Paramus (/pəˈræməs/ pə-RAM-əs[20]) is a borough in the central portion of Bergen County, in the U.S. state of New Jersey. A suburban bedroom community of New York City, Paramus is located 15 to 20 miles (24 to 32 km) northwest of Midtown Manhattan and approximately 8 miles (13 km) west of Upper Manhattan. The Wall Street Journal characterized Paramus as "quintessentially suburban".[21] The borough is also a major commercial hub for North Jersey (home to Garden State Plaza and various corporate headquarters).[22]
Paramus, New Jersey | |
|---|---|
 Route 17 from the overpass ramp to Route 4; both are heavily trafficked American corridors in Bergen County. | |
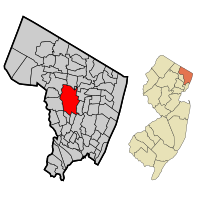 Location of Paramus in Bergen County highlighted in red (left). Inset map: Location of Bergen County in New Jersey highlighted in orange (right).
| |
| Coordinates: 40°56′50″N 74°04′13″W / 40.947299°N 74.070169°W[1][2] | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| County | Bergen |
| Incorporated | April 4, 1922 |
| Government | |
| • Type | Borough |
| • Body | Borough Council |
| • Mayor | Christopher DiPiazza (R, term ends December 31, 2026)[3][4] |
| • Administrator | Hector Olmo[5] |
| • Municipal clerk | Annemarie Krusznis[6] |
| Area | |
• Total | 10.51 sq mi (27.21 km2) |
| • Land | 10.45 sq mi (27.05 km2) |
| • Water | 0.06 sq mi (0.16 km2) 0.60% |
| • Rank | 206th of 565 in state 2nd of 70 in county[1] |
| Elevation | 49 ft (15 m) |
| Population | |
• Total | 26,698 |
| 26,282 | |
| • Rank | 95th of 565 in state 8th of 70 in county[13] |
| • Density | 2,556.1/sq mi (986.9/km2) |
| • Rank | 247th of 565 in state 49th of 70 in county[13] |
| Time zone | UTC−05:00 (Eastern (EST)) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−04:00 (Eastern (EDT)) |
| ZIP Codes | |
| Area code(s) | 201 and 551[16] |
| FIPS code | 3400355950[1][17][18] |
| GNIS feature ID | 0885340[1][19] |
| Website | www |
As of the 2020 United States census, the borough's population was 26,698,[10][11] an increase of 356 (+1.4%) from the 2010 census count of 26,342,[23][24] which in turn reflected an increase of 605 (+2.4%) from the 25,737 counted in the 2000 census.[25]
Paramus was incorporated as a borough by an act of the New Jersey Legislature on March 2, 1922, and ratified by a referendum held on April 4, 1922, that passed by a vote of 238 to 10.[26][27] Paramus was created from portions of Midland Township, which now exists as Rochelle Park.[26][28] The borough's name is thought to have originated from the Unami language spoken by the Lenape Native Americans, derived from words meaning "land of the turkeys"[20] or "pleasant stream."[29]
Paramus has some of the most restrictive blue laws in the United States, dating back to the 17th century, banning nearly all white-collar and retail businesses from opening on Sundays except for gas stations, restaurants and grocery stores, and a limited number of other businesses.[30][31] Despite this, the borough is one of the largest shopping destinations in the country, generating over $6 billion in annual retail sales, more than any other ZIP Code in the United States.[32]
History
editPre-settlement
editThe area that ultimately became the present-day North Jersey had been occupied for thousands of years by prehistoric indigenous peoples. At the time of European encounter, it was settled by the Lenape Native Americans. The Lenape language word for the area, Peremessing, which meant that it had an abundant population of wild turkey, was anglicized to become the word "Paramus".[33][34] A large metal statue of a wild turkey in the Paramus Park mall commemorates this history.[34] Another alternative derivation is that the word means "pleasant stream".[35]
18th century
editAlbrycht Zaborowski, whose descendants became known by the family name "Zabriskie",[36] immigrated from Poland via the Dutch ship Deb Ves[37] in 1662. He settled in the Dutch West Indies Company town of Ackensack, site of the present-day Hackensack. A son, Jacob, was captured by the Lenape and held for 15 years. When he was returned to his family, the Lenape explained to Saboroweski that they had taken the child in order to teach him their language so that he could serve as a translator. They granted Saboroweski approximately 2,000 acres (8.1 km2) of land which became known as the "Paramus Patent".[38]
During the American Revolutionary War, the county included both Loyalists and Patriots, with Patriots "greatly outnumbering" Tories.[39] Although no major battles were fought in Bergen County, Paramus was part of the military activity, as colonial troops were stationed in Ramapo under the command of Aaron Burr.[40] In 1777, the British raided the Hackensack area and Burr marched troops to Paramus, where he attacked the British, forcing them to withdraw.[41] General George Washington was in Paramus several times during the War: December 1778; July 1780; and, December 1780.[42] Following the Battle of Monmouth, Washington established his headquarters in Paramus in July 1778.[43] Over the advice of his staff, Washington moved his headquarters to Westchester County, New York.[44]
A section of Paramus known as Dunkerhook, meaning dark corner in Dutch, was a free African-American community dating to the early 18th century. Although historical markers on the current site and local oral tradition maintain that this was a slave community, contemporary records document that it was a community of free blacks, not slaves.[45] A group of houses built on Dunkerhook Road by the Zabriskies in the late 18th to early 19th centuries was the center of a community of black farmers, who had been slaves held by the Zabriskie family.[46]
20th century
editIn 1909, the Arcola Country Club and golf course was created in 1909 and the neighborhood by that name grew around it.[47] Farview Avenue, located at the highest elevation in Paramus, has a clear view of the Manhattan skyline.[48]
Paramus became one of the truck farming areas that helped New Jersey earn its nickname as the "Garden State".[49] By 1940, Paramus' population was just 4,000, with no town center and 94 retail establishments.[50] Although the opening of the George Washington Bridge in 1931 and the widening of Route 17 and Route 4 (which intersect in southern Paramus), made the area accessible to millions, "it was not until the 1950s that massive development hit this section of northern New Jersey".[51]
During the 1950s and 1960s, Paramus, lacking any master plan until 1969, was redeveloped into two shopping corridors when its farmers and outside developers saw that shopping malls were more lucrative than produce farming.[51] "It was a developer's dream: flat cleared land adjacent to major arterials and accessible to a growing suburban population and the country's largest city – with no planning restrictions".[51] New York had a state sales tax, but New Jersey had none, so with the opening of Manhattan department stores in the Bergen Mall (1957), the Garden State Plaza (1957) and Alexander's (1961), Paramus became the "first stop outside New York City for shopping".[51]
From 1948 to 1958, the population of Paramus nearly quadrupled, from 6,000 to 23,000, while the number of retail establishments tripled from 111 to 319, and annual retail sales increased twenty-fold in nominal dollars, from $5.5 million (equivalent to $69.7 million in 2023) to $112 million (equal to $1.2 billion in 2023).[51] By the 1980s, when the population had increased slightly over 1960s levels, retail sales had climbed to $1 billion.[51]
21st century
editParamus was the scene of one of the worst COVID-19 outbreaks in the U.S. when an outbreak at the New Jersey Veterans Home resulted in 74 deaths, all former soldiers through May 2020, with some 60% of the home's 314 residents being infected.[52]
Geography
editAccording to the United States Census Bureau, the borough had a total area of 10.51 square miles (27.21 km2), including 10.45 square miles (27.05 km2) of land and 0.06 square miles (0.16 km2) of water (0.60%).[1][2]
The borough borders the Bergen County municipalities of Emerson, Fair Lawn, Glen Rock, Hackensack, Maywood, Oradell, Ridgewood, River Edge, Rochelle Park, Saddle Brook and Washington Township.[53][54][55]
Named neighborhoods within the borough include Arcola, Bergen Place, Dunkerhook, Fairway Oaks, and Spring Valley.[56]
Demographics
edit| Census | Pop. | Note | %± |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1900 | 889 | — | |
| 1910 | 779 | −12.4% | |
| 1920 | 1,321 | 69.6% | |
| 1930 | 2,649 | 100.5% | |
| 1940 | 3,688 | 39.2% | |
| 1950 | 6,268 | 70.0% | |
| 1960 | 23,238 | 270.7% | |
| 1970 | 28,381 | 22.1% | |
| 1980 | 26,474 | −6.7% | |
| 1990 | 25,067 | −5.3% | |
| 2000 | 25,737 | 2.7% | |
| 2010 | 26,342 | 2.4% | |
| 2020 | 26,698 | 1.4% | |
| 2023 (est.) | 26,282 | [10][12] | −1.6% |
| Population sources: 1930[57] 1900–1900–2020[58][59] 2000[60][61] 2010[23][24] 2020[10][11] | |||
2010 census
editThe 2010 United States census counted 26,342 people, 8,630 households, and 6,939 families in the borough. The population density was 2,516.0 per square mile (971.4/km2). There were 8,915 housing units at an average density of 851.5 per square mile (328.8/km2). The racial makeup was 72.29% (19,042) White, 1.42% (374) Black or African American, 0.11% (28) Native American, 22.28% (5,869) Asian, 0.05% (13) Pacific Islander, 1.39% (366) from other races, and 2.47% (650) from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino residents of any race were 7.26% (1,913) of the population.[23] 6.9% of residents self-identified as being Korean American, which makes it the largest ethnic minority group in the borough.[23]
Of the 8,630 households, 33.8% had children under the age of 18; 68.4% were married couples living together; 9.1% had a female householder with no husband present and 19.6% were non-families. Of all households, 17.8% were made up of individuals and 13.3% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.92 and the average family size was 3.32.[23]
21.5% of the population were under the age of 18, 7.1% from 18 to 24, 19.2% from 25 to 44, 30.2% from 45 to 64, and 21.9% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 46.3 years. For every 100 females, the population had 94.9 males. For every 100 females ages 18 and older there were 91.7 males.[23]
The Census Bureau's 2006–2010 American Community Survey showed that (in 2010 inflation-adjusted dollars) median household income was $104,986 (with a margin of error of +/− $9,111) and the median family income was $123,848 (+/− $7,952). Males had a median income of $77,325 (+/− $5,222) versus $52,702 (+/− $4,983) for females. The per capita income for the borough was $40,024. About 1.6% of families and 2.8% of the population were below the poverty line, including 3.0% of those under age 18 and 4.1% of those age 65 or over.[62]
Same-sex couples headed 35 households in 2010, more than double the 17 counted in the 2000 census.[63]
2000 census
editAs of the 2000 United States census[17] there were 25,737 people, 8,082 households, and 6,780 families residing in the borough. The population density was 2,457.7 inhabitants per square mile (948.9/km2). There were 8,209 housing units at an average density of 783.9 per square mile (302.7/km2). The racial makeup of the borough was 79.19% White, 1.13% African American, 0.05% Native American, 17.23% Asian, 0.01% Pacific Islander, 0.89% from other races, and 1.51% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino residents of any race were 4.87% of the population.[60][61]
There were 8,082 households, out of which 37.0% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 73.3% were married couples living together, 8.0% had a female householder with no husband present, and 16.1% were non-families. 14.4% of all households were made up of individuals, and 9.4% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 3.00 and the average family size was 3.32.[60][61]
In the borough 23.2% of the population was under the age of 18, 5.5% was from 18 to 24, 24.7% from 25 to 44, 25.0% from 45 to 64, and 21.5% was 65 years of age or older. The median age was 43 years. For every 100 females, there were 94.4 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 90.4 males.[60][61]
The median income for a household in the borough was $76,918, and the median income for a family was $84,406. Males had a median income of $56,635 versus $37,450 for females. The per capita income for the borough was $29,295. About 1.4% of families and 3.3% of the population were below the poverty line, including 3.4% of those under age 18 and 5.0% of those age 65 or over.[60][61]
Economy
editCorporate headquarters
editParamus was home to the America regional headquarters of Hanjin Shipping, located on the eastbound side of Route 4 before it declared bankruptcy in 2017.[64] Hudson City Bancorp had its headquarters located at West 80 Century Road until its acquisition by M&T Bank, which was completed in 2015.[65][66] Movado Group Inc. is a watchmaker with its headquarters on From Road.[67] Suez North America, founded as Hackensack Water Company in 1869 and later named United Water, is an American water service company headquartered in Paramus.[68] Coach USA is a large tour operator with its headquarters in Paramus, at the offices of its Community Coach subsidiary.[69] Kristian Regale is a non-alcoholic beverage company based in Paramus.[70]
Paramus was the former headquarters location for Toys "R" Us before the company relocated to Wayne, New Jersey, in 2002 and went bankrupt.[71] Paramus was also the headquarters of Magic Solutions, a defunct computer software company that specialized in help desk automation and asset management software.[72]
Malls
editParamus is known for its multitude of stores and malls. It has five major indoor shopping centers, serving residents in the areas of Bergen County and Passaic County in New Jersey and Rockland County in New York. New Jersey does not levy a sales tax on clothes and shoes, which makes it an attractive shopping destination for people even further away in New York City, who pay sales tax on clothing items above $110 in price, in addition to the lower standard rate of 6.625% in New Jersey, compared to 8.875% in New York City.[73][74] The borough is one of the largest shopping destinations in the country, generating over $6 billion in annual retail sales, more than any other ZIP Code in the United States despite the county's blue laws.[32] At the intersection of Routes 4 and 17 is Garden State Plaza, the largest and best-known mall in the borough. Westfield Garden State Plaza is the largest mall in the Westfield Group's global portfolio and the largest in New Jersey, with a gross leasable area of 2,128,402 square feet (200,000 m2).[75] On Route 4, are Bergen Town Center (known as the Bergen Mall until 2006), Paramus Place and The Shoppes on IV. On Route 17, are Paramus Park, Paramus Towne Square, Paramus Design Center, and the Fashion Center.
Many national chain stores have at least one location in Paramus. Nordstrom's Paramus location was its first New York–area store when it opened in September 1990, with strong sales volume.[76] There are 25 retailers that occupy multiple stores in Paramus, including Macy's, which had outlets in three malls for a period of time. Some retail analysts view Paramus as being two distinct markets, centered on the two major highways. Lord & Taylor had locations at both Westfield Garden State Plaza and Fashion Center, giving Paramus the distinction of being the only town with more than one Lord & Taylor location. However, by 2021, both locations closed, due to the company's bankruptcy from the COVID-19 pandemic. Toys "R" Us had two locations: at the Fashion Center, and at a location on the eastbound side of Route 4 near Forest Avenue. Paramus also housed a Babies "R" Us on the northbound side of Route 17, but it closed in 2018. Later that year, the Fashion Center and Route 4 Toys "R" Us locations both closed due to the company's bankruptcy. In 1983, Paramus was the location of one of the first Kids "R" Us stores.[77] When Toys "R" Us was revived in 2019 after emerging from bankruptcy, the first new Toys "R" Us store opened at Garden State Plaza on November 27, 2019. However, it closed again on January 26, 2021, as a result of financial losses caused by the COVID-19 pandemic.[78][79]
Blue laws
editIn addition to the state blue laws that apply to all of Bergen County,[80][81][82] Paramus has even stricter restrictions, preventing stores selling non-food items from opening at all on Sundays.[83][84] These laws were enacted shortly after Garden State Plaza opened, out of fear that the mall would cause high levels of congestion in the borough.[85] It is one of the last places in the United States to have such an extensive blue law. This law was called into question when a BJ's Wholesale Club opened at the junction between Routes 4/17. BJ's was allowed to open on Sundays, but is only allowed to sell food and basic necessities. The store has been structured to restrict access to items that cannot be purchased on Sunday.
