The Pampas fox (Lycalopex gymnocercus), also known as grey pampean fox, Pampas zorro, Azara's fox, or Azara's zorro (in Guaraní also called aguará chaí, anglicized as aguarachay, in Portuguese also called graxaim ([ɡɾaʃaˈĩ]),[4] is a medium-sized zorro, or "false" fox, native to the South American Pampas. Azara in some of its alternative common names is a reference to Spanish naturalist Félix de Azara.
| Pampas fox[1] | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Family: | Canidae |
| Genus: | Lycalopex |
| Species: | L. gymnocercus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Lycalopex gymnocercus (G. Fischer, 1814)
| |
| Subspecies | |
| |
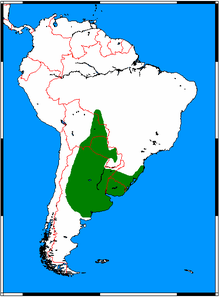
| |
| Natural range shown in green | |
Description
editThe Pampas fox resembles the culpeo or Andean fox in appearance and size, but has a proportionately wider snout, reddish fur on the head and neck, and a black mark on the muzzle. Its short, dense fur is grey over most of the body, with a black line running down the back and onto the tail, and pale, almost white, underparts. The ears are triangular, broad, and relatively large, and are reddish on the outer surface and white on the inner surface. The inner surfaces of the legs are similar in color to the underparts, while the outer surface is reddish on the fore limbs, and grey on the hind limbs; the lower hind limb also bears a distinctive black spot. Adults range from 51 to 80 cm (20 to 31 in) in body length, and weigh 2.4 to 8.0 kg (5.3 to 17.6 lb); males are about 10% heavier than females.[5]
In the northern part of its range, the pampas fox is more richly colored than in the southern part.[6]
Distribution and habitat
editThe Pampas fox can be found primarily in northern and central Argentina, Uruguay, eastern Bolivia, Paraguay, and southern Brazil. It prefers open pampas habitats, often close to agricultural land, but can also be found in montane or chaco forest, dry scrubland, and wetland habitats. It is most common below 1,000 m (3,300 ft) elevation, but can inhabit puna grasslands up to 3,500 m (11,500 ft).[4]
Five subspecies of L. gymnocercus are generally recognized as of 2005:[update][7]
- L. g. antiquus (Ameghino, 1889:298); — Found in the Pampas grasslands, Monte shrublands and Espinal open woodlands of central Argentina, from Córdoba and San Luis Provinces to the Río Negro and the Atlantic coast.
- L. g. domeykoanus (Philippi, 1901:168); Found in Copiapó Province, Chile.
- L. g. gracilis (Burmeister, 1861:406); Found in the Pampas surrounding Mendoza, Argentina.
- L. g. gymnocercus (Fischer, 1814:178); Found in the subtropical grasslands of northeastern Argentina, Uruguay, Paraguay, Bolivia and eastern Brazil.
- L. g. maullinicus (Philippi, 1903:158); Found in Llanquihue Province, Chile, east of Llanquihue Lake
An earlier (1982) taxonomical revision recognized only L. g. antiquus and L. g. gymnocercus, along with the otherwise unaccepted subspecies L. g. lordi (Massoia, 1982:149), which is restricted to the Chaco-Yungas Mountain Tropical Forest in Salta and Jujuy Provinces. That revision classified L. g. domeykoanus, L. g. gracilis, and L. g. maullinicus as subspecies of L. griseus, in part due to their falling outside the known present range of L. gymnocercus.[8][9]
Fossils of this species are known from the late Pliocene to early Pleistocene in Argentina.[10]
Local names
editIn the Spanish-speaking areas of its habitat, the Pampas fox is known by the common names of zorro de las pampas or zorro gris pampeano. In Portuguese-speaking Brazil, it is called by the common names of graxaim or sorro.
