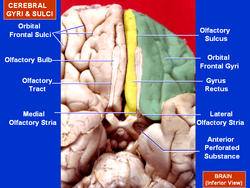
The inferior or orbital surface of the frontal lobe is concave, and rests on the orbital plate of the frontal bone. It is divided into four orbital gyri by a well-marked H-shaped orbital sulcus. These are named, from their position, the medial, anterior, lateral, and posterior, orbital gyri. The medial orbital gyrus presents a well-marked antero-posterior sulcus, the olfactory sulcus, for the olfactory tract; the portion medial to this is named the straight gyrus, and is continuous with the superior frontal gyrus on the medial surface.
| Orbital gyri | |
|---|---|
 Human brain bottom view. Orbital gyri shown in green. | |
 Orbital surface of left frontal lobe. Orbital gyri shown in orange. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | gyri orbitales |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_1223 |
| TA98 | A14.1.09.216 |
| TA2 | 5464 |
| FMA | 72020 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
Function
editBailey and Bremer reported that stimulation to the central end of the vagus nerve caused electrical activity in the inferior orbital surface (http://brain.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/pdf_extract/75/2/244)
Additional images
edit-
Orbital gyri shown in red.
-
Orbital surface of brain.
-
Close up of orbital gyri.
-
Human brain bottom view. Orbital gyri shown in red.
-
Human brain bottom view. Orbital gyri not labelled, but seen at top.
References
editThis article incorporates text in the public domain from page 822 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
edit