The loudness war (or loudness race) is a trend of increasing audio levels in recorded music, which reduces audio fidelity and—according to many critics—listener enjoyment. Increasing loudness was first reported as early as the 1940s, with respect to mastering practices for 7-inch singles.[1] The maximum peak level of analog recordings such as these is limited by varying specifications of electronic equipment along the chain from source to listener, including vinyl and Compact Cassette players. The issue garnered renewed attention starting in the 1990s with the introduction of digital signal processing capable of producing further loudness increases.
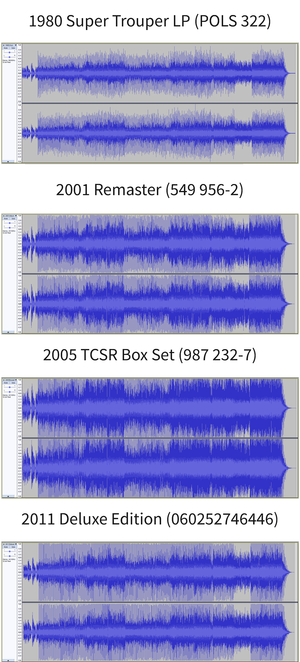
With the advent of the compact disc (CD), music is encoded to a digital format with a clearly defined maximum peak amplitude. Once the maximum amplitude of a CD is reached, loudness can be increased still further through signal processing techniques such as dynamic range compression and equalization. Engineers can apply an increasingly high ratio of compression to a recording until it more frequently peaks at the maximum amplitude. In extreme cases, efforts to increase loudness can result in clipping and other audible distortion.[2] Modern recordings that use extreme dynamic range compression and other measures to increase loudness therefore can sacrifice sound quality to loudness. The competitive escalation of loudness has led music fans and members of the musical press to refer to the affected albums as "victims of the loudness war".
History
editThe practice of focusing on loudness in audio mastering can be traced back to the introduction of the compact disc,[3] but also existed to some extent when the vinyl phonograph record was the primary released recording medium and when 7-inch singles were played on jukebox machines in clubs and bars. The so-called wall of sound (not to be confused with the Phil Spector Wall of Sound) formula preceded the loudness war, but achieved its goal using a variety of techniques, such as instrument doubling and reverberation, as well as compression.[4]
Jukeboxes became popular in the 1940s and were often set to a predetermined level by the owner, so any record that was mastered louder than the others would stand out. Similarly, starting in the 1950s, producers would request louder 7-inch singles so that songs would stand out when auditioned by program directors for radio stations.[1] In particular, many Motown records pushed the limits of how loud records could be made; according to one of their engineers, they were "notorious for cutting some of the hottest 45s in the industry."[5] In the 1960s and 1970s, compilation albums of hits by multiple different artists became popular, and if artists and producers found their song was quieter than others on the compilation, they would insist that their song be remastered to be competitive.