Local blue laws in Paramus were first proposed in 1957, while the Bergen Mall and Garden State Plaza were both under construction. The legislation was motivated by fears that the two new malls would increase the already-severe highway congestion caused by local retail operations along the borough's highways.[31]
The Paramus Borough Code forbids the performance of any "worldly employment" on Sunday, with exceptions for charity, and the sale of newspapers, medicinal drugs, meals, prepared food and cigarettes, among a limited numbers of exceptions. Even work performed inside one's own home is prohibited on Sundays.[83] In spite of its six-day shopping week, Paramus consistently has the most retail sales of any ZIP Code in the United States.[86]
More than 63% of Bergen County voters rejected a referendum on the ballot in 1993 that would have repealed the county's blue laws, though the Paramus restrictions would have remained in place.[87] An unsuccessful 2010 proposal by Governor of New Jersey Chris Christie would have ended the state's blue laws, now only enforced in Bergen County, with the governor citing industry estimates that the $1.1 billion in added retail revenue on Sundays would generate an additional $65 million in sales taxes for the state.[88]
In November 2012, Governor Chris Christie issued an executive order temporarily suspending the blue laws in both Bergen County and Paramus due to the effects of Hurricane Sandy, a decision that was upheld despite a court challenge by the Borough of Paramus.[89] The blue law suspension was in effect on Sunday, November 11, but was back in effect the following Sunday.[90]
Timeline of malls and shopping centers
edit- 1957 – Garden State Plaza was built by Muscarelli Construction Company on 198 acres (0.80 km2) at the intersection of Routes 4 and 17.
- 1957 – The Bergen Mall was built on 101 acres (41 ha) on an area east of the Plaza on Route 4.
- 1963 – Paramus Place was built on the north side of Route 4 across from Bergen Mall.[91]
- 1967 – The Fashion Center was built on a 33-acre (13 ha) site of old celery farms, aimed at quality-oriented shoppers by developer Associated Dry Goods, with a 135,000-square-foot (12,500 m2) Lord & Taylor and a 176,000-square-foot (16,400 m2) B. Altman as anchors and 25 other retailers sandwiched in between[92] The owners originally referred to its location as being in Ridgewood/Paramus to appeal to the Ridgewood population.
- 1972 – The 35 Plaza Shopping Center is built on Route 4, just located 2 minutes away from Paramus Place.[93]
- 1974 – Paramus Park was built by the Rouse Company, offering a gross leasable area of 755,000 square feet (70,100 m2). The most recent of the large centers was built on 66 acres (270,000 m2) in the middle of an area where the old farms were located.[94]
- 1986 – The Shoppes on IV opened up and was built on 236 acres (96 ha) in the westbound area of Route 4.[95]
- 1998 – The Paramus Towne Square opened up and was built on the north side of Route 17.[96]
- 2003 – IKEA opens a 370,000-square-foot (34,000 m2) store, its second-largest location in North America, at the intersection of Routes 4 and 17 on the site of the old Alexander's department store.[97] It was joined the next year by three other retailers, Bed Bath and Beyond, Christmas Tree Shops, and Sports Authority to form a shopping center with a combined gross leasable area of 719,226 square feet (66,818.3 m2). However, when Sports Authority went out of business in 2016, the store was closed.[98]
- 2015 – The Paramus Design Center opens up on the northbound side of Route 17.[99]
- 2018 – The Paramus Crossroads shopping center, located on the southbound side of Route 17, officially opened in summer 2018.[100]
Due to the stricter version of the blue laws in Paramus, malls (and almost all retail establishments) in the borough are closed on Sunday except for restaurants and other exempted establishments. Stores may not open before 7:00 am or remain open after 11:00 pm.[101]
Arts and culture
editOne of the earliest drive-in theaters opened in Paramus, featuring what was said to be the world's largest and brightest screen, located behind what is now Westfield Garden State Plaza. The Paramus Drive-In closed in 1987 after the last movie presentation, a double-feature of "Crocodile" Dundee and The Untouchables.[102]
Currently, Paramus' lone movie theater complex is a 16-screen AMC Theatres located in an area of new construction at Westfield Garden State Plaza. Prior to the opening of the AMC complex, a number of theatres were closed in the borough, including the Route 4 Tenplex and the Cineplex Odeon Route 17 Triplex, once located next to Westfield Garden State Plaza on Route 17. The Triplex and Tenplex theatres was opened on October 12, 1965, by Century Theatres and was closed on May 24, 2007, by Loews Cineplex Entertainment.[103] On May 25, 2007, the new AMC Theatres opened at Westfield Garden State Plaza.[104] The Paramus Picture Show, known as Cinema 35 until 1997,[105] closed in December 2004 in the wake of declining attendance.[106] A 12-screen Regal Cinemas was planned to open at Paramus Park as part of renovations that would have replaced the Sears store with a Stew Leonard's location.[107][108][109][110] However, the plans were cancelled after Stew Leonard's took up more space than expected.[111]
The Bergen Town Center had a performing arts theater called "Playhouse on the Mall". It had a seating capacity of 635 seats and was opened in 1960. From 1960 to 1970, author Robert Ludlum was the manager of the theater. The theater closed in 1982 due to rising costs and low attendance and was converted into retail space in 1986.[112]
In 2016, the Garden State Plaza added a Bergen Performing Arts Center performance area for shows and performances located near Macy's, which took up the former space of the Venetian carousel. There was also a Bergen PAC ticket center located near the performance area. The Bergen PAC performance area, however, was short lived as it was replaced by a video game theater, then it became a lounge area in 2017.[113]
The glam metal band, Trixter, formed in Paramus.[114] The hardcore/punk rock band The Escape Engine formed in the borough from 2002 to 2006.[115]
Parks and recreation
editParamus is the home to two county parks. On the eastern side of the borough is Van Saun County Park, a 146-acre (59 ha) park that features Bergen County's only zoo, home to a wide variety of wild and domestic animals living in recreated habitats natural to each species.[116] Van Saun Park also has a playground, train ride, carousel, athletic fields, and pony rides. The Washington Spring site in the park takes its name from reports that General Washington drank water from the spring here while his troops were encamped nearby, west of the Hackensack River.[117] The Continental Army is reported to have utilized the old spring at the base of these slopes during the September encampment west of the Hackensack River.
On the western side of the borough is Saddle River County Park which features a 6-mile (9.7 km) bike path reaching from Ridgewood to Rochelle Park.[118]
The borough has four golf courses. Two are open to the public, with the Paramus Golf Course operated by the borough[119] and Orchard Hills County Golf Course operated by the county.[120] The two private golf course located in Paramus are the Ridgewood Country Club and Arcola Country Club. Ridgewood Country Club was ranked as the #6 Center Ranked Among Top 500 Holes in the World Golf Magazine – 2000 and Ranked # 84 on the list of Most Prestigious Clubs in America Golf Connoisseur – 2006.
In 2008, the Paramus Golf Course opened a miniature golf course that is themed after the borough of Paramus as well as the state of New Jersey. Turkey statues are scattered around the course to celebrate Paramus as the "land of the wild turkeys."[121]
Paramus has an outdoor municipal swimming pool complex on Van Binsberger Boulevard. It has three pools: a main pool, a pool for younger swimmers, and a baby pool.[122] Paramus Little League were the 2011 New Jersey State Little League Baseball Champions.[123]
Arcola Park was an outdoor amusement park built in 1926. It had a huge swimming pool, a convention hall, a dance pavilion, an auditorium, and rides. A fire in 1929 destroyed the entire park, with the exception of the pool. The pool was destroyed by another fire in 1970 and closed down for good.[124] The park site was replaced by a Ramada Inn, the hotel extending into a small portion of Rochelle Park.[125]
Annual events
editDuring the week of the 4th of July, Paramus holds its own Independence Day celebration. First, there is the performance of the Paramus Community Orchestra at the Paramus Bandshell which takes place on July 2. Next, on the 3rd, there is a softball game between the Paramus Fire Department and the Paramus Police Department, held annually since 2011. On the 4th, there is a parade. The parade route starts at the intersection of Century Road and Farview Avenue and ends at Memorial Elementary School. On the 5th, there is a fireworks display at the Cliff Gennarelli Paramus Sportsplex.[126]
Paramus also holds its own Memorial Day parade every year.[127]
Paramus hosts an annual National Night Out. The event typically includes games and activities as well as a concert. The borough's fire, rescue, police, and ambulance vehicles are also displayed.[128]
The Paramus Rescue Squad and Fire Department Companies 2 & 3 host a Halloween party every October called, "Safe Halloween" to ensure every child has a safe and fun Halloween.[129]
The Paramus Fire Department also has its annual "Santa Detail" every December. The fire department drives throughout the borough on the Sunday before Christmas with Santa riding atop the fire apparatus. Members of the department accompany Santa and give out lollipops to residents who come outside during the tour.
Government
editLocal government
editParamus is governed under the borough form of New Jersey municipal government, which is used in 218 municipalities (of the 564) statewide, making it the most common form of government in New Jersey.[130] The governing body is comprised of a mayor and a borough council, with all positions elected at-large on a partisan basis as part of the November general election. A mayor is elected directly by the voters to a four-year term of office. The borough council includes six members elected to serve three-year terms on a staggered basis, with two seats coming up for election each year in a three-year cycle.[7] The borough form of government used by Paramus is a "weak mayor / strong council" government in which council members act as the legislative body with the mayor presiding at meetings and voting only in the event of a tie. The mayor can veto ordinances subject to an override by a two-thirds majority vote of the council. The mayor makes committee and liaison assignments for council members, and most appointments are made by the mayor with the advice and consent of the council.[131][132]
As of 2024[update], the mayor is Republican Christopher DiPiazza, whose term of office ends December 31, 2026. Borough Council members are Ace A. Antonio (R, 2024), Robert Kaiser (R, 2024), Alfredo U. Nadera (R, 2026), Jorge E. Quintana (R, 2025), Mary Ellen Rizzo (R, 2026) and Jeanne T. Weber (R, 2025).[3][133][134][135][136][137]
In February 2023, the borough council appointed Al Nadera to fill the seat expiring in December 2023 that became vacant when Chris DiPiazza took office as mayor.[138]
In October 2015, Moody's Investors Service upgraded general obligation debt of the Borough of Paramus from Aa1 to Aaa, in light of the low levels of debt and the strength of the borough's financial operations, reserve levels, tax base, management practices and levels of wealth.[139]
Federal, state and county representation
editParamus is located in the 5th Congressional District[140] and is part of New Jersey's 38th state legislative district.[141][142][143]
For the 118th United States Congress, New Jersey's 5th congressional district is represented by Josh Gottheimer (D, Wyckoff).[144][145] New Jersey is represented in the United States Senate by Democrats Cory Booker (Newark, term ends 2027)[146] and George Helmy (Mountain Lakes, term ends 2024).[147][148]
For the 2024-2025 session, the 38th legislative district of the New Jersey Legislature is represented in the State Senate by Joseph Lagana (D, Paramus) and in the General Assembly by Lisa Swain (D, Fair Lawn) and Chris Tully (D, Bergenfield).[149]
Bergen County is governed by a directly elected County Executive, with legislative functions performed by a Board of County Commissioners composed of seven members who are elected at-large to three-year terms in partisan elections on a staggered basis, with either two or three seats coming up for election each November; a Chairman and Vice Chairman are selected from among its seven members at a reorganization meeting held every January. As of 2024[update], the county executive is James J. Tedesco III (D, Paramus), whose four-year term of office ends December 31, 2026.[150]
Bergen County's Commissioners are: Thomas J. Sullivan Jr. (D, Montvale, 2025),[151] Chair Germaine M. Ortiz (D, Emerson, 2025),[152] Joan Voss (D, Fort Lee, 2026),[153] Vice Chair Mary J. Amoroso (D, Mahwah, 2025),[154] Rafael Marte (D, Bergenfield, 2026),[155] Steven A. Tanelli (D, North Arlington, 2024)[156] and Tracy Silna Zur (D, Franklin Lakes, 2024).[157][158][159][160][161][162][163][164]
Bergen County's constitutional officials are: Clerk John S. Hogan (D, Northvale, 2026),[165][166] Sheriff Anthony Cureton (D, Englewood, 2024)[167][168] and Surrogate Michael R. Dressler (D, Cresskill, 2026).[169][170][160][171]
Politics
editAs of March 2011, there were a total of 16,874 registered voters in Paramus, of which 4,454 (26.4% vs. 31.7% countywide) were registered as Democrats, 3,474 (20.6% vs. 21.1%) were registered as Republicans and 8,938 (53.0% vs. 47.1%) were registered as Unaffiliated. There were 8 voters registered as Libertarians or Greens.[172] Among the borough's 2010 Census population, 64.1% (vs. 57.1% in Bergen County) were registered to vote, including 81.6% of those ages 18 and over (vs. 73.7% countywide).[172][173]
In the 2016 presidential election, Republican Donald Trump received 6,565 votes (49.5% vs. 41.1% countywide), ahead of Democrat Hillary Clinton with 6,312 votes (47.6% vs. 54.2%) and other candidates with 389 votes (2.9% vs. 4.6%), among the 13,434 ballots cast by the borough's 18,526 registered voters, for a turnout of 72.5% (vs. 72.5% in Bergen County).[174] In the 2012 presidential election, Republican Mitt Romney received 6,123 votes here (50.0% vs. 43.5% countywide), ahead of Democrat Barack Obama with 5,907 votes (48.3% vs. 54.8%) and other candidates with 105 votes (0.9% vs. 0.9%), among the 12,234 ballots cast by the borough's 17,617 registered voters, for a turnout of 69.4% (vs. 70.4% in Bergen County).[175][176] In the 2008 presidential election, Republican John McCain received 6,885 votes here (51.1% vs. 44.5% countywide), ahead of Democrat Barack Obama with 6,386 votes (47.4% vs. 53.9%) and other candidates with 106 votes (0.8% vs. 0.8%), among the 13,470 ballots cast by the borough's 17,747 registered voters, for a turnout of 75.9% (vs. 76.8% in Bergen County).[177][178] In the 2004 presidential election, Republican George W. Bush received 6,868 votes here (52.3% vs. 47.2% countywide), ahead of Democrat John Kerry with 6,103 votes (46.5% vs. 51.7%) and other candidates with 87 votes (0.7% vs. 0.7%), among the 13,123 ballots cast by the borough's 17,206 registered voters, for a turnout of 76.3% (vs. 76.9% in the whole county).[179]
In the 2013 gubernatorial election, Republican Chris Christie received 64.4% of the vote (4,888 cast), ahead of Democrat Barbara Buono with 34.8% (2,641 votes), and other candidates with 0.8% (60 votes), among the 7,809 ballots cast by the borough's 17,083 registered voters (220 ballots were spoiled), for a turnout of 45.7%.[180][181] In the 2009 gubernatorial election, Republican Chris Christie received 4,298 votes here (49.7% vs. 45.8% countywide), ahead of Democrat Jon Corzine with 3,857 votes (44.6% vs. 48.0%), Independent Chris Daggett with 376 votes (4.3% vs. 4.7%) and other candidates with 32 votes (0.4% vs. 0.5%), among the 8,656 ballots cast by the borough's 17,354 registered voters, yielding a 49.9% turnout (vs. 50.0% in the county).[182]
Education
editThe Paramus Public Schools serve students in pre-kindergarten through twelfth grade. As of the 2019–20 school year, the eight-school district had an enrollment of 3,760 students and 332.7 classroom teachers (on an FTE basis), for a student–teacher ratio of 11.3:1.[183] Schools in the district, with 2019–20 enrollment data from the National Center for Education Statistics,[184] are Memorial Elementary School[185] (302 students in grades K–4), Midland Elementary School[186] (177 students in grades K–4), Parkway Elementary School[187] (314 students in grades Pre-K–4), Ridge Ranch Elementary School[188] (337 students in grades K–4), Stony Lane Elementary School[189] (186 students in grades K–4), East Brook Middle School[190] (575 students in grades 5–8), West Brook Middle School[191] (577 students in grades 5–8) and Paramus High School[192] (1,253 students in grades 9–12).[193][194]
Three of the district's schools have been formally recognized with the National Blue Ribbon School Award of Excellence: Paramus High School in 1988–1989, Parkway Elementary School in 1987–1988 and Ridge Ranch Elementary School in 1998–1999.[195][196]
Public school students from the borough, and all of Bergen County, are eligible to attend the secondary education programs offered by the Bergen County Technical Schools, which include the Bergen County Academies in Hackensack, and the Bergen Tech campus in Teterboro or Bergen Tech campus in Paramus. The district offers programs on a shared-time or full-time basis, with admission based on a selective application process and tuition covered by the student's home school district.[197][198]
Paramus is home to many private religious schools. Paramus Catholic High School is a co-educational Roman Catholic high school founded in 1965 and operated by the Archdiocese of Newark.[199] With more than 1,500 students, it has the largest enrollment of any Roman Catholic high school in the state of New Jersey.[200] It is also the location of Visitation Academy, a Pre-K3–8 Catholic school also overseen by the Newark Archdiocese.[201]
K–8 co-ed Jewish day schools in Paramus include Yavneh Academy;[202] Yeshivat Noam, founded in 2001;[203] and Ben Porat Yosef, which was established in 2001 and relocated to Paramus in 2008.[204] Frisch School is a Modern Orthodox Jewish yeshiva serving grades 9–12 that describes itself as the nation's second-largest coed yeshiva high school.[205]
Bergen Community College is based in Paramus, with other satellite centers located around the county. The bulk of the college's 17,000 students working towards degrees are located at the main campus in Paramus.[206] The Bergen campus of Berkeley College is located in Paramus.[207] There is also a DeVry University campus located at the 35 Plaza Shopping Center in Paramus.[208] There is a Lincoln Tech campus at Bergen Town Center.[209]
Paramus is home to five special education schools. New Alliance Academy, located on Midland Ave, provides educational and ancillary therapeutic services for high school teenagers experiencing acute psychological distress.[210] Bleshman Regional Day School, located on East Ridgewood Avenue, serves students ages three through twenty-one years of age with multiple disabilities.[211] The EPIC School (Educational Partnership for Instructing Children) is located on North Farview Avenue, next to the Our Lady of Visitation Church.[212] The Alpine Learning Group is located on County Route 62, close to Linwood Avenue,[213] and P.R.I.D.E. School, which is a part of the ECLC school, which serves three other locations in New Jersey, has a location on Sette Drive.[214] The Bergen County Special Services School District, which provides public special education services on a countywide basis, is headquartered in Paramus.[215]
Public library
editThe borough's public library maintains two locations—the Main Library on Century Road and the Charles E. Reid Branch library on Midland Avenue, which was originally a four-room schoolhouse built in 1876.[216]
The borough's original public library, known locally as the Howland House, was originally located at the intersection of Spring Valley Road and Howland Avenue. It was demolished sometime in the late 1990s. A September 11, 2001 memorial park now exists at the site known as Howland Memorial Grove.[217]
Healthcare
edit- Atlantic Health System Paramus Pavillion – located at Paramus Park in the former Sears Auto Center. This facility offers services such as physical therapy and rehabilitation services.
