The genus Nimbacinus contains two species of carnivorous, quadrupedal marsupials in Australia both of which are extinct:
- Nimbacinus dicksoni Muirhead & Archer, 1990[1]
- Nimbacinus peterbridgei Churchill, Archer & Hand, 2024[3]
| Nimbacinus Temporal range: Late Oligocene to Middle Miocene
| |
|---|---|
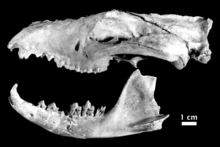
| |
| Skull and mandible of N. dicksoni | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Infraclass: | Marsupialia |
| Order: | Dasyuromorphia |
| Family: | †Thylacinidae |
| Genus: | †Nimbacinus Muirhead & Archer, 1990 |
| Type species | |
| Nimbacinus dicksoni | |
| Other species | |
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |

Like all thylacinids, Nimbacinus dicksoni was a dog-like marsupial, though its smaller size makes its appearance more comparable to that of a fox. Unlike its relatives, its jaws were likely strong enough for it to take down prey larger than itself.[4]
The name of the genus combines Nimba and cinus, derived from a word meaning "little" in the Wanyi language, indigenous peoples associated with the Riversleigh fossil site, and the Ancient Greek word kynos, meaning dog.[1]
Taxonomy
editThe description of N. richi was published in 2000 by researchers Peter F. Murray, working at the Museum of Central Australia and Dirk Megirian of the Northern Territory Museum.[5] The holotype is fossilised material excavated at "Top Site" at the Bullock Creek fossil area, a partial left dentary with a premolar and several molars that is dated to the mid-Miocene. The specific epithet commemorates Tom Rich, who introduced the authors to the site of their discovery.[5]
References
edit- ^ a b c Muirhead, J.; Archer, M. (1990). "Nimbacinus dicksoni, a plesiomorphic thylacine (Marsupialia: Thylacinidae) from Tertiary deposits of Queensland and the Northern Territory". Memoirs of the Queensland Museum. 28: 203–221.
- ^ Rovinsky, Douglass S.; Evans, Alistair R.; Adams, Justin W. (2019-09-02). "The pre-Pleistocene fossil thylacinids (Dasyuromorphia: Thylacinidae) and the evolutionary context of the modern thylacine". PeerJ. 7: e7457. doi:10.7717/peerj.7457. ISSN 2167-8359. PMC 6727838.
- ^ Churchill, T. J.; Archer, M.; Hand, S. J. (2024). "Three new thylacinids (Marsupialia, Thylacinidae) from late Oligocene deposits of the Riversleigh World Heritage Area, northwestern Queensland". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. doi:10.1080/02724634.2024.2384595.
- ^ Attard, Marie R. G.; Parr, William C. H.; Wilson, Laura A. B.; Archer, Michael; Hand, Suzanne J.; Rogers, Tracey L.; Wroe, Stephen (2014). "Virtual Reconstruction and Prey Size Preference in the Mid Cenozoic Thylacinid, Nimbacinus dicksoni (Thylacinidae, Marsupialia)". PLOS ONE. 9 (4): e93088. Bibcode:2014PLoSO...993088A. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0093088. PMC 3981708. PMID 24718109.
- ^ a b Murray, P.; Megirian, D. (2000). "Two New Genera and Three New Species of Thylacinidae (Marsupialia) from the Miocene of the Northern Territory, Australia". The Beagle: Occasional Papers of the Northern Territory Museum of Arts and Sciences. 16: 145–162.