The Sangha River (Kikongo: Nzâdi Sangha, Swahili: Mto Sanga, French: Rivière Sangha), a tributary of the Congo River, is located in Central Africa.
| Designations | |
|---|---|
| Official name | Partie camerounaise du fleuve Sangha |
| Designated | 2 February 2008 |
| Reference no. | 1739[1] |
| Official name | Sangha-Nouabalé-Ndoki |
| Designated | 4 March 2009 |
| Reference no. | 1858[2] |
| Official name | Riviere Sangha située en République Centrafricaine |
| Designated | 5 November 2009 |
| Reference no. | 1889[3] |

Geography
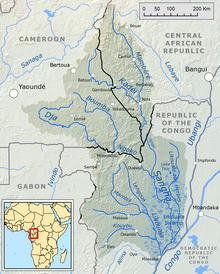
editThe Sangha River is formed at the confluence of the Mambéré River and the Kadéï River at Nola in the western Central African Republic (3°30′55″N 16°2′50″E / 3.51528°N 16.04722°E). The Sangha flows along the border of Cameroon, with the Central African Republic, and then the Republic of Congo. It joins the Congo River at 1°12′45″S 16°49′40″E / 1.21250°S 16.82778°E.
The tributaries of the Sangha River include the Ngoko River (Dja river). Its river mouth and confluence with the Sangha is at Ouésso, in the Republic of the Congo (1°39′5″N 16°3′25″E / 1.65139°N 16.05694°E).
Ecology
editThe Sangha River is a Freshwater ecoregion of Africa. Its wetlands in the Central African Republic, Cameroon and Congo are protected Ramsar sites.
References
edit- ^ "Partie camerounaise du fleuve Sangha". Ramsar Sites Information Service. Retrieved 25 April 2018.
- ^ "Sangha-Nouabalé-Ndoki". Ramsar Sites Information Service. Retrieved 25 April 2018.
- ^ "Riviere Sangha située en République Centrafricaine". Ramsar Sites Information Service. Retrieved 25 April 2018.