- New Bridge Medical Center – located at 230 East Ridgewood Avenue, this medical center is a 1,070-bed hospital that is a clinical affiliate of Rutgers Biomedical and Health Sciences. It was founded in 1916 and is the largest hospital and licensed nursing home in the entire state of New Jersey.[218]
- Oradell Animal Hospital – located on Winters Avenue, across from Paramus Park, this facility provides medical care and treatments for all animals.[219]
- Paramus has a St. Joseph's Regional Medical Center campus located on Century Road.
- The Valley Hospital has a health and fitness center on the southbound side of Route 17 and is specialized in recovery physical therapy. Valley Hospital also has support offices at the Kraft Center, located on 15 Essex Avenue. In addition, the Luckow Pavilion, located at 1 Valley Health Plaza, near the Fashion Center, specializes in cancer treatment, fertility, gamma knife surgery, and pharmacy.
Transportation
editRoads and highways
editAs of July 2015[update], the borough had a total of 121.92 miles (196.21 km) of roadways, of which 90.93 miles (146.34 km) were maintained by the municipality, 18.86 miles (30.35 km) by Bergen County, 7.72 miles (12.42 km) by the New Jersey Department of Transportation, and 4.41 miles (7.10 km) by the New Jersey Turnpike Authority.[220]
Highways in Paramus include Route 17,[221] Route 4[222] and the Garden State Parkway[223] (including the Paramus Toll Plaza at Interchange 165).[224]
Public transportation
editNJ Transit bus routes 144, 145, 148, 155, 157, 162, 163, 164, 165 and 168 serve the Port Authority Bus Terminal in Midtown Manhattan; the 171 and 175 routes provide service to the George Washington Bridge Bus Station; and local service is offered on the 709, 722, 751, 752, 753, 755, 756, 758, 762 and 770 routes.[225][226] Nine of the 22 NJ Transit buses that serve Paramus do not provide service on Sundays. The 722 does not provide services on Saturdays and Sundays.
Coach USA provides bus service to the Port Authority Bus Terminal via Rockland Coaches route 45 from Pomona, New York, and via Short Line on Route 17.[227]
Spanish Transportation and several other operators provide frequent jitney service along Route 4 between Paterson, New Jersey, and the George Washington Bridge Bus Station.[228][229]
Points of interest
editHistoric sites
editParamus is home to the following locations on the National Register of Historic Places:[230]
- Easton Tower – Intersection of Red Mill Road and Paramus Road (added 2007). The tower was built in 1899 and was originally housed as a water pump that sits alongside the Saddle River. The tower was named after businessman Edward D. Easton.[231]
- Midland School – 239 W. Midland Avenue (added 1978). The school was constructed in 1876, and was used as a branch of the Paramus Public Library after Midland School was moved.[232]
- Terhune House – 470 Paramus Road (added 1996). An 18th-century Dutch Colonial home constructed of sandstone, that was later modified to add Victorian features, including a mansard roof.[233]
- Terhune-Gardner-Lindenmeyr House – 218 Paramus Road (added 1972). A Federal Period home constructed on the last remaining portion of untouched land from Terhune's farm, as taken from the original Zabriskie patent. The oldest known portion that can be reliably dated is from 1807 to 1808, with an older adjoining section of the house dating back as far as 1707.[234]
- Harmon Van Dien House – 449 Paramus Road (added 1983).[235]
- Albert J. Zabriskie Farmhouse – 7 East Ridgewood Avenue (added 1977).[236]
- Zabriskie Tenant House – 273 Dunkerhook Road (added 1984). The house was demolished in July 2012 by a housing developer who owned the property, after efforts to preserve or relocate the house failed.[237]
Other points of interest
edit- Buehler Challenger and Science Center, located on the campus of Bergen Community College, is a space museum where children learn about outer space and missions through simulations. The science center is also available to adults and educators.[238]
- Fritz Behnke Historical Museum, located on Paramus Road. It is open every Sunday and has exhibits about Paramus' past.[239]
- New Jersey Children's Museum. Opened in 1992, it featured hands-on exhibits for children such as a fire truck, a news studio, a helicopter, and other fun pretend attractions that drew 700,000 visitors per year. It closed in 2014 after Valley Hospital bought the property near its Ridgewood location.[240]
Emergency services
editFire and rescue services
editThe Paramus Fire Department is a volunteer fire department that has a total of about 130 members who are on call around-the-clock, 365 days a year. Over the last several years, the number of calls for service that the fire department has responded to averages about 1,300 calls per year. The mission of the Paramus Fire Department is to protect the lives and property of the community. The fire department comprises four fire companies:[241]
- Fire Company 1 (Engine 1 and Ladder Truck 1) is located at East Firehouse Lane, across from the Fashion Center.
- Fire Company 2 (Engine 2 and Engine 22-a spare) is located on Spring Valley Road, and is nicknamed "Spring Valley Fire Company #2."
- Fire Company 3 (Engine 3, HazMat 3 – staffed by HazMat Technicians from all four fire companies, Utility 3, and Foam 3 – which carries AFFF firefighting foam) is located at 198 West Midland Avenue.
- Fire Company 4 (Engine 4, Ladder Truck 4, and Engine 44 – a mini-pumper) is on Farview Avenue, and is nicknamed "Farview Fire Company #4."
Paramus also has a separate volunteer rescue squad (Rescue 7 & Rescue 9) located on West Jockish Square that specializes in motor vehicle extrication, as well as a marine unit for responses involving water rescues.[242]
Ambulance and police
editThe borough's Emergency Medical Services department is staffed 24 hours a day.[243] A separate volunteer Ambulance Corps exists, largely for stand-by purposes at large events. The Volunteer Ambulance Corps station is located on East Midland Avenue.[244] The Paramus Police Department, which responds to 60,000 calls annually, is located on Carlough Drive right next to borough hall.[245]
Emergency management
editThe borough of Paramus has an emergency management department that is required by state and law to develop emergency plans to protect people and property in the event of any emergency or disaster. The Emergency Management offices are located on Carlough Drive in the Paramus Life Safety Complex next to borough hall, the police department, and the rescue squad.[246]
In popular culture
edit- Rock band Black Sabbath made stops in Paramus during their Paranoid Tour in 1970 and 1971.[247]
- Rockapella, the a cappella group best known for performing on the children's game show Where in The World Is Carmen Sandiego?, had their first public gig at the former Bamberger's store (currently Macy's) at Garden State Plaza on October 11, 1986, after performing at a private party in Oradell six months earlier.[248]
- The 1993 Saturday Night Live spin-off movie Coneheads is set in Paramus.[249] Dan Aykroyd and Jane Curtin's characters decide to move to and permanently reside in the borough so daughter Michelle Burke can attend Paramus High School. Aykroyd's character "Beldar Conehead" spends his days in Paramus giving driving lessons and playing golf.
- Scenes from the 2008 film Burn After Reading by the Coen Brothers were filmed in Paramus at the site of the old Tower Records annex building located on Route 17S that had been transformed into Hardbodies Fitness Center.[250]
- A scene from the 1996 film Ransom was filmed on Route 4 in Paramus where Mullen is driving to Stone Quarry.[251]
- Paramus was one of the filming locations in the 1986 film Something Wild.[252]
- Several episodes of the HBO crime drama The Sopranos used Paramus locations. Throughout the series, Garden State Plaza and the Ramsey Outdoor store (the now closed store in Ramsey) on Route 17 were both featured, and a character was "whacked" at the remnants of the Old Mill Bathing Beach on Paramus Road.[253] Also near the Garden State Plaza, Tony Soorano uses a pay phone in front of the Hannah Krause store on Rt 17. In the series finale, a scene with Paulie Gualtieri was filmed in Paramus, in which he drove past a gas station.[254]
- The Real Housewives of New Jersey frequently film in Paramus locations as Jennifer Aydin, a star of the show since 2018, lives in Paramus.[255]
- Avril Lavigne performed at Westfield Garden State Plaza on March 17, 2004, as part of her Live by Surprise Tour.
- The 2005 Sesame Street direct-to-video All Star Alphabet, featuring Stephen Colbert and Nicole Sullivan, was filmed on location at Garden State Plaza.[256]
- The former Paramus Bowling Center was the filming site of the bowling competition shows Make That Spare and Championship Bowling.[257]
- Hanson's 1997 video "Tulsa, Tokyo & the Middle of Nowhere", features the band travelling to Paramus Park on May 7, 1997, performing in the food court in front of 600 screaming fans.[258] The performance was their first public appearance after the release of "MMMBop".[259]
- Garden State Plaza is the setting for Tricia Sullivan's science fiction novel Maul (2002). The novel takes its title from the way that the word "mall" is pronounced with the New Jersey accent. In the novel, three teenage girls start a shoot out with a local gang.[260]
- American ska punk band Less Than Jake has a song entitled 24 Hours in Paramus on their 1995 album Losers, Kings and Things We Don't Understand.
