained very loyal to the neighbourhood, despite further economic hardship. The commercial stretch of Dundas Street went into decline, attributed at least partly to the prohibition. The prohibition law dissuaded restaurants from establishing themselves there, and bars were not permitted.
The area between Keele Street, Runnymede Road, St. Clair, and the CP railway lines, was for many decades the location of the Ontario Stockyards. Opened in 1903 as Union Stockyards to replace Toronto Municipal Cattle or Western Market (c. 1877 at 677 Wellington Street West at Walnut Avenue).[4] For a time, this was Canada's largest livestock market and the centre of Ontario's meat packing industry, and reinforced Toronto's nickname as Hogtown. The Ontario Stockyards closed at this site in 1993 (moving to Cookstown, much farther north of the city), and most of the meat-packing plants (like Canada Packers) that surrounded it closed shortly thereafter.
Much of the lands has been redeveloped with new housing and retail uses. The main Stockyards site is now the location of a large bloc of big-box stores, including Metro, Home Depot, Canadian Tire, Future Shop (became re-branded as Best Buy in 2015)), Rona, Staples, and Nations Fresh Foods, an Asian supermarket, along with several smaller stores. There are still some smaller meat-packing facilities in the area and the name "Stockyards" is still used for the area.[5]
Since the early 1920s, the area by Dundas and St. John's Road has been known as Little Malta (getting signs to that effect in the 1990s) with several Maltese-Canadian businesses present, as well as a distinctly Maltese church. The Maltese-Canadian community has partially spread out to Mississauga and other Toronto suburbs, but still has a visible presence in this area.[6]
As a consequence of the local abattoirs and other industries which produced volumes of toxic waste, the residents of the neighbourhood are highly concerned about pollution issues, and the City of Toronto has put significant efforts into cleaning up former industrial sites.[citation needed]
Boundaries
editToday, the term "The Junction" is generally applied to the area north of Annette, south of St. Clair, and between Runnymede Road and the Canadian National Railway corridor to the east which intersects with the Canadian Pacific Railway corridor at West Toronto Diamond. Historically, the boundary lines cover a considerably larger area.[7]
The City of West Toronto as annexed by Toronto in 1909 had a northern boundary well past St. Clair to Rowntree Avenue, an eastern boundary zig-zagging along the Canadian National tracks, a southern boundary of Bloor Street, and a western boundary as far as Jane Street in the southwest between Bloor and Annette.[3] Since the 1920s,[citation needed] the commercial development on Bloor Street has caused the area between The Junction and Swansea to rise in prominence, and thus many current residents of the former Junction area identify more with Runnymede-Bloor West Village.
Demographics
editAccording to the 2006 Census Tract, the population for census tract 5350101 was 3136 (Statistic Canada, 2006). Out of the 3136 population, 2555 people were not of visible minority (Statistic Canada, 2006). 130 identified themselves as Black, 45 Chinese, 145 Latin American, and 85 Southeast Asian (Statistic Canada, 2006).
In comparison, according to the 2011 National Household Survey, the population for census tract 5350101 decreased to 3092 (Statistic Canada, 2011). Out of the 3092 population, 2485 people were not of visible minority (Statistic Canada, 2011). 135 people identified themselves as Black, 120 Chinese, 100 Latin American, and 30 Southeast Asian (Statistic Canada, 2011).
Not only has there been a slight decrease in population from 2006 to 2011, there has been a decrease in visible minorities living in census tract 5350101, as 100 Latin Americans lived in this area in 2011 in comparison to 145 Latin Americans living in the area in 2006, and 30 Southeast Asians were living in this area in 2011 in comparison to 85 in 2006 (Statistic Canada, 2006; Statistic Canada, 2011). However, there have been more people who identify themselves as Black living in the area in 2011 (135) than in 2006 (130), as well as Chinese (120) in 2011 versus (45) in 2006 (Statistic Canada, 2006; Statistic Canada, 2011). The Latin American population was the biggest visible minority in this area in 2006, but in 2011, the black population seemed to be the largest visible minority (Statistic Canada, 2006; Statistic Canada, 2011).