Behavior and diet
editThe Pampas foxes mostly live a solitary life, but come together as monogamous pairs in the breeding season to raise their young. They are mainly nocturnal, becoming active at dusk, although may also be active during the day. They den in any available cavity, including caves, hollow trees, and the burrows of viscachas or armadillos.[5] Even when raising young together, adult foxes generally hunt alone, marking their territory by defecating at specific latrine sites.[11] Although considerable variation is seen, the home range of a typical Pampas fox has been estimated to be around 260 hectares (640 acres).[5]
Pampas foxes are more omnivorous than most other canids, and have a varied and opportunistic diet. Their primary prey consists of birds, rodents, hares, fruit, carrion, and insects, although they also eat lizards, armadillos, snails and other invertebrates, lambs, and the eggs of ground-nesting birds.[5] Their primary predators are pumas, domesticated dogs, and anacondas, most notably the yellow anaconda.[4][12]
Reproduction
editPampas foxes breed in the early spring, with the female coming into heat just once each year. After a gestation period of 55 to 60 days, the mother gives birth to a litter of up to eight kits. The young are born between September and December, and are weaned around two months of age. Females reach sexual maturity in their first year, and animals have lived for up to 14 years in captivity.[5]
Pups remain in dens until at least the age of 3 months,[5] when they start hunting with parents. The males bring food to their females who stay at the den with kits.[9]
Threats
editThe main threats to the Pampas fox comes from humans hunting them for their fur[13] or to prevent them from attacking livestock; they may be affected by the loss of their natural habitat.[4] However, because they remain common in most areas where they have been studied, the Pampas fox is not presently considered a threatened species.[2]
Hybridisation with dog
editCrossings between canids of different genera are extremely rare. In 2021, a female canid with unusual phenotypic characteristics was found in Vacaria, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. DNA analysis indicates that the canid was a hybrid between a Pampas fox and a domestic dog.[14] Dubbed a 'Dogxim' or 'graxorra',[15] this finding is the first documented case of hybridisation detected between these two species.[14]
References
edit- ^ Wozencraft, W. C. (2005). "Order Carnivora". In Wilson, D. E.; Reeder, D. M. (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.
- ^ a b Lucherini, Mauro (2016). "Lycalopex gymnocercus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T6928A85371194. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T6928A85371194.en. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- ^ "Appendices | CITES". cites.org. Retrieved 2022-01-14.
- ^ a b c d Lucherini, Mauro; Pessino, Marcelo; Farias, Ariel A. (2004). "South America (Neotropical): 3.7 Pampas Fox". In Sillero-Zubiri, Claudio; Hoffmann, Michael; Macdonald, David W. (eds.). Canids: Foxes, Wolves, Jackals, and Dogs. Status Survey and Conservation Action Plan. Gland, Switzerland: IUCN Species Program. pp. 63–68. Archived from the original on 2011-10-06.
- ^ a b c d e f Lucherini, Mauro & Luengos Vidal, Estela M. (2008). "Lycalopex gymnocercus (Carnivora: Canidae)". Mammalian Species. 820: 1–9. doi:10.1644/820.1. hdl:11336/115900.
- ^ Cooper, Travis. "Lycalopex gymnocercus (pampas fox)". Animal Diversity Web.
- ^ Lucherini & Luengos Vidal (2008), p. 2.
- ^ Lucherini & Luengos Vidal (2008), p. 3.
- ^ a b Castelló, José R. (2018-09-11). Canids of the World: Wolves, Wild Dogs, Foxes, Jackals, Coyotes, and Their Relatives. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-17685-7.
- ^ Lucherini & Luengos Vidal (2008), pp. 3–4.
- ^ García, Verónica B. & Kittlein, M.J. (2005). "Diet, Habitat Use, and Relative Abundance of Pampas Fox (Pseudalopex gymnocercus) in northern Patagonia, Argentina". Mammalian Biology. 70 (4): 218–226. doi:10.1016/j.mambio.2004.11.019.
- ^ Chatellenaz, Mario L.; Müller, Gisela C.; Vallejos, Gilberto A. (2018). "Pampas Foxes as Prey of Yellow Anacondas". Canid Biology & Conservation. 21 (1): 1–3 – via ResearchGate.
- ^ "Zorro gris chico (Pseudalopex gymnocercus) — Ficha Ecológica de la Especie". Proyecto Zorros (in Spanish). Buenos Aires, Argentina: Secretaría de Ambiente y Desarrollo Sustentable. Archived from the original on 2012-03-11.
- ^ a b Szynwelski, Bruna Elenara; Kretschmer, Rafael; Matzenbacher, Cristina Araujo; Ferrari, Flávia; Alievi, Marcelo Meller; de Freitas, Thales Renato (2023). "Hybridization in Canids—A Case Study of Pampas Fox (Lycalopex gymnocercus) and Domestic Dog (Canis lupus familiaris) Hybrid". Animals. 13 (15): 2505. doi:10.3390/ani13152505. PMC 10417603. PMID 37570312.
- ^ Vera, Fabricio (2023-09-16). "Cientisas identificam primeiro cruzamento entre raposa e cachorro" [Scientists identify first cross between fox and dog]. Jornal Opção (in Brazilian Portuguese). Goiânia, Brazil. Retrieved 2023-09-17.