- The ABC situational hidden camera show, What Would You Do? filmed some episodes in Paramus at the Tom Sawyer Diner.[261][262]
Notable people
editPeople who were born in, residents of, or otherwise closely associated with Paramus include:
- John Bancker Aycrigg (1798–1856), member of the United States Congress from New Jersey[263]
- Joe Benigno (born 1953), sports radio personality on WFAN on Joe & Evan show with Evan Roberts[264]
- Chase Blackburn (born 1983), linebacker for the New York Giants and a member of the Super Bowl XLII and Super Bowl XLVI champion Giants[265]
- Juwann Bushell-Beatty (born 1996), offensive lineman for the Ottawa Redblacks of the Canadian Football League[266]
- Galit Chait (born 1975), ice dancer who represented Israel internationally from 1995 to 2006[267]
- Lizabeth Cohen (born 1952), historian, college professor and author, whose 2003 work A Consumer's Republic builds on her experience growing up in post-war Paramus[268]
- Joseph Coniglio (born 1943), former member of the New Jersey Senate[269]
- Paul Contillo (1929–2024), politician who served in both houses of the New Jersey Legislature after serving on the Paramus Borough Council from 1971 to 1973[270]
- Howard Cross III, American football nose tackle for the Notre Dame Fighting Irish[271]
- Stacey Dash (born 1967), film and television actress who appeared in the 1995 film Clueless and its TV spinoff[272]
- Spero Dedes (born 1979), Los Angeles Lakers radio commentator, NFL Network television host, and CBS NCAA tournament basketball announcer[273]
- Bill DeMott (born 1966), retired professional wrestler and road agent best known for his appearances with World Championship Wrestling as Hugh Morrus and World Wrestling Federation/Entertainment under his real name[274]
- Jim Dray (born 1986), tight end who has played for the Arizona Cardinals[275]
- Warren Farrell (born 1943), educator, gender equality activist and author[276]
- Fat Joe (born 1970), rapper, actor, CEO of Terror Squad Entertainment, and member of musical groups D.I.T.C. and Terror Squad[277][278]
- Mark Fields (born c. 1961), former Ford Motor Company President and Chief Executive Officer[279]
- Dean Friedman (born 1955), one-hit wonder with the top tune "Ariel" in 1977, which includes lyrics mentioning "the waterfall in Paramus Park"[280][281]
- Fred C. Galda (c. 1918–1997), former mayor of Paramus who oversaw the implementation of the borough's blue laws in 1958[282]
- Peter Gennaro (1919–2000), Tony Award-winning dancer and choreographer[283]
- Matt Ghaffari (born 1961), Olympic wrestler[284]
- Jamie Gold (born 1969), winner of the 2006 World Series of Poker[285][286]
- Victoria Herrmann, polar geographer and climate change communicator[287]
- Matt Hunter (born 1998), singer, songwriter and voice actor[288]
- Charles Samuel Joelson (1916–1999), politician who represented New Jersey's 8th congressional district[289]
- Louis F. Kosco (born 1932), politician who served in both the New Jersey General Assembly and the New Jersey Senate[290]
- Joseph Lagana (born 1978), member of the New Jersey Senate since 2018[291]
- Lloyd Levin (born 1958), film producer whose work includes United 93[292]
- Tony Lip (1930–2013), actor who appeared on The Sopranos, playing the role of Carmine Lupertazzi,[293] and whose story was dramatized in the Oscar-winning film Green Book
- Howard Lorber (born 1948), CEO of the Vector Group[294]
- Herbert F. Maddalene (born 1928), architect best known for his work designing churches with the firm of Genovese & Maddalene[295]
- Trisha Meili, the "Central Park jogger", a 28-year-old woman who was raped and beaten while jogging in New York City's Central Park in 1989[296]
- Bob Menendez (born 1954), U.S. Senator[297]
- Liv Morgan (born 1994), professional wrestler[298]
- Dean Obeidallah (born 1969), Arab/Italian-American comedian[299]
- George Olsen (1893–1971), bandleader and proprietor of Olsen's Restaurant in the 1950s and 1960s[300]
- Ken Oringer (born 1965), chef[301]
- John Bartow Prevost (1766–1825), first Judge of the Superior Court of the Territory of Orleans[302]
- Kenneth W. Regan (born 1959), professor, chess player, statistician and computer scientist[303]
- John Robertson (born 1993), quarterback for the Villanova Wildcats football team who won the 2014 Walter Payton Award[304]
- Ira Rubin (1930–2013), world champion professional contract bridge player[305]
- Gary Saul Stein (born 1933), attorney and former Associate Justice on the New Jersey Supreme Court, who served for 17 years where he wrote over 365 published opinions[306]
- Nick Suriano (born 1997), freestyle and folkstyle wrestler, NCAA wrestling champion at Rutgers and Michigan[307]
- Kazbek Tambi (born 1961), former professional soccer player[308]
- Steven H. Temares (born 1958), Chief Executive Officer of Bed, Bath & Beyond[309]
- Theodore Trautwein (1920–2000), judge who sentenced a reporter from The New York Times to 40 days in jail in the "Dr. X" trial of Mario Jascalevich[310]
- Connie Wagner (born 1948), member of the New Jersey General Assembly from 2008 to 2013[311]
- Yoojin Grace Wuertz (born 1980), novelist who wrote the 2017 book Everything Belongs To Us[312]
- Elaine Zayak (born 1965), one of the world's top figure skaters in the early 1980s[313]
References
editCitations
edit- ^ a b c d e 2019 Census Gazetteer Files: New Jersey Places Archived March 21, 2021, at the Wayback Machine, United States Census Bureau. Accessed July 1, 2020.
- ^ a b US Gazetteer files: 2010, 2000, and 1990 Archived August 24, 2019, at the Wayback Machine, United States Census Bureau. Accessed September 4, 2014.
- ^ a b Mayor & Council, Borough of Paramus. Accessed April 21, 2024.
- ^ 2023 New Jersey Mayors Directory Archived March 11, 2023, at the Wayback Machine, New Jersey Department of Community Affairs, updated February 8, 2023. Accessed February 10, 2023.
- ^ Administration, Borough of Paramus. Accessed April 21, 2024.
- ^ Boro Clerk, Borough of Paramus. Accessed April 21, 2024.
- ^ a b 2012 New Jersey Legislative District Data Book, Rutgers University Edward J. Bloustein School of Planning and Public Policy, March 2013, p. 160.
- ^ "ArcGIS REST Services Directory". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 13, 2023. Retrieved October 11, 2022.
- ^ "Borough of Paramus". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior. Retrieved March 8, 2013.
- ^ a b c d e QuickFacts Paramus borough, New Jersey Archived October 19, 2020, at the Wayback Machine, United States Census Bureau. Accessed December 20, 2022.
- ^ a b c Total Population: Census 2010 - Census 2020 New Jersey Municipalities Archived February 13, 2023, at the Wayback Machine, New Jersey Department of Labor and Workforce Development. Accessed December 1, 2022.
- ^ a b Annual Estimates of the Resident Population for Minor Civil Divisions in New Jersey: April 1, 2020 to July 1, 2023, United States Census Bureau, released May 2024. Accessed May 16, 2024.
- ^ a b Population Density by County and Municipality: New Jersey, 2020 and 2021 Archived March 7, 2023, at the Wayback Machine, New Jersey Department of Labor and Workforce Development. Accessed March 1, 2023.
- ^ Look Up a ZIP Code for Paramus, NJ Archived May 28, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, United States Postal Service. Accessed November 24, 2011.
- ^ Zip Codes Archived June 17, 2019, at the Wayback Machine, State of New Jersey. Accessed August 29, 2013.
- ^ Area Code Lookup – NPA NXX for Paramus, NJ Archived June 28, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, Area-Codes.com. Accessed August 29, 2013.
- ^ a b U.S. Census website Archived December 18, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, United States Census Bureau. Accessed September 4, 2014.
- ^ Geographic Codes Lookup for New Jersey Archived November 19, 2018, at the Wayback Machine, Missouri Census Data Center. Accessed April 1, 2022.
- ^ US Board on Geographic Names Archived February 4, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, United States Geological Survey. Accessed September 4, 2014.
- ^ a b Waggoner, Walter H. "Paramus Is Honored in Clean-Up Contest; Bergen Town Happy but Not Surprised by National Award" Archived October 16, 2018, at the Wayback Machine, The New York Times, February 16, 1966. Accessed October 16, 2018. "Paramus – pronounced puh-RAHM-us, with the accent on the second syllable – may have taken its name from 'perremus' or 'perymus,' Indian for 'land of the turkey'."
- ^ Minaya, Ezequiel. "Paramus, the Quintessential Suburb; Residents say the Bergen County borough has a small-town feel" Archived February 5, 2018, at the Wayback Machine, The Wall Street Journal, April 29, 2016. Accessed May 30, 2018. "Paramus, in New Jersey’s Bergen County, is quintessentially suburban but without a main street downtown lined with stores and restaurants and maybe a theater."
- ^ Lynn, Kathleen."Paramus, N.J.: Low Taxes and Lots of Shopping" Archived May 4, 2022, at the Wayback Machine, The New York Times, April 7, 2021. Accessed May 3, 2022.
- ^ a b c d e f DP-1 – Profile of General Population and Housing Characteristics: 2010 for Paramus borough, Bergen County, New Jersey Archived February 12, 2020, at archive.today, United States Census Bureau. Accessed December 25, 2011.
- ^ a b Table DP-1. Profile of General Demographic Characteristics: 2010 for Paramus borough Archived October 6, 2011, at the Wayback Machine, New Jersey Department of Labor and Workforce Development. Accessed December 25, 2011.
- ^ Table 7. Population for the Counties and Municipalities in New Jersey: 1990, 2000 and 2010 Archived June 2, 2022, at the Wayback Machine, New Jersey Department of Labor and Workforce Development, February 2011. Accessed May 1, 2023.
- ^ a b Snyder, John P. The Story of New Jersey's Civil Boundaries: 1606–1968, Bureau of Geology and Topography; Trenton, New Jersey; 1969. p. 84. Accessed May 30, 2024.
- ^ Paramus History, Borough of Paramus. Accessed June 1, 2015.
- ^ Staff. Acts of the One Hundred and Forty-Sixth Legislature of the State of New Jersey, pp. 81-83. New Jersey Secretary of State, 1922. Accessed October 17, 2015. "An Act to incorporate the borough of Paramus, in the county of Bergen"
- ^ Hutchinson, Viola L. The Origin of New Jersey Place Names Archived November 15, 2015, at the Wayback Machine, New Jersey Public Library Commission, May 1945. Accessed September 8, 2015.
- ^ Thomas, Lauren (October 20, 2019). "A law from the 1600s will keep retail shops closed on Sundays at the nation's newest shopping mall". CNBC. Archived from the original on January 28, 2022. Retrieved January 28, 2022.
- ^ a b Tompkins, John. "Sunday Selling Plaguing New Jersey" Archived October 24, 2017, at the Wayback Machine, The New York Times, June 2, 1957. Accessed December 18, 2017. "The battle over whether retailers should be allowed to sell on Sunday is becoming more intense in New Jersey as lobbyists on both sides increase their efforts."
- ^ a b Pries, Allison. "Inside the N.J. town where retail spending beats Hollywood and tourism rivals Disney" Archived October 30, 2019, at the Wayback Machine, NJ Advance Media for NJ.com, March 10, 2019, updated June 19, 2019. Accessed October 6, 2019. "The former farming community already sees more retail sales than any other ZIP Code in the country.... More than $6 billion in retail sales happen in Paramus each year."
- ^ Citizens Semi-Centennial Assoc., 1919, Ridgewood, Bergen County, New Jersey, Past and Present Archived September 30, 2023, at the Wayback Machine, p. 3. Accessed October 6, 2019. "The name 'Paramus' is said to be derived from the Indian 'Peremessing', descriptive of the fact that the country abounded in wild turkey. The first white settlers called it 'Peremesse' from which the transition was gradually made to the present form, Paramus."
- ^ a b Cheslow, Jerry. "If You're Thinking of Living In/Paramus; In Shopping Mecca, Houses Sell Well Too" Archived April 24, 2017, at the Wayback Machine, The New York Times, April 15, 2001. Accessed May 23, 2012.
- ^ Hutchinson, Viola L. The Origin of New Jersey Place Names Archived November 15, 2015, at the Wayback Machine, New Jersey Public Library Commission, May 1945. Accessed November 13, 2015.
- ^ The Zabriskie House, built in 1796 in nearby Ho-Ho-Kus, New Jersey, is an area landmark.
- ^ ""Paramus, or land of the wild turkey"". July 21, 2011. Archived from the original on May 7, 2012. Retrieved July 22, 2011.
- ^ History of Bergen and Passaic Counties, New Jersey Archived September 30, 2023, at the Wayback Machine, pp. 321–322. Accessed October 6, 2019.
- ^ Ridgewood Past and Present, p. 4
- ^ Hamilton, Alexander. The Papers of Alexander Hamilton, Columbia University Press, 1977, p. 296. While stationed in Ramapo, Burr met the woman he later married. The 1782 ceremony was held in Paramus.
- ^ Ridgewood Past and Present, p. 7.
- ^ Ridgewood Past and Present, p. 6
- ^ Bake, William Spohn. Itinerary of General Washington from June 15, 1775, to December 23, 1783, J. B. Lippincott Company, 1892, p. 137
- ^ Leiby, Adrian Coulter. The Revolutionary War in the Hackensack Valley Archived September 30, 2023, at the Wayback Machine, p. 158. Rutgers University Press, 1980. ISBN 9780813508986. Accessed October 6, 2019.
- ^ Dunkerhook: Slave Community? Archived September 27, 2006, at the Wayback Machine, accessed November 11, 2006.
- ^ Cardwell, Diane. "For House Telling Paramus's History, End May Be Near" Archived November 23, 2018, at the Wayback Machine, The New York Times, June 27, 2011. Accessed December 25, 2011. "The two houses, at 273 and 263 Dunkerhook, and a third one down the road and just over the line in Fair Lawn, were originally built, historians say, by one of the founding families of Bergen County, the Zabriskies. The house at 273 Dunkerhook dates to around 1790; the one at 263 Dunkerhook dates to 1803. As the Paramus houses passed from the Zabriskies to black farmers believed to be former Zabriskie slaves, they helped seed a thriving black settlement of several houses and a church that lasted into the 1930s."
- ^ Craffey, Jim. How Arcola Came To Be - An Abridged History Archived February 27, 2022, at the Wayback Machine, Arcola Country Club. Accessed March 18, 2022.
- ^ Staff. "Flat In Jersey City Resold To Investor; Patrick J. Kennedy Acquires the Comfort Apartment on Bergen Avenue. Acreage Deal At Paramus Two Yonkers Plots Are Included in Westchester Transfers—Building Projects." Archived July 22, 2018, at the Wayback Machine, The New York Times, March 28, 1928. Accessed December 25, 2011. "Conrad Roes bought fourteen acres on the west side of Farview Avenue, Paramus, in Bergen County. The property is said to have the second highest elevation in the county and overlooks the Manhattan skyline."
- ^ Satterthwaite, Ann. Going Shopping: Consumer Choices and Community Consequence, Yale University Press, 2001, p. 256
- ^ Going Shopping, p. 256.
- ^ a b c d e f Going Shopping, p. 257
- ^ Tully, Tracey. "‘The Whole Place Is Sick Now’: 74 Deaths at a Home for U.S. Veterans" Archived May 23, 2022, at the Wayback Machine, The New York Times, May 10, 2020, updated September 25, 2020. Accessed May 25, 2022. "But nowhere has the devastation been starker than at the New Jersey Veterans Home at Paramus, a state-run home for former members of the U.S. military, where on Tuesday 74 deaths had been linked to virus.... The virus has swept through the facility, which in late March had 314 residents, infecting 60 percent of its patients."
- ^ Areas touching Paramus Archived May 14, 2018, at the Wayback Machine, MapIt. Accessed March 2, 2020.
- ^ Bergen County Map of Municipalities Archived December 2, 2020, at the Wayback Machine, Bergen County, New Jersey. Accessed March 2, 2020.
- ^ New Jersey Municipal Boundaries Archived December 4, 2003, at the Wayback Machine, New Jersey Department of Transportation. Accessed November 15, 2019.
- ^ Locality Search Archived July 9, 2016, at the Wayback Machine, State of New Jersey. Accessed May 21, 2015.
- ^ Fifteenth Census of the United States : 1930 – Population Volume I Archived July 27, 2023, at the Wayback Machine, United States Census Bureau, p. 714. Accessed December 25, 2011.
- ^ Table 6: New Jersey Resident Population by Municipality: 1940 - 2000 Archived October 5, 2022, at the Wayback Machine, Workforce New Jersey Public Information Network, August 2001. Accessed May 1, 2023.
- ^ Historical Population Trends in Bergen County 1900-2020 Archived May 28, 2023, at the Wayback Machine, Bergen County, New Jersey Department of Planning and Engineering, 2022. Accessed May 1, 2023.