Because of the limitations of the vinyl format, the ability to manipulate loudness was also limited. Attempts to achieve extreme loudness could render the medium unplayable. One example was the hot master of Led Zeppelin II by mastering engineer Bob Ludwig which caused some cartridges to mistrack; the album was recalled and issued with compression lower levels.[6] Digital media such as CDs remove these restrictions and as a result, increasing loudness levels have been a more severe issue in the CD era.[7] Modern computer-based digital audio effects processing allows mastering engineers to have greater direct control over the loudness of a song: for example, a brick-wall limiter can look ahead at an upcoming signal to limit its level.[8]
1980s
editSince CDs were not the primary medium for popular music until the late 1980s, there was little motivation for competitive loudness practices then. The common practice of mastering music for CD involved matching the highest peak of a recording at, or close to, digital full scale, and referring to digital levels along the lines of more familiar analog VU meters. When using VU meters, a certain point (usually −14 dB below the disc's maximum amplitude) was used in the same way as the saturation point (signified as 0 dB) of analog recording, with several dB of the CD's recording level reserved for amplitude exceeding the saturation point (often referred to as the red zone, signified by a red bar in the meter display), because digital media cannot exceed 0 decibels relative to full scale (dBFS).[citation needed] The average RMS level of the average rock song during most of the decade was around −16.8 dBFS.[10]: 246
1990s
editBy the early 1990s, mastering engineers had learned how to optimize for the CD medium and the loudness war had not yet begun in earnest.[11] However, in the early 1990s, CDs with louder music levels began to surface, and CD levels became more and more likely to bump up to the digital limit,[note 1] resulting in recordings where the peaks on an average rock or beat-heavy pop CD hovered near 0 dBFS,[note 2] but only occasionally reached it.[citation needed]
The concept of making music releases hotter began to appeal to people within the industry, in part because of how noticeably louder some releases had become and also in part because the industry believed that customers preferred louder-sounding CDs, even though that may not have been true.[12] Engineers, musicians, and labels each developed their own ideas of how CDs could be made louder.[13] In 1994, the first digital brick-wall limiter with look-ahead (the Waves L1) was mass-produced; this feature, since then, has been commonly incorporated in digital mastering limiters and maximizers.[note 3] While the increase in CD loudness was gradual throughout the 1990s, some opted to push the format to the limit, such as on Oasis's widely popular album (What's the Story) Morning Glory?, whose RMS level averaged −8 dBFS on many of its tracks—a rare occurrence, especially in the year it was released (1995).[11] Red Hot Chili Peppers's Californication (1999) represented another milestone, with prominent clipping occurring throughout the album.[13]
2000s
editBy the early 2000s, the loudness war had become fairly widespread, especially with some remastered re-releases and greatest hits collections of older music. In 2008, loud mastering practices received mainstream media attention with the release of Metallica's Death Magnetic album. The CD version of the album has a high average loudness that pushes peaks beyond the point of digital clipping, causing distortion. This was reported by customers and music industry professionals, and covered in multiple international publications, including Rolling Stone,[14] The Wall Street Journal,[15] BBC Radio,[16] Wired,[17] and The Guardian.[18] Ted Jensen, a mastering engineer involved in the Death Magnetic recordings, criticized the approach employed during the production process.[19] When a version of the album without dynamic range compression was included in the downloadable content for the video game Guitar Hero III, copies of this version were actively sought out by those who had already purchased the official CD release. The Guitar Hero version of the album songs exhibit much higher dynamic range and less clipping than those on the CD release, as can be seen from the illustration.[20]
In late 2008, mastering engineer Bob Ludwig offered three versions of the Guns N' Roses album Chinese Democracy for approval to co-producers Axl Rose and Caram Costanzo. They selected the one with the least compression. Ludwig wrote, "I was floored when I heard they decided to go with my full dynamics version and the loudness-for-loudness-sake versions be damned." Ludwig said the "fan and press backlash against the recent heavily compressed recordings finally set the context for someone to take a stand and return to putting music and dynamics above sheer level."[21]
