Orbital part of inferior frontal gyrus
The orbital part of inferior frontal gyrus also known as the pars orbitalis is the orbital part of the inferior frontal gyrus.[1]
| Orbital part of inferior frontal gyrus | |
|---|---|
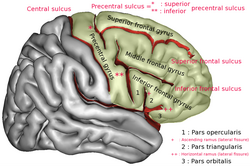 Orbital part of inferior frontal gyrus labelled 3. | |
 Lateral surface of cerebral cortex | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | pars orbitalis gyri frontalis inferioris |
| NeuroNames | 2410 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_1207 |
| TA98 | A14.1.09.114 |
| TA2 | 5448 |
| FMA | 61982 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
In humans, this region is bordered by the triangular part of the inferior frontal gyrus (pars triangularis) and, surrounding the anterior horizontal limb of the lateral sulcus, a portion of the opercular part of inferior frontal gyrus (pars opercularis). Bounded caudally by the anterior ascending limb of the lateral sulcus, it borders on the insula in the depth of the lateral sulcus. It is bordered anteriorly/inferiorly by the lateral orbital sulcus.[2][3]
Cytoarchitectonically it is most closely represented by Brodmann area 47 (BA47).[4] However, BA47 and pars orbitalis are not synonymous, as pars orbitalis specifically refers to a grossly visible gyral region and BA47 refers to the cytoarchitectonic features of brain tissue. In vivo neuroscience research almost exclusively discusses the gyral region, although the gyral and cytoarchitectonic terms are frequently used synonymously.
Additional images
edit-
Lateral view of a human brain showing main gyri labeled.
-
Animated view of orbital part of inferior frontal gyrus
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ "BrainInfo". braininfo.rprc.washington.edu.
- ^ Keller, Simon S.; Crow, Timothy; Foundas, Anne; Amunts, Katrin; Roberts, Neil (April 2009). "Broca's area: Nomenclature, anatomy, typology and asymmetry". Brain and Language. 109 (1): 29–48. doi:10.1016/j.bandl.2008.11.005.
- ^ Desikan, Rahul S.; Ségonne, Florent; Fischl, Bruce; Quinn, Brian T.; Dickerson, Bradford C.; Blacker, Deborah; Buckner, Randy L.; Dale, Anders M.; Maguire, R. Paul; Hyman, Bradley T.; Albert, Marilyn S.; Killiany, Ronald J. (July 2006). "An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on MRI scans into gyral based regions of interest". NeuroImage. 31 (3): 968–980. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.01.021.
- ^ Brodmann, K. (1909). Vergleichende Lokalisationslehre der Grosshirnrinde in ihren Prinzipien dargestellt auf Grund des Zellenbaues. Leipzig, Germany: Barth.