- ^ a b c d e Census 2000 Profiles of Demographic / Social / Economic / Housing Characteristics for Paramus borough, New Jersey Archived February 1, 2015, at the Wayback Machine, United States Census Bureau. Accessed July 16, 2012.
- ^ a b c d e DP-1: Profile of General Demographic Characteristics: 2000 – Census 2000 Summary File 1 (SF 1) 100-Percent Data for Paramus borough, Bergen County, New Jersey Archived February 12, 2020, at archive.today, United States Census Bureau. Accessed July 16, 2012.
- ^ DP03: Selected Economic Characteristics from the 2006–2010 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates for Paramus borough, Bergen County, New Jersey Archived February 12, 2020, at archive.today, United States Census Bureau. Accessed December 25, 2011.
- ^ Lipman, Harvy; and Sheingold, Dave. "North Jersey sees 30% growth in same-sex couples", The Record, August 14, 2011, backed up by the Internet Archive as of February 3, 2013. Accessed October 24, 2014.
- ^ Office Network Archived August 10, 2015, at the Wayback Machine, Hanjin Shipping. Accessed August 11, 2015.
- ^ Institution History for Hudson City Bancorp, Inc. (2367556) Archived December 8, 2015, at the Wayback Machine, National Information Center. Accessed December 2, 2015.
- ^ Ensign, Rachel Louise. "M&T Bank Completes Acquisition of Hudson City After 3-Year Delay; Delay stalled deal making in the banking sector as M&T worked to improve controls" Archived March 12, 2017, at the Wayback Machine, Wall Street Journal, November 2, 2015. Accessed January 7, 2017. "M&T Bank Corp. completed its acquisition of Hudson City Bancorp Inc. on Sunday after a three-year delay that chilled appetite for deal making in the banking sector."
- ^ Movado Group, Inc Corporate Office Archived April 15, 2016, at the Wayback Machine, CorporateOffice.com. Accessed June 19, 2016.
- ^ Moss, Linda. "United Water moving to Paramus from Harrington Park " Archived May 13, 2016, at the Wayback Machine, The Record, July 23, 2014. Accessed April 13, 2016. "United Water Inc. is moving its headquarters from Harrington Park to Paramus, signing a 20-year lease for 116,360 square feet at a Mack-Cali Realty Corp. office building."
- ^ Working at Coach USA Archived April 25, 2016, at the Wayback Machine, Glassdoor. Accessed April 13, 2016.
- ^ "Kristian Regale". Archived from the original on July 6, 2022. Retrieved July 21, 2022.
- ^ DeMasters, Karen. "Briefing: Business; Toys 'R' Us Layoffs" Archived May 31, 2016, at the Wayback Machine, The New York Times, February 3, 2002. Accessed August 10, 2015. "Toys R Us will move its corporate headquarters from Paramus to Wayne, close 64 stores nationwide and lay off 1,900 employees, the company announced last week."
- ^ "Company Overview of Magic Solutions International, Inc." Archived March 7, 2016, at the Wayback Machine, Bloomberg.com. Accessed April 13, 2016. "The company was founded in 1988 and is based in Paramus, New Jersey."
- ^ City of New York. "New York Sales and Use Tax" Archived November 5, 2013, at the Wayback Machine. Accessed November 4, 2013. "The City Sales Tax rate is 4.5%, NY State Sales and Use Tax is 4% and the Metropolitan Commuter Transportation District surcharge of 0.375% for a total Sales and Use Tax of 8.875 percent"
- ^ Belson, Ken; and Schweber, Nate. "Sales Tax Cut in City May Dim Allure of Stores Across Hudson" Archived May 14, 2018, at the Wayback Machine. The New York Times. January 18, 2007. Accessed August 22, 2011. "For years, shoppers from New York City have played a game of retail arbitrage, traveling to the many malls in northern New Jersey, a state where there is no tax on clothing and shoes. Even accounting for tolls, gas and time, shoppers could save money by visiting the Westfield Garden State Plaza and other malls here, escaping the 8.375 percent sales tax they must pay in New York City on clothing and shoes that cost more than $110 per item."
- ^ Westfield Garden State Plaza Archived February 24, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, Westfield Group. Accessed December 25, 2011. "Total retail space: 2,128,402ft2 or 197,728m2 (approx)"
- ^ Barmash, Isadore. "Sales Strong for Jersey Nordstrom's" Archived July 2, 2017, at the Wayback Machine, The New York Times, October 9, 1990. Accessed August 11, 2015. "Nordstrom Inc.'s store here, its first in the New York metropolitan area, appears to be off to a strong start in its first month, industry analysts and company executives say. Nordstrom executives refused to give details on the store's sales but said it had had the best initial sales volume of any of the company's three East Coast stores."
- ^ Our History Archived April 18, 2019, at the Wayback Machine, Toys "R" Us. Accessed August 11, 2015. "In 1983, the company branched out into children's clothing when it opened its first Kids 'R' Us® stores in Paramus, New Jersey and Brooklyn, New York."
- ^ "Toys R Us opens 'new' kind of store, with its first US location in Garden State Plaza" Archived November 28, 2019, at the Wayback Machine NorthJersey.com. Accessed November 27, 2019.
- ^ "Toys R Us retrenches again, shutters its last 2 US stores" Archived January 30, 2021, at the Wayback Machine "ABC7NY.com" Accessed January 29, 2021.
- ^ Mack Paramus Co. v. Mayor and Council Archived November 30, 2022, at the Wayback Machine, Casetext. Accessed November 30, 2022. "The State's statutory Sunday blue law, as incorporated in the Code, restricts the sale on Sunday of only five categories of goods. N.J.S.A. 2A:171-5.18. The provisions of the State law are not operative unless the voters of a county adopt the State law by referendum, upon which the statutory prohibition will be applicable on a county-wide basis. N.J.S.A. 2A:171-5.12. The voters in Bergen County, in which Midland Park and Paramus are located, have adopted the State Sunday blue law."
- ^ The Sunday Closing Law Archived February 7, 2018, at the Wayback Machine, Bergen County, New Jersey. Accessed January 28, 2018. "Bergen County has by referendum become the last county in New Jersey to retain the Sunday Closing Law, N.J.S.A. 2A:171-5.8 et seq. As a result, the sale of certain items is still prohibited and the law should still be enforced."
- ^ Brennan, John. "11 things you might not know about Bergen County's blue laws" Archived December 9, 2017, at the Wayback Machine, The Record, June 23, 2017. Accessed January 28, 2018. "A key moment in time was the 1959 vote to allow each of New Jersey's 21 counties to make individual decisions on blue laws. Ten counties preferred the status quo — at first. Hudson County voters decided in 1985 to become the 20th of 21 counties to repeal the state's blue laws."
- ^ a b Paramus Borough Code: Chapter 391: Sunday Activities Archived April 25, 2023, at the Wayback Machine, Borough of Paramus. Accessed April 25, 2023. "391-2. Sunday activities restricted. No worldly employment or business, except works of necessity and charity, shall be performed or practiced by any person within the Borough on the first day of the week, commonly called and hereinafter designated as 'Sunday.'"
- ^ Brennan, John. "11 things you might not know about Bergen County's blue laws" Archived December 9, 2017, at the Wayback Machine, The Record, June 23, 2017. Accessed December 18, 2017. "In Jan. 1986, Gov. Tom Kean signed a bill into law that allowed Bergen municipalities to have their own blue laws, even if the county at some point removed its bans. The state Supreme Court upheld that option six months later. That decision allowed Paramus to maintain even stricter blue laws than in the rest of the county."
- ^ Staff. "Sunday Selling Plaguing Jersey; Local Businesses Pushing Fight Against Activities of Stores on Highways" Archived October 24, 2017, at the Wayback Machine, The New York Times, June 2, 1957. Accessed January 28, 2018.
- ^ Paramus 07652 Archived May 17, 2008, at the Wayback Machine, GlobeSt. Retail, October 3, 2005.
- ^ Staff. "The 1993 Elections: Ballots Measures; New Brooms Sweep In Power of Recall and Term Limits as Well as Candidates" Archived March 7, 2016, at the Wayback Machine, The New York Times, November 4, 1993. Accessed December 25, 2011. "Residents of Bergen County decided that they wanted to keep the state's only countywide blue laws, which prohibit most shopping on Sunday. Voters rejected the effort to repeal the laws by 63 percent to 37 percent, with 99 percent of the county's precincts reporting."
- ^ Gartland, Michael. "Christie's blue law repeal proposal criticized", The Record, March 17, 2010. Accessed June 29, 2011. "Macy's declined to comment, referring questions to the New Jersey Retail Merchants Association, which supports lifting the blue laws. The association said that Sunday hours would generate $1.1 billion a year in extra business for Bergen County retailers, along with $65 million in state sales tax revenues."
- ^ Verdon, Joan. "Judge sides with county executive over Bergen blue laws" Archived October 4, 2013, at the Wayback Machine, The Record, November 9, 2012. Accessed November 19, 2012. "Paramus must set aside its blue laws this Sunday due to the unprecedented damage caused by Superstorm Sandy, a Bergen County Superior Court Judge ruled today."
- ^ Sullivan, S.P. "Bergen County exec makes clear: Blue laws are back this weekend" Archived November 20, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, The Star-Ledger, November 16, 2012. Accessed November 19, 2012.
- ^ Paramus Place in Paramus, NJ - (shopping mall) Archived July 1, 2015, at the Wayback Machine, MallsDb.com. Accessed June 28, 2015.
- ^ Barmash, Isadore. "Stores for the Quality-Minded Rise on Site of Former Celery Farms; Shopping Center Opens In Paramus Lord & Taylor and Altman Lead Quality Complex" Archived July 22, 2018, at the Wayback Machine, The New York Times, February 15, 1967. Accessed October 30, 2013. "Paramus, N.J., Feb. 14 A new shopping center for the quality minded, The Fashion Center, will open here to the public tomorrow in a 33-acre hollow scooped out of former celery farms on Route 17 at Ridgewood Avenue."
- ^ "Plaza to Celebrate Alvin and Susan Sauer on Friday" Archived March 4, 2016, at the Wayback Machine, Paramus Patch. Accessed June 29, 2015.
- ^ McQuaid, Kevin L. "Rouse Co. buys out partner in Paramus Park mall in N.J.", The Baltimore Sun, August 30, 1995. Accessed October 30, 2013. "The stake in the Paramus Park Mall from Rodamco N.V., a Dutch investment firm, marks the fourth time this year that Rouse has solidified its ownership of a retail property. With the purchase, a Rouse subsidiary will control the entire 755,000-square-foot mall.... Paramus Park, completed in 1974 and anchored by Sears, Roebuck & Co. and Macy's, is typically one of the best performers in Rouse's 75-property retail portfolio."
- ^ Shoppes at IV in Paramus, NJ - (shopping mall) Archived June 23, 2015, at the Wayback Machine, MallsDb.com. Accessed October 9, 2015.
- ^ Paramus Towne Square in Paramus, NJ - (shopping mall) Archived July 1, 2015, at the Wayback Machine, MallsDb.com. Accessed October 9, 2015.
- ^ Sloan, Carole. "Ikea adds breathing space in Paramus" Archived November 2, 2013, at the Wayback Machine, Furniture Today, August 10, 2003. Accessed October 30, 2013. "More lifestyle vignettes, fewer rigid product displays, and more places for shoppers to relax are key elements in the furniture presentation at the just-opened Ikea store in Paramus, N.J., said Ian Wrling, U.S. deputy manager, North America. The store, at 370,000-square-feet, is the second-largest of Ikea's North American units, and 'offers us the opportunity to give customers breathing space in what had been a very rigid furniture presentation,' he said."
- ^ Paramus-IKEA Shopping Center Archived March 4, 2016, at the Wayback Machine, Malls and Outlets. Accessed June 1, 2015.
- ^ Paramus Design Center Archived January 11, 2016, at the Wayback Machine Accessed January 6, 2016.
- ^ Hubbard, Daniel. "New Shopping, Dining Center Approved For Route 17 In Paramus; Breaking: Paramus Crossroads will be located very near the Westfield Garden State Plaza." Archived September 17, 2017, at the Wayback Machine, Paramus Patch. Accessed May 8, 2017. Accessed December 18, 2017. "Paramus Crossroads, a new 40,000-square-foot retail and dining center on Route 17, is slated to open in summer 2018."
- ^ Paramus Borough Code: Chapter 191: BUSINESSES – Article II: Retail Business Closing Hours Archived November 2, 2013, at the Wayback Machine, Borough of Paramus. Accessed October 30, 2013. "Every retail business within the Borough of Paramus shall be closed to the public and business with the public therein shall be and is hereby prohibited after the hour of 11:00 p.m. and before the hour of 7:00 a.m. of any day."
- ^ Ervolino, Bill. "Paramus parking lot was once a cinema under the stars", The Record, September 6, 2012. Accessed August 10, 2013.
- ^ 70mm Equipped Theatre Pictures Archived March 4, 2020, at the Wayback Machine, From Script to DVD. Accessed November 4, 2017. "Stanley-Warner Route Four opened on October 12, 1965."
- ^ Gartland, Michael. "Epic theater soon to play its final reel", The Record, May 19, 2007. Accessed August 2, 2015. "The AMC Paramus Route 4 10 — known affectionately to locals simply as the Tenplex — will run its projectors for the last time Thursday, just one day before a bigger, more advanced cineplex opens down the road at the Garden State Plaza."
- ^ Brody, Leslie. "No Need To Go Into Manhattan -- Paramus Gets Art Cinema", The Record, July 25, 1997. Accessed August 2, 2015. "The Paramus Picture Show will be in the spot known for 20 years as Cinema 35, a discount movie house that sold tickets for $3."
- ^ Spelling, Ian. "Theater closing down with a hunger benefit", The Record, December 3, 2004. Accessed August 2, 2015. "Unfortunately, too few people turned out to see such shows, and Paramus Picture Show will close Dec. 13."
- ^ Grand Openings Archived October 11, 2016, at the Wayback Machine, Regal Entertainment Group. Accessed September 24, 2016.
- ^ Verdon, Joan. "Paramus Park awaits its renaissance" Archived October 9, 2016, at the Wayback Machine, The Record, February 7, 2016. Accessed February 26, 2016. "In 2014, before the Sears deal was struck, Paramus Park received approval from the borough of Paramus for an expansion project that included a 13-screen movie theater and several restaurants."
- ^ Sullivan, S.P. "Paramus Park Mall moving forward with 13-screen movie theater addition plan" Archived September 17, 2016, at the Wayback Machine, NJ Advance Media for NJ.com, May 24, 2013. Accessed September 26, 2016. "The Paramus Park Mall will move forward with plans to add a 13-screen movie theater to its stable of retails stores after a unanimous vote from the local zoning board Thursday, Paramus Patch reported."
- ^ Verdon, Joan. "Stew Leonard's to replace Paramus Sears" Archived October 14, 2017, at the Wayback Machine, The Record, October 13, 2017. Accessed October 16, 2017. "The Sears department store that has been an anchor of the Paramus Park mall since it opened in 1974 will be replaced by a Stew Leonard’s farm-style supermarket and a 12-screen movie theater under a plan submitted to Paramus zoning officials Thursday."
