Norwich City Council is the local authority for Norwich, a non-metropolitan district with city status in Norfolk, England. It consists of 39 councillors, elected to represent 13 wards, each with three councillors. It forms the lower tier of local government in Norwich, responsible for local services such as housing, planning, leisure and tourism.
Norwich City Council | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| Type | |
| Type | |
| Leadership | |
Louise Rawsthorne since 1 May 2023[2] | |
| Structure | |
| Seats | 39 councillors[3] |
 | |
Political groups |
|
| Elections | |
| First past the post | |
Last election | 2 May 2024 |
Next election | 7 May 2026 |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| City Hall, St Peter's Street, Norwich, NR2 1NH | |
| Website | |
| www | |
History
editNorwich was an ancient borough and held city status from 1094 when the Bishop of the East Angles moved the seat of the diocese to Norwich.[4] The city was governed by a corporation, also known as the city council. In 1404 the city was made a county corporate with its own sheriffs and quarter sessions, making it administratively separate from the surrounding county of Norfolk.[5]
The city was reformed in 1836 to become a municipal borough under the Municipal Corporations Act 1835. When elected county councils were established in 1889 under the Local Government Act 1888, Norwich was considered large enough to provide its own county-level services, and so it was made a county borough, independent from Norfolk County Council.[6] In 1910 the city council was given the right to appoint a lord mayor.[7]
The city was reconstituted as a non-metropolitan district on 1 April 1974 under the Local Government Act 1972, becoming a lower-tier district authority with Norfolk County Council providing county-level functions to the city for the first time. The city kept the same outer boundaries, but did gain an exclave from Norfolk containing the Shirehall.[8][9] Norwich kept its borough and city statuses and its lord mayoralty.[10][11]
In 2010 it was proposed to convert Norwich to a unitary authority, making it independent from Norfolk County Council. A structural change order was due to take effect on 1 April 2011. Following the 2010 general election, the coalition government came into office and passed the Local Government Act 2010 cancelling the changes.[12]
During November 2023, four Norwich Labour councillors and two Norfolk Labour councillors resigned from the Labour Party and became independent councillors. Four of the councillors issued a statement saying "[W]e no longer consider the current national and local Labour Party matches the overriding principles that guide our work as Town Close councillors".[13][14]
Governance
editNorwich City Council provides district-level services, including housing, town planning, leisure and tourism. County-level services, including schools, social services and libraries and transport, are provided by Norfolk County Council.[15] There are no civil parishes in Norwich, which has been an unparished area since the 1974 reforms.[16]
The city's territory includes part of The Broads, where town planning is the responsibility of the Broads Authority. The city council appoints one of its councillors to sit on that authority.[17]
Political control
editThe council was under Labour majority control from 2012 until November 2023, when four Labour councillors resigned the whip and the council fell under no overall control.[18]
Political control of the council since the 1974 reforms took effect has been as follows:[19][20]
| Party in control | Years | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour | 1974–2002 | |
| Liberal Democrats | 2002–2004 | |
| No overall control | 2004–2012 | |
| Labour | 2012–2023 | |
| No overall control | 2023–present | |
Leadership
editThe role of Lord Mayor of Norwich is largely ceremonial, and is generally held by a different person each year. Political leadership is provided instead by the leader of the council. The leaders since 1974 have been:[21]
| Councillor | Party | From | To | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arthur South | Labour | 1974 | 1978 | |
| Len Stevenson[22] | Labour | 1978 | 1983 | |
| Patricia Hollis[23] | Labour | 1983 | 1988 | |
| Janet Sillett[24] | Labour | 1988 | 1993 | |
| Alan Waters[25] | Labour | 1993 | 1998 | |
| Nick Williams[26] | Labour | 1998 | 2002 | |
| Ian Couzens[27] | Liberal Democrats | 2002 | 2006 | |
| Steve Morphew | Labour | 2006 | 2011 | |
| Brenda Arthur[28] | Labour | 17 May 2011 | 26 May 2015 | |
| Alan Waters | Labour | 26 May 2015 | 7 May 2023 | |
| Mike Stonard | Labour | 23 May 2023 | ||
Composition
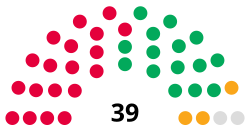
editFollowing the 2024 election, the composition of the council was:[29]
| Party | Councillors | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour | 19 | |
| Green | 15 | |
| Liberal Democrats | 3 | |
| Independent | 2 | |
| Total | 39 | |
The next election is due in 2026.