2010s
editIn March 2010, mastering engineer Ian Shepherd organised the first Dynamic Range Day,[22] a day of online activity intended to raise awareness of the issue and promote the idea that "Dynamic music sounds better". The day was a success and its follow-ups in the following years have built on this, gaining industry support from companies like SSL, Bowers & Wilkins, TC Electronic and Shure as well as engineers like Bob Ludwig, Guy Massey and Steve Lillywhite.[23] Shepherd cites research showing there is no connection between sales and loudness, and that people prefer more dynamic music.[4][24] He also argues that file-based loudness normalization will eventually render the war irrelevant.[25]
One of the biggest albums of 2013 was Daft Punk's Random Access Memories, with many reviews commenting on the album's great sound.[26][27] Mixing engineer Mick Guzauski deliberately chose to use less compression on the project, commenting "We never tried to make it loud and I think it sounds better for it."[28] In January 2014, the album won five Grammy Awards, including Best Engineered Album (Non-Classical).[29]
Analysis in the early 2010s suggests that the loudness trend may have peaked around 2005 and subsequently reduced, with a pronounced increase in dynamic range (both overall and minimum) for albums since 2005.[30]
In 2013, mastering engineer Bob Katz predicted that the loudness war would be over by mid-2014, claiming that mandatory use of Sound Check by Apple would lead to producers and mastering engineers to turn down the level of their songs to the standard level, or Apple will do it for them. He believed this would eventually result in producers and engineers making more dynamic masters to take account of this factor.[31][32][33]
Earache Records reissued much of its catalog as part of its Full Dynamic Range series, intended to counteract the loudness war and ensure that fans hear the music as it was intended.[34]
2020s
editBy the late 2010s/early 2020s, most major U.S. streaming services began normalizing audio by default.[35] Target loudness for normalization varies by platform:
| Service | Loudness (measured in LUFS) |
|---|---|
| Amazon Music | −13 LUFS[36] |
| Apple Music | −16 LUFS[36] |
| SoundCloud | −14 LUFS[36] |
| Spotify | −14 LUFS, −11 and −19 available in premium[37][38] |
| Tidal | −14 (default) or −18 LUFS[39][36] |
| YouTube | −14 LUFS[40] |
Measured LUFS may further vary among streaming services due to differing measurement systems and adjustment algorithms. For example, Amazon, Tidal, and YouTube do not increase the volume of tracks.[36]
Some services do not normalize audio, for example Bandcamp.[36]
Radio broadcasting
editWhen music is broadcast over radio, the station applies its own signal processing, further reducing the dynamic range of the material to closely match levels of absolute amplitude, regardless of the original recording's loudness.[41]
Competition for listeners between radio stations has contributed to a loudness war in radio broadcasting.[42] Loudness jumps between television broadcast channels and between programmes within the same channel, and between programs and intervening adverts are a frequent source of audience complaints.[43] The European Broadcasting Union has addressed this issue in the EBU PLOUD Group with publication of the EBU R 128 recommendation. In the U.S., legislators passed the CALM act, which led to enforcement of the formerly voluntary ATSC A/85 standard for loudness management.
Criticism
editIn 2007, Suhas Sreedhar published an article about the loudness war in the engineering magazine IEEE Spectrum. Sreedhar said that the greater possible dynamic range of CDs was being set aside in favor of maximizing loudness using digital technology. Sreedhar said that the over-compressed modern music was fatiguing, that it did not allow the music to breathe.[44]
The production practices associated with the loudness war have been condemned by recording industry professionals including Alan Parsons and Geoff Emerick,[45] along with mastering engineers Doug Sax, Stephen Marcussen, and Bob Katz.[5] Musician Bob Dylan has also condemned the practice, saying, "You listen to these modern records, they're atrocious, they have sound all over them. There's no definition of nothing, no vocal, no nothing, just like—static."[46][47] Music critics have complained about excessive compression. The Rick Rubin–produced albums Californication and Death Magnetic have been criticised for loudness by The Guardian; the latter was also criticised by Audioholics.[48][49] Stylus Magazine said the former suffered from so much digital clipping that "even non-audiophile consumers complained about it".[11]