- ^ NJ.com, Allison Pries | NJ Advance Media for (December 29, 2019). "These 8 N.J. malls are all upping their game. See the new plans". nj. Archived from the original on December 29, 2019. Retrieved November 20, 2020.
- ^ Garvie, Glenn. "Remembering Playhouse on the Mall" Archived July 21, 2015, at the Wayback Machine, (201) magazine. Accessed August 2, 2015.
- ^ Garden State Plaza carousel stops spinning. "NorthJersey.com" Archived February 4, 2016, at the Wayback Machine. Accessed February 2, 2016.
- ^ Jaeger, Barbara. "Paramus Band Feels At Home In The Studio", The Record, July 17, 1992. Accessed October 15, 2007. "For all those Trixter fans who've been wondering when the Paramus-based band will be releasing a new album, guitarist Steve Brown has these encouraging words..."
- ^ Pryor, Terrance. "The Escape Engine announce new album & reunion show" Archived October 24, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, FakeWalls.com, March 21, 2012. Accessed October 24, 2014. "Paramus rock group The Escape Engine have announced the release of their sophomore album: When You Dance With The Devil."
- ^ Van Saun County Park Archived May 9, 2015, at the Wayback Machine, Bergen County Parks. Accessed June 1, 2015.
- ^ Revolutionary War Sites in Paramus, New Jersey Archived March 24, 2016, at the Wayback Machine, Revolutionary War New Jersey. Accessed June 19, 2016.
- ^ Saddle River County Park Archived October 7, 2019, at the Wayback Machine, Bergen County Parks. Accessed July 6, 2022. "Multi-use pathway/Bicycle-Pedestrian Path: This bike and pedestrian path travels from Ridgewood to Rochelle Park and is approximately 6 miles in length. This continuous path runs through Ridgewood, Glen Rock, Fair Lawn, Paramus, Saddle Brook and Rochelle Park and under Route 4."
- ^ Golf Course, Borough of Paramus. Accessed December 25, 2011.
- ^ Orchard Hills Golf Course Archived June 7, 2015, at the Wayback Machine, Bergen County, New Jersey. Accessed June 1, 2015.
- ^ Home Page Archived July 7, 2022, at the Wayback Machine, Paramus Mini Golf, Borough of Paramus. Accessed July 6, 2022.
- ^ Pool Archived July 23, 2022, at the Wayback Machine, Borough of Paramus. Accessed July 6, 2022.
- ^ New Jersey State Tournament Major Baseball Division Archived September 25, 2015, at the Wayback Machine, Unpage. Accessed September 24, 2015.
- ^ Early 1900s – A New Town Emerges Archived June 29, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, Paramus Public Schools. Accessed June 1, 2015.
- ^ of Paramus/Historical Overview/Early 1900s.htm Early 1900s – A New Town Emerges[permanent dead link], Paramus Public Schools. Accessed April 9, 2014.
- ^ Home Page Archived July 5, 2015, at the Wayback Machine, Paramus 4th of July Celebration. Accessed July 4, 2015.
- ^ Fabrikant, Mel. "Paramus Memorial Day, A Ceremony To Remember" Archived July 5, 2015, at the Wayback Machine, The Paramus Post, May 26, 2015. Accessed August 2, 2015.
- ^ National Night Out 2015 Archived September 19, 2015, at the Wayback Machine, Paramus Regional Chamber of Commerce. Accessed July 26, 2015.
- ^ "Safe Halloween in Paramus, The Town Cares" Archived November 17, 2015, at the Wayback Machine, The Paramus Post, November 2, 2014. Accessed November 15, 2015.
- ^ Inventory of Municipal Forms of Government in New Jersey Archived June 1, 2023, at the Wayback Machine, Rutgers University Center for Government Studies, July 1, 2011. Accessed June 1, 2023.
- ^ Cerra, Michael F. "Forms of Government: Everything You've Always Wanted to Know, But Were Afraid to Ask" Archived September 24, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, New Jersey State League of Municipalities. Accessed November 30, 2014.
- ^ "Forms of Municipal Government in New Jersey" Archived June 4, 2023, at the Wayback Machine, p. 6. Rutgers University Center for Government Studies. Accessed June 1, 2023.
- ^ 2023 Municipal Data Sheet, Borough of Paramus. Accessed April 21, 2024.
- ^ 2024 County and Municipal Directory, Bergen County, New Jersey, April 2024. Accessed April 15, 2024.
- ^ Official Statement of Vote 2023 General Election - November 7, 2023 Official Results, Bergen County, New Jersey, November 27, 2023. Accessed January 1, 2024.
- ^ Bergen County November 8, 2022 General Election Statement of Vote, Bergen County, New Jersey Clerk, updated November 21, 2022. Accessed January 1, 2023.
- ^ Bergen County Statement of Vote November 2, 2021 Official results, Bergen County, New Jersey, updated November 17, 2021. Accessed January 1, 2022.
- ^ Noda, Stephanie. "Paramus swears in Filipino councilman who hopes to be a voice for the borough's diversity" Archived September 30, 2023, at the Wayback Machine, The Record, February 3, 2023. Accessed February 3, 2023. "'I'm very excited to work with the residents of Paramus, improve their quality of care and improve the state of the borough,' said Al Nadera, who was sworn into office on Tuesday. Nadera, a Republican, was appointed to fill the one year remaining in the term of Chris DiPiazza, who became mayor last month after winning the November election."
- ^ "Rating Action: Moody's upgrades Paramus, NJ's GO to Aaa from Aa1" Archived March 4, 2016, at the Wayback Machine, Moody's Investors Service, October 8, 2015. Accessed October 25, 2015. "Moody's Investors Service has upgraded the borough of Paramus, NJ to Aaa from Aa1.... The upgrade to Aaa rating reflects the borough's strong financial operations with healthy reserve levels, sizeable tax base, conservative management practices, strong socioeconomic wealth levels, and low debt burden."
- ^ Plan Components Report Archived February 19, 2020, at the Wayback Machine, New Jersey Redistricting Commission, December 23, 2011. Accessed February 1, 2020.
- ^ Municipalities Sorted by 2011-2020 Legislative District Archived November 20, 2021, at the Wayback Machine, New Jersey Department of State. Accessed February 1, 2020.
- ^ 2019 New Jersey Citizen's Guide to Government Archived November 5, 2019, at the Wayback Machine, New Jersey League of Women Voters. Accessed October 30, 2019.
- ^ Districts by Number for 2011–2020 Archived July 14, 2019, at the Wayback Machine, New Jersey Legislature. Accessed January 6, 2013.
- ^ Directory of Representatives: New Jersey, United States House of Representatives. Accessed January 3, 2019.
- ^ Biography, Congressman Josh Gottheimer. Accessed January 3, 2019. "Josh now lives in Wyckoff, New Jersey with Marla, his wife who was a federal prosecutor, and their two young children, Ellie and Ben."
- ^ U.S. Sen. Cory Booker cruises past Republican challenger Rik Mehta in New Jersey, PhillyVoice. Accessed April 30, 2021. "He now owns a home and lives in Newark's Central Ward community."
- ^ https://www.nytimes.com/2024/08/23/nyregion/george-helmy-bob-menendez-murphy.html
- ^ Tully, Tracey (August 23, 2024). "Menendez's Senate Replacement Has Been a Democrat for Just 5 Months". The New York Times. Retrieved August 23, 2024.
- ^ Legislative Roster for District 38, New Jersey Legislature. Accessed January 20, 2024.
- ^ County Executive, Bergen County, New Jersey. Accessed March 16, 2023.
- ^ Vice Chairman Commissioner Chairman Thomas J. Sullivan, Bergen County, New Jersey. Accessed March 16, 2023.
- ^ Commissioner Vice Chairwoman Germaine M. Ortiz, Bergen County, New Jersey. Accessed March 16, 2023.
- ^ Commissioner Chair Pro Tempore Dr. Joan M. Voss, Bergen County, New Jersey. Accessed March 16, 2023.
- ^ Commissioner Mary J. Amoroso, Bergen County, New Jersey. Accessed March 16, 2023.
- ^ Cattafi, Kristie. "Democrats pick Bergenfield councilman to fill vacancy on Bergen County commissioners board", The Record, March 13, 2023. Accessed March 16, 2023. "A Democratic councilman from Bergenfield will be sworn in as a Bergen County commissioner Wednesday night, filling a vacancy on the governing body for almost 1 million residents. Rafael Marte will serve until Dec. 31, taking on the unexpired term left by former Commissioner Ramon Hache, a Democrat who resigned last week to lead the Ridgewood YMCA as its chief executive officer."
- ^ Commissioner Steven A. Tanelli, Bergen County, New Jersey. Accessed March 16, 2023.
- ^ Commissioner Tracy Silna Zur, Bergen County, New Jersey. Accessed March 16, 2023.
- ^ Board of County Commissioners, Bergen County, New Jersey. Accessed March 16, 2023.
- ^ 2022 County Data Sheet, Bergen County, New Jersey. Accessed March 16, 2023.
- ^ a b 2022 County and Municipal Directory, Bergen County, New Jersey, March 2022. Accessed January 30, 2023.
- ^ Bergen County November 8, 2022 General Election Statement of Vote, Bergen County, New Jersey Clerk, updated November 21, 2022. Accessed January 1, 2023.
- ^ Bergen County Statement of Vote November 2, 2021 Official results, Bergen County, New Jersey, updated November 17, 2021. Accessed January 1, 2022.
- ^ Precinct Summary Results Report - Combined 2020 Bergen County General Election - November 3, 2020 Official Results, Bergen County, New Jersey, December 3, 2020. Accessed January 1, 2021.
- ^ Bergen County November 5, 2019 General Election Statement of Vote, Bergen County, New Jersey Clerk, updated December 10, 2019. Accessed January 1, 2020.
- ^ About the Clerk, Bergen County Clerk. Accessed March 16, 2023.
- ^ Clerks, Constitutional Officers Association of New Jersey. Accessed March 16, 2023.
- ^ Sheriff Anthony Cureton, Bergen County Sheriff's Office. Accessed March 16, 2023.
- ^ Sheriffs, Constitutional Officers Association of New Jersey. Accessed March 16, 2023.
- ^ Michael R. Dressler, Bergen County Surrogate's Court. Accessed March 16, 2023.
- ^ Surrogates, Constitutional Officers Association of New Jersey. Accessed March 16, 2023.
- ^ Constitutional Officers, Bergen County, New Jersey. Accessed March 16, 2023.
- ^ a b Voter Registration Summary – Bergen Archived September 25, 2018, at the Wayback Machine, New Jersey Department of State Division of Elections, March 23, 2011. Accessed December 12, 2013.
- ^ GCT-P7: Selected Age Groups: 2010 – State – County Subdivision; 2010 Census Summary File 1 for New Jersey Archived February 12, 2020, at archive.today, United States Census Bureau. Accessed December 12, 2013.
- ^ Presidential November 8, 2016 General Election Results - Bergen County Archived November 4, 2020, at the Wayback Machine, New Jersey Department of State Division of Elections, November 8, 2016. Accessed May 24, 2020.
- ^ Presidential November 6, 2012 General Election Results – Bergen County Archived December 7, 2013, at the Wayback Machine, New Jersey Department of State Division of Elections, March 15, 2013. Accessed December 14, 2013.
- ^ Number of Registered Voters and Ballots Cast November 6, 2012 General Election Results – Bergen County Archived December 7, 2013, at the Wayback Machine, New Jersey Department of State Division of Elections, March 15, 2013. Accessed December 14, 2013.
- ^ 2008 Presidential General Election Results: Bergen County Archived September 27, 2018, at the Wayback Machine, New Jersey Department of State Division of Elections, December 23, 2008. Accessed December 12, 2013.
- ^ 2008 General Election Results for Paramus Archived October 5, 2011, at the Wayback Machine, The Record. Accessed August 22, 2011.
- ^ 2004 Presidential Election: Bergen County Archived September 27, 2018, at the Wayback Machine, New Jersey Department of State Division of Elections, December 13, 2004. Accessed December 12, 2013.
- ^ "Governor – Bergen County" (PDF). New Jersey Department of Elections. January 29, 2014. Archived (PDF) from the original on November 28, 2018. Retrieved December 24, 2014.
- ^ "Number of Registered Voters and Ballots Cast – November 5, 2013 – General Election Results – Bergen County" (PDF). New Jersey Department of Elections. January 29, 2014. Archived (PDF) from the original on November 28, 2018. Retrieved December 24, 2014.
- ^ 2009 Governor: Bergen County Archived December 7, 2013, at the Wayback Machine, New Jersey Department of State Division of Elections, December 31, 2009. Accessed December 12, 2013.
- ^ District information for Paramus Public School District Archived November 12, 2020, at the Wayback Machine, National Center for Education Statistics. Accessed April 1, 2020.
- ^ School Data for the Paramus Public Schools Archived February 3, 2023, at the Wayback Machine, National Center for Education Statistics. Accessed December 7, 2016.
- ^ Memorial Elementary School Archived May 4, 2020, at the Wayback Machine, Paramus Public Schools. Accessed May 21, 2020.
- ^ Midland Elementary School Archived May 4, 2020, at the Wayback Machine, Paramus Public Schools. Accessed May 21, 2020.
- ^ Parkway Elementary School Archived May 4, 2020, at the Wayback Machine, Paramus Public Schools. Accessed May 21, 2020.
- ^ Ridge Ranch Elementary School Archived May 4, 2020, at the Wayback Machine, Paramus Public Schools. Accessed May 21, 2020.
- ^ Stony Lane Elementary School Archived May 4, 2020, at the Wayback Machine, Paramus Public Schools. Accessed May 21, 2020.
- ^ Eastbrook Middle School Archived May 20, 2020, at the Wayback Machine, Paramus Public Schools. Accessed May 21, 2020.
- ^ Westbrook Middle School Archived May 4, 2020, at the Wayback Machine, Paramus Public Schools. Accessed May 21, 2020.
- ^ Paramus High School Archived May 20, 2020, at the Wayback Machine, Paramus Public Schools. Accessed May 21, 2020.
- ^ Our Schools Archived May 4, 2020, at the Wayback Machine, Paramus Public Schools. Accessed May 21, 2020.
- ^ New Jersey School Directory for the Paramus Public Schools, New Jersey Department of Education. Accessed February 1, 2024.
- ^ Glovin, David. "Two Bergen Schools Pocket National Awards", The Record, May 22, 1999. Accessed June 29, 2011. "The Cherry Hill School in River Edge and the Ridge Ranch School in Paramus were among the 266 public and private elementary schools that were named 1998–99 Blue Ribbon Schools by the U.S. Education Department."
- ^ Blue Ribbon Schools Program: Schools Recognized 1982–1983 through 1999–2002 (PDF) Archived March 26, 2009, at the Wayback Machine, United States Department of Education, pp. 53–54. Accessed March 27, 2011.
- ^ About Us Archived October 14, 2013, at the Wayback Machine, Bergen County Technical Schools. Accessed December 12, 2013.
- ^ Admissions Archived March 5, 2017, at the Wayback Machine, Bergen County Technical Schools. Accessed December 29, 2016.