Premises
editThe council is based at City Hall on St Peter's Street, overlooking Norwich Market in the city centre. The building was completed in 1938 and is a Grade II* listed building.[30]
Elections
editSince the last boundary changes in 2019 the council has comprised 39 councillors representing 13 wards, with each ward electing three councillors. Elections are held three years out of every four, with a third of the council (one councillor for each ward) elected each time for a four-year term. Norfolk County Council elections are held in the fourth year of the cycle when there are no city council elections.[31]
Coat of arms
editThe city council's arms consist of a red shield featuring a silver-domed castle above a royal lion.[32][33][34] The blazon of the arms is:
Gules, a castle triple-towered and domed Argent; in base a lion passant guardant Or.[32][34]
The arms appeared on a 15th-century seal and were confirmed during a heraldic visitation in 1562 by William Harvey, Clarenceux King of Arms. According to Wilfrid Scott-Giles, the royal lion was said to have been granted by Edward III.[33] By the 19th century the city corporation had added supporters to the arms—two angels—which were surmounted by a fur cap. These apparently originated in a carving of about 1534 outside Norwich Guildhall. A. C. Fox-Davies noted that "whether or not these figures were then intended for heraldic supporters is a matter for dispute. At any rate there is no official authority for their use".[34] Following the abolition of the county borough of Norwich in 1974, an Order in Council transferred the ancient coat of arms (the shield alone) to the newly created city council.[35] The city council has also received the grant of an heraldic badge, depicting the seal of 1404 encircled by the Lord Mayor's chain.[36]
Norwich City Services
edit| Company type | Limited |
|---|---|
| Industry | Municipal services |
| Founded | 9 June 2020 |
| Founder | Norwich City Council |
| Headquarters | , United Kingdom |
Area served | Norwich city and surrounding areas |
| Services | Waste management, street cleaning, pest control, grounds maintenance |
| Owner | Norwich City Council |
| Website | Official website |
Norwich City Services Limited also known as NCSL or Norwich Services Ltd is a municipal services company wholly owned by the council. Founded on 9 June 2020, the company aims to provide essential services to the residents and businesses of Norwich, England.[37] The company offers a range of services beyond those provided on behalf of the City council, including environmental, cleaning, and grounds maintenance services for private businesses, organizations, and schools. Prices are available upon request. The current services available to book include:
References
edit- ^ Storey, Eleanor (22 May 2024). "New Lord Mayor and Sheriff of Norwich named for 2024". Eastern Daily Press. Retrieved 14 July 2024.
- ^ "New permanent chief executive for Norwich City Council confirmed". Norwich City Council. Retrieved 30 June 2023.
- ^ "Norwich Councillors". Open Council Data UK. Retrieved 18 July 2021.
- ^ "General Synod Dioceses Commission – Background and History". Church of England. Archived (PDF) from the original on 7 June 2012. Retrieved 3 March 2013.
- ^ Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 19 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 819–820.
- ^ "Norwich Municipal Borough / County Borough". A Vision of Britain through Time. GB Historical GIS / University of Portsmouth. Retrieved 30 June 2023.
- ^ The King and Norwich, The Times, 7 February 1910
- ^ "The English Non-metropolitan Districts (Definition) Order 1972", legislation.gov.uk, The National Archives, SI 1972/2039, retrieved 28 June 2023
- ^ "1:25000 Administrative Area map 1947". National Library of Scotland. Ordnance Survey. Retrieved 30 June 2023.
- ^ "District Councils and Boroughs". Parliamentary Debates (Hansard). 28 March 1974. Retrieved 4 December 2021.
- ^ "No. 46255". The London Gazette. 4 April 1974. p. 4400.