Opponents have called for immediate changes in the music industry regarding the level of loudness.[47] In August 2006, Angelo Montrone, the vice-president of A&R for One Haven Music (a Sony Music company), in an open letter decrying the loudness war, claimed that mastering engineers are being forced against their will or are preemptively making releases louder to get the attention of industry heads.[7] Some bands are being petitioned by the public to re-release their music with less distortion.[45]
The nonprofit organization Turn Me Up! was created by Charles Dye, John Ralston, and Allen Wagner in 2007 with the aim of certifying albums that contain a suitable level of dynamic range[50] and encourage the sale of quieter records by placing a Turn Me Up! sticker on certified albums.[51] As of 2019[update], the group has not produced an objective method for determining what will be certified.[52]
A hearing researcher at House Ear Institute is concerned that the loudness of new albums could possibly harm listeners' hearing, particularly that of children.[51] The Journal of General Internal Medicine has published a paper suggesting increasing loudness may be a risk factor in hearing loss.[53][54]
A two-minute YouTube video addressing this issue by audio engineer Matt Mayfield[55] has been referenced by The Wall Street Journal[56] and the Chicago Tribune.[57] Pro Sound Web quoted Mayfield, "When there is no quiet, there can be no loud."[58]
The book Perfecting Sound Forever: An Aural History of Recorded Music, by Greg Milner, presents the loudness war in radio and music production as a central theme.[13] The book Mastering Audio: The Art and the Science, by Bob Katz, includes chapters about the origins of the loudness war and another suggesting methods of combating the war.[10]: 241 These chapters are based on Katz's presentation at the 107th Audio Engineering Society Convention (1999) and subsequent Audio Engineering Society Journal publication (2000).[59]
Debate
editIn September 2011, Emmanuel Deruty wrote in Sound on Sound, a recording industry magazine, that the loudness war has not led to a decrease in dynamic variability in modern music, possibly because the original digitally recorded source material of modern recordings is more dynamic than analogue material. Deruty and Tardieu analyzed the loudness range (LRA) over a 45-year span of recordings and observed that the crest factor of recorded music diminished significantly between 1985 and 2010, but the LRA remained relatively constant.[30] Deruty and Damien Tardieu criticized Sreedhar's methods in an AES paper, saying that Sreedhar had confused crest factor (peak to RMS) with dynamics in the musical sense (pianissimo to fortissimo).[60]
This analysis was also challenged by Ian Shepherd and Bob Katz on the basis that the LRA was designed for assessing loudness variation within a track while the EBU R128 peak to loudness ratio (PLR) is a measure of the peak level of a track relative to a reference loudness level and is a more helpful metric than LRA in assessing overall perceived dynamic range. PLR measurements show a trend of reduced dynamic range throughout the 1990s.[61][62]
Debate continues regarding which measurement methods are most appropriate to evaluating the loudness war.[63][64][65]
Examples of loud albums
editAlbums that have been criticized for their sound quality include:
See also
editNotes
edit- ^ Up to 2 or 4 consecutive full-scale samples was considered acceptable.
- ^ Usually in the range of −3 dB.
- ^ Look-ahead is a window of time in which the processor analyzes the audio amplitude in advance and predicts the amount of gain reduction needed to meet the requested output level (0 dBFS); this permits the limiter to react to incoming transients avoiding clipping. Since an audio buffer is needed to achieve this, look-ahead is only possible in the digital domain and introduces a small amount of latency to the output signal.
- ^ Won Grammy Award in 2006 for Best Engineered Album, Non-Classical
- ^ The 2015 remaster of this compilation does not have the same quality issues.
- ^ The Guitar Hero version and 2015 remaster of this album do not have the same quality issues.
- ^ The 2013 remix & remaster of this album does not have the same quality issues.
References
edit- ^ a b "The Loudness Wars: Why Music Sounds Worse". NPR. 31 December 2009. Retrieved 2 September 2010.
- ^ Milner, Greg (7 February 2019). "They Really Don't Make Music Like They Used To". The New York Times.
- ^ Stuart Dredge (25 November 2013). "Pop music is louder, less acoustic and more energetic than in the 1950s". The Guardian. Retrieved 25 November 2013.
- ^ a b Vickers, Earl (4 November 2010). The Loudness War: Background, Speculation and Recommendations (PDF). 129th Audio Engineering Society Convention. San Francisco: Audio Engineering Society. 8175. Retrieved 17 November 2020.
- ^ a b "The Big Squeeze: Mastering engineers debate music's loudness wars", Mix Magazine, 1 December 2005, archived from the original on 25 August 2010, retrieved 2 September 2010
- ^ Chun, Rene (4 March 2015). "Why Audiophiles Are Paying $1,000 for This Man's Vinyl". Wired (magazine). Retrieved 3 September 2024.