- ^ Bergen County Catholic High Schools Archived August 12, 2017, at the Wayback Machine, Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Newark. Accessed July 20, 2016.
- ^ Alex, Patricia. "Pope held special spot in hearts of youth", The Record, April 5, 2005. Accessed August 21, 2008. "Today a memorial Mass will be celebrated at the school – the largest Catholic school in the state, and the rosary will be said in 10 languages..."
- ^ Bergen County Catholic High Schools Archived August 14, 2015, at the Wayback Machine, Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Newark. Accessed June 1, 2015.
- ^ Mission Statement, Yavneh Academy. Accessed December 26, 2011.
- ^ Capital Campaign, Yeshivat Noam. Accessed December 25, 2011.
- ^ Lipowsky, Josh. "Ben Porat Yosef headed for Paramus" Archived January 27, 2020, at the Wayback Machine, Jewish Standard, August 22, 2008. Accessed January 27, 2020. "After seven years of renting space in a Leonia synagogue, Yeshiva Ben Porat Yosef is moving into the old Frisch building rather than the Jewish Center of Teaneck as its board had planned.... Ben Porat Yosef had held classes in Sons of Israel since the school was founded in 2001 and needed more space each year as it added grades... When the prospect arose for BPY to move the entire school to Paramus, however, the yeshiva had to take it, said Yehuda Kohn, BPY’s vice president."
- ^ Thirty-Fifth Annual Dinner Journal Archived March 26, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, Frisch School, February 7, 2009, p. 18. Accessed June 29, 2011. "Under his direction, our school has grown to be the second largest coed yeshiva high school in the United States."
- ^ About Bergen Community College Archived May 19, 2015, at the Wayback Machine. Bergen Community College. Accessed June 1, 2015. Founded in 1965 to satisfy the region's need for a convenient, affordable and comprehensive higher education destination, Bergen Community College now enrolls nearly 17,000 students in its academic degree programs. The College's three sites in Paramus (main campus), Hackensack (Ciarco Learning Center) and Lyndhurst (Bergen Community College at the Meadowlands) serve more than 32,000 students in degree, continuing education and adult education programs."
- ^ Paramus Archived October 24, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, Berkeley College. Accessed October 24, 2014.
- ^ Paramus Archived July 9, 2015, at the Wayback Machine, DeVry University. Accessed August 1, 2015.
- ^ Lincoln Tech | Paramus, NJ Campus Archived August 12, 2015, at the Wayback Machine. Accessed August 14, 2015.
- ^ Overview Archived November 7, 2017, at the Wayback Machine, New Alliance Academy. Accessed October 6, 2019.
- ^ Bleshman Regional Day School, Bergen County Special Services School District. Accessed April 21, 2024.
- ^ Home Page Archived May 6, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, EPIC School. Accessed October 24, 2014.
- ^ History Archived October 25, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, Alpine Learning Group. Accessed October 24, 2014.
- ^ Contact Us Archived October 31, 2016, at the Wayback Machine, ECLC of New Jersey. Accessed October 31, 2016.
- ^ Admissions, Bergen County Special Services School District. Accessed April 21, 2024.
- ^ Home page Archived August 25, 2008, at the Wayback Machine, Paramus Public Library. Accessed August 24, 2008.
- ^ Paramus Municipal Parks, Borough of Paramus. Accessed June 29, 2011.
- ^ Acute and Ambulatory Care, Substance Abuse Treatment, Behavioral Health, Long Term Care Archived July 14, 2018, at the Wayback Machine, New Bridge Health. Accessed August 5, 2018.
- ^ Oradell Animal Hospital | Emergency Veterinarian NJ | Animal Hospital Paramus NJ | Veterinarian Paramus Archived August 6, 2018, at the Wayback Machine. Oradell Animal Hospital. Accessed August 5, 2018.
- ^ Bergen County Mileage by Municipality and Jurisdiction Archived July 17, 2018, at the Wayback Machine, New Jersey Department of Transportation, July 2015. Accessed April 28, 2016.
- ^ Route 17 Straight Line Diagram Archived February 1, 2023, at the Wayback Machine, New Jersey Department of Transportation, updated May 2017. Accessed January 31, 2023.
- ^ Route 4 Straight Line Diagram Archived October 28, 2022, at the Wayback Machine, New Jersey Department of Transportation, updated May 2017. Accessed January 31, 2023.
- ^ Garden State Parkway Straight Line Diagram Archived March 7, 2023, at the Wayback Machine, New Jersey Department of Transportation, updated August 2014. Accessed January 31, 2023.
- ^ Travel Resources: Interchanges, Service Areas & Commuter Lots Archived December 13, 2007, at the Wayback Machine, New Jersey Turnpike Authority. Accessed October 30, 2013.
- ^ Bergen County Bus / Rail Connections, NJ Transit, backed up by the Internet Archive as of May 22, 2009. Accessed November 24, 2011.
- ^ Bergen County System Map Archived August 6, 2019, at the Wayback Machine, NJ Transit. Accessed September 14, 2016.
- ^ Available Schedules from Paramus, NJ to New York, NY.[permanent dead link], Coach USA. Accessed December 12, 2013.
- ^ Jitney Transportation Along New Jersey's Route 4 Corridor Archived November 2, 2013, at the Wayback Machine, Columbia University Urban Transportation Policy, December 2006. Accessed September 14, 2016.
- ^ Paterson – George Washington Bridge Archived February 25, 2017, at the Wayback Machine, Jitney Buses of New Jersey. Accessed September 14, 2016.
- ^ New Jersey and National Registers of Historic Places Archived May 16, 2013, at the Wayback Machine, New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection Historic Preservation Office, updated August 17, 2017. Accessed September 24, 2017.
- ^ Easton Tower Archived August 28, 2017, at the Wayback Machine, Bergen County, New Jersey. Accessed September 24, 2017.
- ^ Midland School – Nomination Form, National Register of Historic Places, received December 12, 1977. Accessed October 30, 2013.
- ^ Terhune House – Nomination Form, National Register of Historic Places, received June 14, 1995. Accessed October 30, 2013.
- ^ Terhune-Gardner-Lindenmeyr House – Nomination Form, National Register of Historic Places, received December 7, 1971. Accessed October 30, 2013.
- ^ Harmon Van Dien House – Nomination Form, National Register of Historic Places. Accessed June 11, 2014.
- ^ Albert J. Zabriskie Farmhouse – Nomination Form, National Register of Historic Places, received April 21, 1977. Accessed June 11, 2014.
- ^ Ensslin, John C. "Preservation effort falls short as Zabriskie house demolition begins (video)" Archived July 17, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, The Record, July 13, 2012. Accessed July 18, 2012. "An irreplaceable link to Bergen's County's early history, particularly for African-Americans, vanished in a cloud of dust on Friday as a backhoe clawed at the splintered wood and brownstone remains of the Zabriskie Tenant House, a 1780s building that later became home to generations of former slaves and their descendents."
- ^ Buehler Challenger & Science Center Archived June 5, 2016, at the Wayback Machine. Accessed May 29, 2016.
- ^ About Us Archived August 3, 2015, at the Wayback Machine, Paramus Fritz Behnke Historical Museum. Accessed August 13, 2015.
- ^ Pries, Allison. "New Jersey Children's Museum to close next month" Archived September 22, 2015, at the Wayback Machine, The Record, August 15, 2014. Accessed August 13, 2015. "It was just another familiar, fun moment for young imaginations at the New Jersey Children's Museum, a community touchstone for thousands of North Jersey children, parents and grandparents over the past 22 years.... The site the museum operates out of was sold in February to Valley Health Systems, which will convert it to its needs, Sumers said."
- ^ Volunteer Fire Department Archived October 6, 2019, at the Wayback Machine, Borough of Paramus. Accessed October 6, 2019.
- ^ Rescue Squad Archived January 22, 2023, at the Wayback Machine, Borough of Paramus. Accessed January 22, 2023.
- ^ Emergency Medical Services department Archived May 24, 2018, at the Wayback Machine, Borough of Paramus. Accessed May 30, 3018
- ^ About Us Archived May 8, 2016, at the Wayback Machine, Paramus Volunteer Ambulance Corps. Accessed May 30, 2018.
- ^ Home page Archived June 3, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, Paramus Police Department. Accessed November 18, 2012.
- ^ Office of Emergency Management Archived January 22, 2023, at the Wayback Machine, Borough of Paramus. Accessed January 22, 2023.
- ^ Paranoid Tour - Black Sabbath Online Archived January 19, 2022, at the Wayback Machine Accessed March 19, 2022.
- ^ Rockapella - Past Tour Dates Archived February 18, 2022, at the Wayback Machine Accessed February 18, 2022.
- ^ Wiggins, Ovetta. "Cone-Town, Usa – Ask Any Alien: It's A Great Place To Live Pointed Praise", The Record, July 24, 1993. Accessed May 28, 2007.
- ^ Levy, Emanuel. "Burn After Reading: Shooting a Joel and Ethan Coen Wild Comedy" Archived July 14, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, Emanuel Levy Cinema 24/7, August 24, 2008. Accessed December 12, 2013. "The unit soon decamped to Paramus, New Jersey, where all the scenes that transpire at Hardbodies Fitness Center the workplace of Linda, Chad, and Ted were filmed. At an abandoned building that had until recently housed a Tower Records, Gonchor and his department with a fitness-equipment assist from Gym Source transformed the newly emptied space into a working gym."
- ^ Schager, Nick. "The 10 Best Movies Set in New Jersey; A state that deserves more cinematic recognition" Archived December 1, 2015, at the Wayback Machine, Esquire, June 20, 2014. Accessed September 7, 2015. "Much of Ron Howard's Ransom was filmed in and around New York and New Jersey, and Mel Gibson's first attempt to hand over money in exchange for his kidnapped son is clearly set at a Haledon, New Jersey, quarry — a location that Gibson arrives at after driving from Manhattan to Jersey City (via the Holland Tunnel), and then on through Paramus."
- ^ Barth, Jack. Roadside Hollywood: The Movie Lover's State-By-State Guide to Film Locations, Celebrity Hangouts, Celluloid Tourist Attractions, and More, p. 192. Contemporary Books, 1991. ISBN 9780809243266. Accessed April 13, 2016. "Directed by New Jersey's Susan Seidelman. Something Wild (Rahway, Paramus, Ringwood, New Jersey Turnpike, Jersey City, 1986)"
- ^ Parrilo, Rosemary. "The Locations" Archived May 15, 2010, at the Wayback Machine, The Star-Ledger, March 4, 2001. Accessed September 10, 2013.
- ^ The Sopranos location guide Archived March 9, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, Accessed October 10, 2013.
- ^ "'RHONJ' Star Jennifer Aydin Shows Off 20,000 Square Foot 'Palace of Paramus'", Accessed April 27, 2024.
- ^ Nash, Margo. "Footlights; All About A, And Don't Forget Z" Archived July 25, 2018, at the Wayback Machine, The New York Times, September 4, 2005. Accessed October 16, 2018. "When it came time to choose a shopping center, the video's makers headed, quite naturally, to New Jersey. Mr. Colbert, dressed as a big blue letter Z, and Ms. Sullivan, appearing as a big red A, are shown in the video ambling around the Garden State Mall [sic], asking people if they know any words with their letters in them. Ms. Sullivan got a lot more responses than Mr. Colbert."
- ^ Galant, Debra. "Bowling, Once a First Date, Now Takes Back Seat" Archived September 25, 2015, at the Wayback Machine, The New York Times, December 10, 2000. Accessed September 30, 2015. "Even people who never set foot there remember seeing Paramus Lanes on the 1950s television shows Make That Spare and Championship Bowling."
- ^ hanson events: 1997 Archived May 28, 2019, at the Wayback Machine. Accessed May 30, 2018.
- ^ Macatee, Rebecca. "Why Hanson's 'Scary' Choices Worked: Zac Hanson Talks 20 Years of 'MMMBop' and His Future With Taylor and Isaac" Archived April 7, 2018, at the Wayback Machine, E!, May 6, 2017. Accessed May 30, 2018. "'The first girls we heard screaming were not at Paramus Park Mall in New Jersey when we did our first public performance after "MMMBop" came out,' the father of four adds with a laugh."
- ^ Sullivan, Tricia. Maul Archived July 6, 2018, at the Wayback Machine, Publishers Weekly. Accessed July 6, 2018.
- ^ Paramus professor shows 'what she would do' on hidden camera show Archived October 29, 2020, at the Wayback Machine NorthJersey.com. Accessed October 26, 2020
- ^ Olympic star Adam Rippon joins 'What Would You Do?' scenario about coming out Archived August 22, 2020, at the Wayback Machine ABCNews.com. Accessed October 26, 2020.
- ^ John Bancker Aycrigg Archived October 25, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, Biographical Directory of the United States Congress. Accessed February 8, 2011.
- ^ Zeitchik, Steven. "In Person; Meet Joe Fan" Archived December 27, 2013, at the Wayback Machine, The New York Times, January 23, 2005. Accessed December 25, 2011. "Amid the swirl of the New York region's media personalities, most people have probably never heard of Mr. Benigno. But as the longtime host of WFAN's overnight program, the Garfield-born, Paramus-bred broadcaster combined an uncommon mix of black humor, esoteric knowledge and incredulity to become a cult figure."
- ^ "Football players make a difference at NFL Alumni's Charity Golf Classic" Archived June 25, 2010, at the Wayback Machine, June 21, 2010. "'Our time in the league typically doesn't last too long but the impact we can make sure can,' said Blackburn, who drove up from Paramus, New Jersey."
- ^ Juwann Bushell-Beatty Archived December 1, 2021, at the Wayback Machine, Michigan Wolverines football. Accessed December 7, 2021. "Hometown: Paramus, N.J. High School: Paramus Catholic"
- ^ Wilner, Barry via Associated Press. "Boundaries Melt As Skating Pair Unites" Archived October 24, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, Rocky Mountain News, January 12, 1992. Accessed February 8, 2011. "Galit Chait, a 16-year-old from Paramus, N.J., and Maxim Sevostianov of Cheljabinsk, Russia, weren't close to the best dancers at the event. They were among the most intriguing."
- ^ Oshinsky, David M. "Charge It!" Archived August 10, 2017, at the Wayback Machine, The New York Times, March 2, 2003. Accessed September 15, 2011. "Cohen belongs to the postwar baby boom generation. Raised in Paramus, N.J., an epicenter of tract housing and highway shopping malls, she has used the experience of the Garden State to probe the larger issues of postwar economic change."
- ^ Whelan, Jeff S. "Former state Sen. Coniglio indicted on corruption charges" Archived October 14, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, The Star-Ledger, February 14, 2008. Accessed February 8, 2011. "Coniglio, a Bergen County Democrat, allegedly helped Hackensack University Medical Center obtain millions of dollars in state funding in exchange for a $5,000 per month-job as a 'hospital relations' consultant, according to the indictment. The 65-year-old retired plumber from Paramus had no prior experience for such a job, authorities said."
