Roluperidone (former developmental code names MIN-101, CYR-101, MT-210) is a 5-HT2A and σ2 receptor antagonist under development by Minerva Neurosciences for the treatment of schizophrenia.[1][2][3][4] One of its metabolites also has some affinity for the H1 receptor.[2] Pre-clinical findings provide evidence of the effect of roluperidone on brain-derived neurotrophic factor ("BDNF"), which has been associated with neurogenesis, neuroplasticity, neuroprotection, synapse regulation, learning and memory.[5]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | MIN-101; CYR-101; MT-210 |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
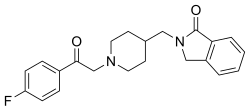
| Formula | C22H23FN2O2 |
| Molar mass | 366.436 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
As of May 2018, the drug was in phase III clinical trials.[6] In May 2020, the shares of Minerva Neurosciences plummeted 67% after the trial "failed to meet its primary endpoint of reduction in negative symptoms, and key secondary endpoints of improvement in personal and social performance measurements."[7] However, in August 2022 Minerva submitted a New Drug Application (NDA) to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the approval of roluperidone for the treatment of schizophrenia.[8] The NDA submission in 2022 followed successful completion of a phase III clinical trial which was published in early 2022. Minerva believed that the findings of this second trial supported the claim that the drug was an effective agent for the treatment of negative symptoms in schizophrenia. However, in October 2022, FDA sent Minerva a refusal to file letter pertaining to the New Drug Application for roluperidone for treating negative symptoms in schizophrenia patients. [9]
Chemistry
editSynthesis
editThe Boc protection of 4-aminomethylpiperidine [7144-05-0] (1) gives tert-Butyl 4-aminomethylpiperidine-1-carboxylate hydrochloride [359629-16-6] (2). The free-radical halogenation of ethyl o-toluate [87-24-1] (3) led to ethyl 2-(bromomethyl)benzoate [7115-91-5] (4). The reaction between the two intermediates led to 2-[(1-tert-Butoxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)methyl]isoindolin-1-one [359629-19-9] (5). Deprotection yielded 2-(Piperidin-4-ylmethyl)-3H-isoindol-1-one;hydrochloride (6). Alkylation of the secondary nitrogen with 2-chloro-4'-fluoroacetophenone [700-35-6] (7) completed the synthesis of Roluperidone (8).
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ Mestre TA, Zurowski M, Fox SH (April 2013). "5-Hydroxytryptamine 2A receptor antagonists as potential treatment for psychiatric disorders". Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs. 22 (4): 411–21. doi:10.1517/13543784.2013.769957. PMID 23409724. S2CID 36268341.
- ^ a b Ebdrup BH, Rasmussen H, Arnt J, Glenthøj B (September 2011). "Serotonin 2A receptor antagonists for treatment of schizophrenia". Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs. 20 (9): 1211–23. doi:10.1517/13543784.2011.601738. PMID 21740279. S2CID 438422.
- ^ Köster LS, Carbon M, Correll CU (December 2014). "Emerging drugs for schizophrenia: an update". Expert Opinion on Emerging Drugs. 19 (4): 511–31. doi:10.1517/14728214.2014.958148. PMID 25234340. S2CID 42729570.
- ^ "Drug Development in Schizophrenia: Summary and Table". Pharmaceutical Medicine. 28 (5): 265–271. 2014. doi:10.1007/s40290-014-0070-6. ISSN 1178-2595. S2CID 256364393.
- ^ "Roluperidone (MIN-101) • Minerva Neurosciences".
- ^ "Roluperidone - Minerva Neurosciences". Adis Insight. Springer Nature Switzerland AG.
- ^ Kilgore T. "Minerva Neurosciences' stock plummets after schizophrenia treatment disappoints in phase 3 study". MarketWatch. Retrieved 2021-03-21.
- ^ "Minerva Neurosciences Submits New Drug Application to FDA for Roluperidone for the Treatment of Negative Symptoms in Patients with Schizophrenia". 22 August 2022.
- ^ "Minerva Neurosciences Receives Refusal to File Letter from FDA for its New Drug Application for Roluperidone for the Treatment of Negative Symptoms in Schizophrenia".
- ^ Haruko Yamabe, et al. U.S. patent 7,166,617 (2003 to Mitsubishi Pharma Corp).
- ^ Haruko Yamabe, et al. U.S. patent 20,030,212,094 (2003 to Mitsubishi Pharma Corp).
- ^ Prugh, J. D., Birchenough, L. A., Egbertson, M. S. (August 1992). "A Simple Method of Protecting a Secondary Amine with Tert Butyloxycarbonyl (Boc) in the Presence of a Primary Amine". Synthetic Communications. 22 (16): 2357–2360. doi:10.1080/00397919208019091.