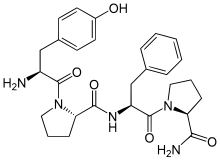
Morphiceptin is a tetrapeptide (Tyr-Pro-Phe-Pro-NH2) that is a selective μ-opioid receptor agonist. It is derived from β-casomorphin and has over 1,000 times selectivity for μ- over δ-opioid receptors. When injected intracerebroventricularly (into the ventricular system of the brain), morphiceptin had an analgesic ED50 of 1.7 nmol per animal. The analgesic effects of morphiceptin were reversed by naloxone, meaning that the analgesic effect is mediated by the μ-opioid receptor.[2]
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2S)-1-[(2S)-2-amino-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoyl]-N-[(2S)-1-[(2S)-2-carbamoylpyrrolidin-1-yl]-1-oxo-3-phenylpropan-2-yl]pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide[1]
| |
| Other names
Tyr-Pro-Phe-Pro-NH2, PLO17
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C28H35N5O5 | |
| Molar mass | 521.6 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Morphiceptin is the (1S,2S,3S,4S)-form whereas deproceptin is the (1S,2S,3S,4R)-form [84799-23-5].
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ "Morphiceptin". ChemBase. Archived from the original on 15 March 2012. Retrieved 1 August 2011.
- ^ Chang, K (3 May 1982). "Analgesic activity of intracerebroventricular administration of morphiceptin and β-casomorphins: Correlation with the morphine (μ) receptor binding affinity". Life Sciences. 30 (18): 1547–1551. doi:10.1016/0024-3205(82)90242-9. PMID 6281604.