- ^ a b c d Joe Gross (2 October 2006), Everything Louder Than Everything Else, Austin 360, archived from the original on 19 October 2006, retrieved 24 November 2010
- ^ Mark Donahue, The Loudness War, Performer, retrieved 24 November 2010
- ^ "Sharp Dressed Man" plotted using MasVis, a freeware mastering analysis program.
- ^ a b Katz, Bob (2013). Mastering Audio: The Art and the Science (3rd ed.). Focal Press. ISBN 978-0-240-81896-2.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Southall, Nick (1 May 2006). "Imperfect Sound Forever". Stylus Magazine. Archived from the original on 12 June 2006.
- ^ Viney, Dave (December 2008). The Obsession With Compression (PDF) (Masters thesis). London College of Music. p. 54. Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 April 2016. Retrieved 24 July 2011.
there is no evidence of any significant correlation between loudness (& implied compression) and commercial success
- ^ a b c Milner, Greg (2012). Perfecting Sound Forever: An Aural History of Recorded Music. Granta Publications. ISBN 9781847086051.
- ^ Kreps, Daniel (18 September 2008). "Fans Complain After 'Death Magnetic' Sounds Better on "Guitar Hero" Than CD". Rolling Stone. Retrieved 15 March 2011.
- ^ Smith, Ethan (25 September 2008). "Even Heavy-Metal Fans Complain That Today's Music Is Too Loud!!!". The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 17 October 2008.
- ^ "'Death Magnetic' Sound Quality Controversy Focus Of BBC RADIO 4 Report". BlabberMouth.net. 10 October 2008. Archived from the original on 13 October 2008. Retrieved 17 October 2008.
- ^ Van Buskirk, Eliot (16 September 2008). "Analysis: Metallica's Death Magnetic Sounds Better in Guitar Hero". Wired. Retrieved 17 September 2008.
- ^ Michaels, Sean (1 October 2008). "Death Magnetic 'loudness war' rages on". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 17 October 2008.
- ^ Michaels, Sean (17 September 2008). "Metallica album latest victim in 'loudness war'?". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 17 September 2008.
- ^ Vinnicombe, Chris (16 September 2008). "Death Magnetic Sounds Better in Guitar Hero". MusicRadar. Retrieved 18 September 2008.
- ^ Ludwig, Bob (25 November 2008). "Guns 'N Roses: Dynamics and quality win the Loudness Wars". Loudness Wars. Gateway Mastering. Archived from the original on 31 January 2009. Retrieved 29 March 2010.
- ^ "Dynamic Range Day".
- ^ Ian Shepherd (14 March 2011). "What do Steve Lillywhite, Guy Massey and Bob Ludwig think of Dynamic Range Day?". DynamicRangeDay.com. Retrieved 17 September 2014.
- ^ Earl Vickers. "The Loudness War: Background, Speculation and Recommendations - Additional material". Retrieved 17 November 2020.
- ^ Ian Shepherd. "Lust for Level – Audio perception and the battle for great sound". Retrieved 8 February 2012.
- ^ Mark Richardson. "Random Access Memories – Pitchfork Review". Pitchfork. Retrieved 6 February 2014.
- ^ Melissa Maerz. "Random Access Memories – Music Review". Entertainment Weekly. Retrieved 6 February 2014.
- ^ Michael Gallant. "Mick Guzauski on Mixing Daft Punk". Retrieved 6 February 2014.
- ^ "Daft Punk get lucky at Grammy Awards". BBC News. 27 January 2014. Retrieved 6 February 2014.
- ^ a b Deruty, Emmanuel (September 2011). "'Dynamic Range' & The Loudness War". Sound on Sound. Retrieved 24 October 2013.
- ^ Bob Katz. "The Loudness War Has Been Won: Press Release". Retrieved 6 February 2014.
- ^ Hugh Robjohns. "The End of the Loudness War?". Sound on Sound. Retrieved 6 February 2014.