- ^ Ensslin, John C. "Former lawmaker Paul Contillo named to fill interim Assembly seat" Archived September 25, 2015, at the Wayback Machine, The Record, October 20, 2013. Accessed September 24, 2015. "A Brooklyn native, Contillo founded and ran two New York printing firms. He has lived since 1955 in Paramus, where he served on the borough council from 1971 to 1973. He previously served in the Assembly from 1973 to 1979."
- ^ Cooper, Darren. "Notre Dame-bound Howard Cross III, of St. Joseph, not held down by family name", The Record, October 2, 2018. Accessed October 19, 2023. "Howard Cross III was born into football, but his love of the game grew organically. Cross III, the St. Joseph Regional senior defensive lineman from Paramus, carries the same name as his father, a Super Bowl winner for the New York Giants, but the elder Cross never pushed his son into the sport."
- ^ Toribio, Elyse. "Paramus High School Grad and Clueless Actress Stacey Dash Gets Backlash for Romney Support" Archived June 1, 2016, at the Wayback Machine, The Beat of North Jersey, October 10, 2012. Accessed June 1, 2015. "The 46-year-old Paramus High School graduate took to the Piers Morgan Show on CNN Tuesday night to express her surprise at all the negative commentary and reiterate her endorsement of Romney."
- ^ Smith, Marcia C. "Behind the scenes with voice of Lakers" Archived October 16, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, The Orange County Register, April 22, 2010. Accessed May 26, 2010.
- ^ Levine, Cecilia. "Paramus Pro Wrestler Who Lost Daughter Has New Purpose: 'End Drunk Driving'" Archived November 24, 2017, at the Wayback Machine, Paramus Daily Voice, October 21, 2017. Accessed November 18, 2017. "Oct. 10, 2015 was the day life both stopped and started for Paramus native Bill DeMott.... DeMott graduated from Paramus High School in 1983, and went on to become a pro wrestler, earning himself the title of world heavyweight champion, and more."
- ^ Ditrani, Vinny. "Paramus' Jim Dray looks to sway NFL teams at combine" Archived July 14, 2011, at the Wayback Machine, The Record, February 26, 2010. Accessed February 16, 2011. "Former Bergen Catholic and Stanford star Jim Dray is among the better blocking tight ends at this year's NFL combine."
- ^ Farrell, Warren; and Gray, John. The Boy Crisis: Why Our Boys Are Struggling and What We Can Do About It Archived September 30, 2023, at the Wayback Machine, p. 222. BenBella Books, 2018. ISBN 9781946885807. Accessed March 26, 2020. "Like Gabriel, I had just moved to a new neighborhood, in Waldwick, New Jersey, and had spent too much time talking positively about my old neighborhood in Paramus."
- ^ Fat Joe Archived March 12, 2016, at the Wayback Machine, MTV Cribs. Accessed March 22, 2016.
- ^ Pinto, Fausto Giovanny. "The hip-hop homes of Bergen County" Archived July 30, 2019, at the Wayback Machine, NJ Advance Media for NJ.com, September 2016. Accessed July 30, 2019. "The Terror Squad founder and 'Lean Back' lyricist's Paramus home was featured on a 2004 episode of MTV Cribs, in which he licked the bottom of a pair of Air Jordan sneakers valued at $5,000."
- ^ Maynard, Micheline. "Private Sector; Rising at Ford, Without Fanfare" Archived March 5, 2016, at the Wayback Machine, The New York Times, May 5, 2002. Accessed December 25, 2011. "Born in Brooklyn and raised in Paramus, N.J., Mr. Fields has an atypical automotive career – he came to Ford from a series of marketing positions at I.B.M."
- ^ Hicks, Robert. "American songwriter finds success in United Kingdom"[permanent dead link], Daily Record, April 20, 2007. Accessed May 28, 2007. "Friedman grew up in Paramus."
- ^ Goulis, Thalia; and Jablonski, Marc. Paramus[permanent dead link], p. 112. Arcadia Publishing, 2015. ISBN 9781439649671. Accessed December 18, 2017. "The glam rock band Trixter, popular in the 1990s, was formed by four of the town's residents, and Dean Friedman, best known for the 1977 hit 'Ariel,' included lyrics in his song about a girl 'standing by the water fall in Paramus Park' and references the town as the 'bosom of suburbia.'"
- ^ Saxon, Wolfgang. "Fred C. Galda, 79, Retired Judge" Archived December 27, 2017, at the Wayback Machine, The New York Times, August 19, 1997. Accessed December 25, 2011. "Fred C. Galda, a retired New Jersey Superior Court judge and former prosecutor and Mayor of Paramus, N.J., died on Thursday at Valley Hospital in Ridgewood, N.J. He was 79 and a resident of Saddle River, N.J."
- ^ Shanley, John P. "Gennaro – Como's Dancing Master" Archived October 16, 2018, at the Wayback Machine, The New York Times, October 15, 1961. Accessed October 16, 2018. ""They live in a converted barn in Paramus, N. J., with their children, Michael, 11 years old, and Liza, 3."
- ^ Robbins, Liz. "Olympics; Beating Unbeatable Foe Makes a Dream Possible" Archived March 5, 2016, at the Wayback Machine, The New York Times, June 23, 2000. Accessed December 25, 2011. "The Iranian-born Greco-Roman heavyweight who moved to Paramus, N.J., at 15 stood on the podium feeling as if he had let down the United States."
- ^ Friess, Steve. "Tournament Winner Says He Was Wrong" Archived November 30, 2018, at the Wayback Machine, The New York Times, February 24, 2007. Accessed December 25, 2011. "In his first interview since the settlement, Gold, a 38-year-old Hollywood producer from Paramus, N.J., said the lawsuit was not difficult to resolve, although the agreement bars him from disclosing the fate of the record-setting $12 million purse."
- ^ Troncone, Tom. "$6M of record poker pot at stake" Archived October 6, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, The Record, September 20, 2006. Accessed July 18, 2012. "On one side of the table sits Jamie Gold, a former Paramus resident who dominated the competition en route to the coveted World Series of Poker championship last month."
- ^ Goldrich, Lois. "Activist helps indigenous communities adapt to changing climate Survivor’s granddaughter pursues a personal commitment to human rights" Archived August 25, 2021, at the Wayback Machine, Jewish Standard, December 7, 2017. Accessed August 30, 2021. "Growing up in Paramus, Victoria Herrmann heard a lot of stories from her grandfather, Fair Lawn’s Siegfried Herrmann."
- ^ Jordan, Chris. "From Paramus to the world: How Matt Hunter became a Latin music star" Archived July 29, 2019, at the Wayback Machine, The Record, July 29, 2019. Accessed July 30, 2019. "Meet Matt Hunter, a contemplative 21-year-old from Paramus who makes them scream in Colombia, Mexico, Chile and beyond."
- ^ Charles Samuel Joelson Archived July 20, 2006, at the Wayback Machine, Biographical Directory of the United States Congress. Accessed February 8, 2011.
- ^ Louis F. Kosco, New Jersey Legislature, archived by the Internet Archive on February 25, 1998. Accessed May 26, 2010.
- ^ Assemblyman Joseph A. Lagana Archived November 2, 2015, at the Wayback Machine, New Jersey Legislature, New Jersey Legislature. Accessed September 24, 2015.
- ^ Beckerman, Jim. "Hollywood weighs in on 9/11", The Record, April 23, 2006. Accessed May 26, 2010. "... you're particularly sensitive and you're out for an evening of fun and the trailer catches you unaware it could be upsetting says Levin a Paramus native ..."
- ^ Coutros, Evonne. "Who's the boss now? – Paramus actor worked his way up to role he couldn't refuse", The Record, February 9, 2003. Accessed October 14, 2007.
- ^ Staff. "The Closing: Howard Lorber" Archived July 4, 2011, at the Wayback Machine, The Real Deal, July 1, 2006. Accessed February 8, 2011. "Where were you born and where did you grow up? I was born in the Bronx and grew up in Paramus, N.J., until I moved to Long Island for college."
- ^ Staff. "Ex-Mayor, Others Are Sued By U.S." Archived November 1, 2013, at the Wayback Machine, The Philadelphia Inquirer, July 21, 1983. Accessed October 30, 2013. "Also named in the action was Herbert Maddalene of Paramus, who was not charged in the racketeering case."
- ^ About Trisha Archived February 28, 2015, at the Wayback Machine, CentralParkJogger.com. Accessed March 3, 2015. "Born and raised in Paramus, New Jersey, and Pittsburgh, Trisha was a Phi Beta Kappa economics major at Wellesley College and a double graduate degree recipient (M.B.A. and M.A.) at Yale University."
- ^ Maag, Christopher. "Sen. Menendez moves to Bergen County", The Record, July 5, 2014. Accessed October 24, 2014. "Menendez first talked publicly about his move at a political fundraiser in Edgewater on Wednesday night, where he announced not only that he will support Democrat James Tedesco's campaign for Bergen County executive, he'll also be voting for Tedesco in the November election. 'Yes that is correct. He lives in Paramus now," said Steven Sandberg, a spokesman for Menendez."
- ^ Liv Morgan Archived March 1, 2017, at the Wayback Machine, Online World of Wrestling. Accessed April 13, 2016. "Hometown: Paramus, New Jersey, USA"
- ^ Fujimori, Sachi. "Edgewater comedian works to counter stereotypes of Muslims" Archived October 10, 2013, at the Wayback Machine, The Record, January 17, 2011. Accessed December 25, 2011. "WHAT: The Big Brown Comedy Hour hosted by Daily Show correspondent Aasif Mandvi and featuring Maysoon Zayid, Dean Obeidallah (grew up in Lodi and Paramus) and others."
- ^ Staff. "George Olsen, 78, Bandleader Of the 20s and 30s, Is Dead" Archived July 11, 2018, at the Wayback Machine, The New York Times, March 19, 1971. Accessed December 18, 2017. "Paramus, N.J., March 18— George Olsen, musician and band leader, perhaps best known as an recording star of the 1920s and 1930s, died here today on his 78th birthday. He lived at 711 Paramus Road."
- ^ Pennington, Juliet. "Ken Oringer is hungry for street food, a good walk" Archived September 25, 2015, at the Wayback Machine, The Boston Globe, December 6, 2014. Accessed September 24, 2015. "When he isn't working at his flagship Clio or one of his other five eateries, Oringer enjoys his time at home in the South End with his wife, Celine, daughter, Verveine, and son, Luca. We caught up with Oringer, 49, a Paramus, N.J., native, to talk about all things travel."
- ^ Staff. "The New York genealogical and biographical record, Volumes 11–13" Archived April 8, 2023, at the Wayback Machine, p. 28. New York Genealogical and Biographical Society, 1880. Accessed February 8, 2011.
- ^ Beam, Chris. "A Cheating Scandal Has Rocked the Chess World. The ‘Chess Detective’ Is on the Case", Time, November 3, 2022. Accessed January 3, 2024. "Growing up in Paramus, New Jersey, Regan began playing chess with his father at five years old and beat him after six months."
- ^ Mills, Ed. "College football: Honors aplenty for Paramus native John Robertson" Archived December 22, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, The Record, December 18, 2014. Accessed December 21, 2014. "The honors just keep pouring in for John Robertson. And the former Paramus High School standout certainly has earned them with exceptional double-duty displays of skill and hard work."
- ^ Levin, Jay. "Ira Rubin, world champion bridge player, dies at 82" Archived March 10, 2016, at the Wayback Machine, The Record, February 7, 2013. Accessed January 6, 2015. "Ira Rubin, who lived in Paramus for 35 years and in Fair Lawn before that, is survived by his children, Loribeth Kimmel, Eric Rubin and Jeffrey Rubin, and his former wife, Harriet Rubin."
- ^ Sullivan, Joseph F. "Man In The News; Agile Nominee For Jersey High Court" Archived November 28, 2018, at the Wayback Machine, The New York Times, October 11, 1984. Accessed November 17, 2017. "He also became interested in local politics in Paramus, where he moved after he married, and made an unsuccessful run for Mayor in 1964."
- ^ Nick Suriano Archived September 30, 2023, at the Wayback Machine, National Wrestling Hall of Fame. Accessed January 1, 2023. "Nick Suriano of Paramus, New Jersey is a four-time New Jersey High School state champion and only the second wrestler in history to finish his career without a loss, going 159-0 for Bergen Catholic High School in Oradell, New Jersey."
- ^ Bell, Jack. "U.S. Women's Coach Pleads for Better Players" Archived September 28, 2010, at the Wayback Machine, The New York Times, May 18, 2009. Accessed February 8, 2011. "'They've made a concerted effort to bring loads of Brazilian players and coaches and have followed the Brazilian philosophy, which is about having great technical skills and playing a beautiful game,' Tambi said during a recent interview at his home in Paramus, N.J."
- ^ "Rutgers Receives $1.5 Million Gift for Neuroscience/Brain Health Faculty Position as Part of "Our Rutgers, Our Future" CampaignDonation answers call to $27 million challenge to establish 18 endowed chairs" Archived November 2, 2013, at the Wayback Machine, Rutgers Today, March 7, 2012. Accessed October 30, 2013. "Temares, who graduated from Rutgers with a bachelor's degree in economics, and went on to earn a law degree from the University of Pennsylvania Law School, was born in the Bronx and grew up in Paramus."
- ^ Corcoran, David. "Theodore Trautwein, Judge in Landmark Press Case, Dies at 80" Archived January 12, 2016, at the Wayback Machine, The New York Times, September 2, 2000. Accessed October 6, 2019. "Theodore Walter Trautwein was born on March 29, 1920, in Paramus, N.J."
- ^ Assemblywoman Connie Wagner Archived June 3, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, New Jersey Legislature. Accessed February 8, 2011.
- ^ Passow, Sam. "Passing Down Stories: Oradell resident Yoojin Grace Wuertz" Archived June 18, 2017, at the Wayback Machine, The Record, April 4, 2017. Accessed June 5, 2017. "Wuertz, who lives in Oradell after growing up in Paramus and Ridgefield Park, released Everything Belongs to Us in February."
- ^ Bondy, Filip. "Figure Skating; Zayak's Biggest Jump: A Leap Into the Past" Archived January 17, 2018, at the Wayback Machine, The New York Times, May 16, 1993. Accessed October 14, 2007. "Her father, Richard Zayak, would drive from their home in Paramus, N.J., to her New York practice rinks in Farmingdale or Monsey and offer his daughter $1 per perfect jump."
General sources
edit- Municipal Incorporations of the State of New Jersey (according to Counties) prepared by the Division of Local Government, Department of the Treasury (New Jersey); December 1, 1958.
- Behnke, Fritz. Paramus: The Way We Were 1922–1960, Destiny Image Publishers, 1997. ISBN 9781560432043.
- Clayton, W. Woodford; and Nelson, William. History of Bergen and Passaic Counties, New Jersey, with Biographical Sketches of Many of its Pioneers and Prominent Men., Philadelphia: Everts and Peck, 1882.
- Harvey, Cornelius Burnham (ed.), Genealogical History of Hudson and Bergen Counties, New Jersey. New York: New Jersey Genealogical Publishing Co., 1900.
- Van Valen, James M. History of Bergen County, New Jersey. New York: New Jersey Publishing and Engraving Co., 1900.
- Westervelt, Frances A. History of Bergen County, New Jersey, 1630–1923, Lewis Historical Publishing Company, 1923.