Education
editThe City of Toronto, including The Junction neighbourhood, is served by two secular school boards, and two Catholic school boards. The two secular school boards are the English first language Toronto District School Board, and the French first language Conseil scolaire Viamonde. The two Catholic school boards are the English first language Toronto Catholic District School Board, and the French first language Conseil scolaire de district catholique Centre-Sud. Elementary schools in The Junction operated by one of the four school boards include:
- Annette Street Public School - A public elementary school located at 265 Annette Street. The original east building was constructed in 1886 and the west wing was added in 1960. The school shares the facilities (including the library, gym, pool and playground) with High Park Alternative School. It also shares space with The Junction Daycare and the Toronto Parks and Recreation Department.
- High Park Alternative School - A public elementary school sharing space in the Annette Street Public School, it was founded in 1981.
- Indian Road Crescent Junior Public School - A public elementary school located at 285 Indian Road Crescent, east of Annette and Keele Streets. Indian Road Crescent serves students from Junior Kindergarten to Grade 6. The school population is approximately 330. It also shares space with Holland-Bloorview Kids Rehabilitation daycare.
- St Cecilia Catholic School - A Catholic public school located at 355 Annette Street. The present St. Cecilia Catholic School, at the corner of Annette Street and Evelyn Avenue, opened in 1914 with additions in 1918, 1954 and 1964.
- St. Clair Avenue Public School - A public elementary school near Britannia Ave constructed in 1912 and demolished in the early 1990s. Townhouses now occupy the site.
Recreation
editIn 2009, the West Toronto Railpath opened, providing a direct link for pedestrians and cyclists from The Junction to the Dundas and Lansdowne area. There are plans to eventually extend the path farther south to the Liberty Village neighbourhood. The Junction Business Improvement Area hosts a variety of public events during the year including:
- The Junction Summer Solstice Festival (June)
- Participates in the Toronto citywide Contact Photography Festival (May)
In popular culture
edit- Murdoch Mysteries, a detective series based in and around Toronto in the early 1900s, made extensive references to the Junction and its place in the temperance movement in an episode of the show's 9th season ("The Local Option"). Most of the story takes place either within the Junction or through characters based there and later interrogated in the main Toronto police buildings.[8]
References
edit- ^ Fancher, Diana (2004). The Leader and Recorder's History of the Junction. Toronto: West Toronto Junction Historical Society. p. 124. ISBN 0-9686636-1-3.
- ^ Wencer, David (25 May 2013). "Historicist: The Rise and Fall of Daniel Webster Clendenan". Torontoist. Torontoist. Retrieved 24 February 2015.
- ^ a b "Map: Boundaries of the City of West Toronto, as amalgamated with the City of Toronto in 1909". Junction History. Toronto: West Toronto Junction Historical Society. Archived from the original on 2012-07-22. Retrieved 2011-12-11.
- ^ "Old Time Trains".
- ^ "A Short History of the Junction". Junction Residents Association. Junction Residents Association. Retrieved 24 February 2015.
- ^ Micallef, Shawn (2005-06-30). "The Maltese have moved away from Little Malta, but their culture remains". Eye Weekly. Archived from the original on 2014-03-08. Retrieved 2006-12-19.
- ^ Raymond L. Kennedy. "The Junction and Its Railways". Retrieved 2009-09-27.
- ^ "Season 9 - The Local Option - Murdoch Mysteries".
- Statistics Canada, 2006; Statistics Canada, 2011
External links
editHistory
edit- The West Toronto Junction Historical Society maintains archives of historical documents, pictures and other interesting information about this neighbourhood's past.
- Photos of The Junction Tracks circa 1980s
- Historic photos from around The Junction