- ^ Ian Shepherd (24 October 2013). "Has The Loudness War Been Won?". Retrieved 6 February 2014.
- ^ "Earache Records Closes Chapter On "Loudness War" With Full Dynamic Range Vinyl Reissues". BraveWords. 21 February 2017. Retrieved 21 December 2022.
- ^ "Mastering audio for Soundcloud, iTunes, Spotify, Amazon Music and Youtube". Mastering The Mix. Retrieved 8 June 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f "Mastering for Streaming: Platform Loudness and Normalization Explained". Sage Audio. Retrieved 12 October 2022.
- ^ "Help - Loudness normalization - Spotify for Artists". Retrieved 12 October 2022.
- ^ Romani, Bruno (28 July 2017). "Why Spotify Lowered the Volume of Songs and Ended Hegemonic Loudness". VICE News. Retrieved 8 June 2020.
- ^ Shepherd, Ian (17 November 2016). "Tidal Loudness". Production Advice. Retrieved 5 November 2021.
Over AirPlay, normalisation will be at −18 LUFS, whereas on mobile devices and browsers, all music will be initially be played back at an integrated loudness of −14 LUFS.
- ^ Shepherd, Ian (18 September 2019). "YouTube Changes Loudness Reference to −14 LUFS". MeterPlugs. Retrieved 5 November 2021.
- ^ What Happens To My Recording When It's Played On The Radio? also available from the AES library
- ^ "Interview with Inovonics CEO Jim Wood at Radioworld". Archived from the original on 4 November 2004.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ Moerman, Jean Paul (1 May 2004), Loudness in TV Sound, Audio Engineering Society,
We started this paper with viewer complaints. At Belgian National Broadcasters VRT, located in Brussels, about 140 complaints per year were about sound. Since the implementation of the master plan there was a spectacular downfall to 3 complaints in 2003. This demonstrates again the efficiency of the master plan.
- ^ "The Future of Music". IEEE. August 2007. Archived from the original on 14 October 2007.
- ^ a b Adam, Sherwin (7 June 2007), "Why music really is getting louder", The Times, archived from the original on 11 May 2008, retrieved 12 June 2007
- ^ "Dylan rubbishes modern recordings". BBC News. 23 August 2006. Retrieved 11 July 2019.
- ^ a b Llewellyn Hinkes-Jones (25 November 2013). "The Real Reason Music's Gotten So Loud". The Atlantic.
- ^ "Metallica Death Magnetic Sounds Better on Guitar Hero III". 19 September 2008.
- ^ a b c Martin, Dan (17 September 2008). "Was the Metallica album too loud for you?". The Guardian. Retrieved 26 March 2020.
- ^ Will the loudness wars result in quieter CDs?, The Guardian, 10 January 2008
- ^ a b Emery, Chris (25 November 2007). "Audio gain in volume signals loss for listeners". The Baltimore Sun. Retrieved 2 September 2010.
- ^ "About Us". Turn Me Up!. Retrieved 2 January 2019.
- ^ Amsen, Eva (30 July 2019). "Why We Don't Turn Down The Volume When The Music Gets Louder". Forbes. Retrieved 5 August 2019.
- ^ Hourmazd, Haghbayan (24 July 2019). "Temporal Trends in the Loudness of Popular Music over Six Decades". General Internal Medicine. 35 (1): 394–395. doi:10.1007/s11606-019-05210-4. PMC 6957604. PMID 31342330.
- ^ The Loudness War on YouTube
- ^ Even Heavy-Metal Fans Complain That Today's Music Is Too Loud!!!, The Wall St. Journal, 25 September 2008
- ^ Loudness war stirs quiet revolution by audio engineers, Chicago Tribune, 4 January 2008
- ^ "Video: The Loudness Wars Exposed: "When there is no quiet, there can be no loud."". Study Hall. Pro Sound Web. 30 March 2011. Retrieved 4 April 2011.