- ^ "The Coalition: our programme for government" (PDF). HM Government, United Kingdom. 20 May 2010. Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 June 2011. Retrieved 24 May 2010.
- ^ "Labour loses control of Norwich City Council after four resign". BBC News. 28 November 2023. Retrieved 30 November 2023.
- ^ Sinclair, Andrew (29 November 2023). "Sixth Norwich Labour councillor resigns in party row". BBC News. Retrieved 29 November 2023.
- ^ Local government in England and Wales: A Guide to the New System. London: HMSO. 1974. p. 72. ISBN 0-11-750847-0.
- ^ "Election maps". Ordnance Survey. Retrieved 30 June 2023.
- ^ "Who we are". Broads Authority. Retrieved 6 December 2023.
- ^ George Thompson. "With four members gone from Norwich City Council, Labour no longer holds a majority. Before this evening Labour held 23 seats on the city council, the Greens 13 and the Lib Dems three. The make-up is now Labour 19, Greens 13, Independents four, and Lib Dems three". Twitter/X. Retrieved 28 November 2023.
- ^ "Compositions calculator". The Elections Centre. 4 March 2016. Retrieved 1 June 2023.
- ^ "Norwich". BBC News Online. 19 April 2008. Retrieved 17 September 2009.
- ^ "Council minutes". Norwich City Council. Retrieved 24 June 2022.
- ^ "Len Stevenson". Eastern Daily Press. 22 March 2007. Retrieved 25 June 2022.
- ^ Cope, Lauren (15 October 2018). "'Champion of Norwich' and Labour peer dies aged 77". Eastern Daily Press. Retrieved 25 June 2022.
- ^ Greenaway, John; Grantham, Andrew (2000). "Transport Policy Paradigms at the Local Level: The Norwich Inner Ring Road". Public Administration. 78 (4). Retrieved 25 June 2022.
Interviews... Sillett, Janet, Labour Leader of Norwich City Council, 1988-93
- ^ Grimmer, Dan (12 May 2015). "Labour leadership battle at Norwich City Council ends in triumph for Alan Waters". Eastern Daily Press. Retrieved 25 June 2022.
- ^ Hetherington, Peter (30 April 2002). "Socialist stronghold faces Lib Dem assault". The Guardian. Retrieved 25 June 2022.
- ^ "City Lib Dem leader steps down". Eastern Daily Press. 5 September 2006. Retrieved 25 June 2022.
- ^ "Norwich City Council appoints its new leader". BBC News. 17 May 2011. Retrieved 25 June 2022.
- ^ "Result of 2024 local elections in Norwich". Norwich City Council. Retrieved 5 May 2024.
- ^ Historic England. "City Hall including Police Station (1210484)". National Heritage List for England. Retrieved 17 February 2017.
- ^ "The Norwich (Electoral Changes) Order 2019", legislation.gov.uk, The National Archives, SI 2019/199, retrieved 30 June 2023
- ^ a b Briggs, Geoffrey (1971). Civic and Corporate Heraldry: A Dictionary of Impersonal Arms of England, Wales and N. Ireland. London: Heraldry Today. pp. 8, 287. ISBN 0-900455-21-7.
- ^ a b Scott-Giles, C Wilfrid (1953). Civic Heraldry of England and Wales, 2nd edition. London: J M Dent & Sons. p. 290.
- ^ a b c Fox-Davies, A C (1915). The Book of Public Arms, 2nd edition. London: T C & E C Jack. p. 564.
- ^ The Local Authorities (Armorial Bearings) Order 1974 (S.I. 1974 No. 869)
- ^ Robert Young. "East Anglia and Essex Area". Civic Heraldry of England and Wales. Archived from the original on 28 August 2009. Retrieved 13 February 2010.
- ^ "Norwich City Services Ltd (NCSL)".
- ^ Council, Norwich City. "Pest control | Norwich City Council". www.norwich.gov.uk. Retrieved 21 December 2023.
- ^ Council, Norwich City. "Tractor services | Norwich City Council". www.norwich.gov.uk. Retrieved 21 December 2023.
- ^ Council, Norwich City. "Cleaning | Norwich City Council". www.norwich.gov.uk. Retrieved 21 December 2023.