Perosamine (or GDP-perosamine) is a mannose-derived 4-aminodeoxysugar produced by some bacteria.
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
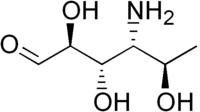
| IUPAC name
4-Amino-4,6-dideoxy-D-mannose
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2S,3S,4R,5R)-4-Amino-2,3,5-trihydroxyhexanal | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H13NO4 | |
| Molar mass | 163.172 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Biological role
editN-acetyl-perosamine is found in the O-antigen of Gram-negative bacteria such as Vibrio cholerae O1, E. coli O157:H7 and Caulobacter crescentus CB15.[1] The sugar is also found in perimycin, an antibiotic produced by the Gram-positive organism Streptomyces coelicolor var. aminophilus.[2]
Biosynthesis
editIts biosynthesis from mannose-1-phosphate follows a pathway similar to that of colitose, but is different in that it is aminated and does not undergo 3-OH deoxygenation or C-5 epimerization.[3]
GDP-4-keto-6-deoxymannose-4-aminotransferase (GDP-perosamine synthase)
editGDP-perosamine synthase is a PLP-dependent enzyme that transfers a nitrogen from glutamate to the 4-keto position of GDP-4-keto-6-deoxymannose during the biosynthesis of GDP-perosamine.[1]
References
edit- ^ a b Samuel G, Reeves P (2003). "Biosynthesis of O-antigens: genes and pathways involved in nucleotide sugar precursor synthesis and O-antigen assembly". Carbohydr. Res. 338 (23): 2503–19. doi:10.1016/j.carres.2003.07.009. PMID 14670712.
- ^ Pawlak J, Sowiński P, Borowski E, Gariboldi P (September 1995). "Stereostructure of perimycin A". J. Antibiot. 48 (9): 1034–8. doi:10.7164/antibiotics.48.1034. PMID 7592049.
- ^ Albermann C, Piepersberg W (August 2001). "Expression and identification of the RfbE protein from Vibrio cholerae O1 and its use for the enzymatic synthesis of GDP-D-perosamine". Glycobiology. 11 (8): 655–61. doi:10.1093/glycob/11.8.655. PMID 11479276.