The Northern Lakes and Forests are an ecoregion in northern Minnesota,[1] northern Wisconsin,[2] and northern Michigan[3] in the United States. It is a Level III ecoregion in the United States Environmental Protection Agency's (EPA's) classification system, where it is designated as ecoregion number 50. The ecoregion is characterized by coniferous and northern hardwoods forests, morainal hills, large lake basins, and broad areas of sandy outwash plains, with numerous lakes and wetlands. The Northern Lakes and Forests are less well-suited to agriculture than ecoregions to the south, owing to shorter growing seasons, lower temperatures, and soils formed mainly from nutrient-poor sandy and loamy glacial drift material.[4][5]
| Northern Lakes and Forests | |
|---|---|
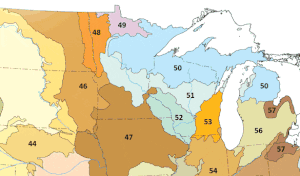 Map of ecoregions of the Upper Midwest, with Northern Lakes and Forests shown as number 50 | |
| Ecology | |
| Realm | Nearctic |
| Geography | |
| Country | United States |
| States | |
Level IV ecoregions
editFollowing is a list of smaller Level IV ecoregions within the Northern Lakes and Forests ecoregion, as defined by the EPA.[1][2][3]
| Number | Ecoregion name | Michigan | Minnesota | Wisconsin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50a | Lake Superior Clay Plain | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| 50b | Minnesota/Wisconsin Upland Till Plain | ✔ | ✔ | |
| 50c | St. Croix Pine Barrens | ✔ | ||
| 50d | Superior Mineral Ranges/
Ontonagon Lobe Moraines and Gogebic Iron Range |
✔ | ✔ | |
| 50e | Chequamegon Moraine and Outwash Plain | ✔ | ||
| 50f | Blue Hills | ✔ | ||
| 50g | Chippewa Lobe Rocky Ground Moraines | ✔ | ||
| 50h | Perkinstown End Moraine | ✔ | ||
| 50i | Northern Wisconsin Highlands Lakes Country | ✔ | ✔ | |
| 50j | Brule and Paint River Drumlins | ✔ | ✔ | |
| 50k | Wisconsin/Michigan Pine and Oak Barrens | ✔ | ✔ | |
| 50l | Menominee Drumlins and Ground Moraine | ✔ | ✔ | |
| 50m | Mesabi Range | ✔ | ||
| 50n | Boundary Lakes and Hills | ✔ | ||
| 50o | Glacial Lakes Upham and Aitkin | ✔ | ||
| 50p | Toimi Drumlins | ✔ | ||
| 50q | Itasca and St. Louis Moraines | ✔ | ||
| 50r | Chippewa Plains | ✔ | ||
| 50s | Nashwauk/Marcell Moraines and Uplands | ✔ | ||
| 50t | North Shore Highlands | ✔ | ||
| 50u | Keweenaw-Baraga Moraines | ✔ | ||
| 50v | Winegar Dead Ice Moraine | ✔ | ||
| 50w | Michigamme Highland | ✔ | ||
| 50x | Grand Marais Lakeshore | ✔ | ||
| 50y | Seney-Tahquamenon Sand Plain | ✔ | ||
| 50z | Rudyard Clay Plain | ✔ | ||
| 50aa | Menominee-Drummond Lakeshore | ✔ | ||
| 50ab | Cheboygan Lake Plain | ✔ | ||
| 50ac | Onaway Moraines | ✔ | ||
| 50ad | Vanderbilt Moraines | ✔ | ||
| 50ae | Mio Plateau | ✔ | ||
| 50af | Cadillac Hummocky Moraines | ✔ | ||
| 50ag | Newaygo Barrens | ✔ | ||
| 50ah | Tawas Lake Plain | ✔ |
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ a b "Minnesota level III and IV ecoregions" (PDF). United States Environmental Protection Agency. 2015. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2018-04-21. Retrieved 2018-04-21.
- ^ a b "Level III and IV ecoregions of Wisconsin" (PDF). United States Environmental Protection Agency. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2018-04-21. Retrieved 2018-04-21.
- ^ a b "Level III and IV ecoregions of Michigan" (PDF). United States Environmental Protection Agency. June 2010. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2018-04-21. Retrieved 2018-04-21.
- ^ "Michigan level III and IV ecoregion descriptions/mapping issues" (PDF). United States Environmental Protection Agency. 2007-12-27. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2018-04-21. Retrieved 2018-04-21.
- ^ Wilson, Tamara; L. Ryan, Christy (2015-12-11). Northern Lakes and Forests Ecoregion. pp. 33–42.