- ^ Integrated Approach to Metering, Monitoring and Leveling Practices (article text) accessed 24 February 2019.
- ^ Emmanuel Deruty, Damien Tardieu (January 2014). "About Dynamic Processing in Mainstream Music". Journal of the Audio Engineering Society. 62 (1/2): 42–55. doi:10.17743/jaes.2014.0001.
- ^ Ian Shepherd (18 August 2011). "Why the Loudness War hasn't reduced 'Loudness Range'". Retrieved 6 February 2014.
- ^ Jason Victor Serinus (23 November 2012). "Winning the Loudness Wars". Stereophile. Retrieved 6 February 2014.
- ^ Esben Skovenborg (April 2012). "Loudness Range (LRA) – Design and Evaluation". AES 132nd Convention. Retrieved 25 October 2014.
- ^ Jon Boley, Michael Lester and Christopher Danner (November 2010). "Measuring Dynamics: Comparing and Contrasting Algorithms for the Computation of Dynamic Range". AES 129th Convention. Retrieved 25 October 2014.
- ^ Jens Hjortkjær, Mads Walther-Hansen (January 2014). "Perceptual Effects of Dynamic Range Compression in Popular Music Recordings". Journal of the Audio Engineering Society. 62 (1/2): 42–55. Retrieved 6 June 2014.
- ^ Ratliff, Ben (7 June 2013). "Black Sabbath's New Album, '13'". The New York Times.
- ^ Doran, John (27 September 2008). "Review The Cure 4:13 Dream". The Quietus. Archived from the original on 15 July 2012. Retrieved 30 June 2011.
- ^ a b Michaels, Sean (15 July 2010). "EMI defends Duran Duran remasters". The Guardian. Retrieved 25 July 2020.
- ^ a b Levine, Robert. "The Death of High Fidelity: In the age of MP3s, sound quality is worse than ever". Rolling Stone. Archived from the original on 1 July 2008. Retrieved 1 December 2010.
- ^ "Metallica Face Criticism Over Sound Quality of 'Death Magnetic'". Rolling Stone. Archived from the original on 2 October 2008.
- ^ Smith, Ethan. "Even Heavy-Metal Fans Complain That Today's Music Is Too Loud!!!". The Wall Street Journal.
- ^ "Miranda Lambert - Revolution". Country Weekly. 19 October 2009. Archived from the original on 30 October 2009.
- ^ Anderson, Tim (10 January 2008). "Will the loudness wars result in quieter CDs?". The Guardian.
- ^ a b c Anderson, Tim (18 January 2007). "How CDs are remastering the art of noise." Retrieved on 12 March 2012.
- ^ Matt Medved. "Taylor Swift's '1989' Is Louder Than AC/DC's 'Back in Black' – Here's Why". Billboard. Retrieved 29 March 2018.
Further reading
edit- Thomas Lund (April 2007), Level and distortion in digital broadcasting (PDF), EBU
- Florian Camerer (2010), On the way to Loudness Nirvana – Audio levelling with EBU R 128 (PDF), EBU
- Wickham, Chris (26 July 2012). "Pop music too loud and all sounds the same: official". Reuters.
- Serrà, J; Corral, A; Boguñá, M; Haro, M; Arcos, JL (26 July 2012). "Measuring the Evolution of Contemporary Western Popular Music". Scientific Reports. 2: 521. arXiv:1205.5651. Bibcode:2012NatSR...2E.521S. doi:10.1038/srep00521. PMC 3405292. PMID 22837813.
- Devine, K. (2013). "Imperfect sound forever: Loudness wars, listening formations and the history of sound reproduction" (PDF). Popular Music. 32 (2): 159–176. doi:10.1017/S0261143013000032. hdl:10852/59847. S2CID 162636724.
- Robert Toft (2023), Song Dynamics, the Chiaroscuro of Loudness in Selected Pop/Rock Recordings, 1971-2021, Popular Music Forum, Western University