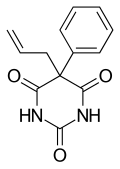
Alphenal, also known as 5-allyl-5-phenylbarbituric acid, is a barbiturate derivative developed in the 1920s.[1] It has primarily anticonvulsant properties and was used occasionally for the treatment of epilepsy or convulsions, although not as commonly as better known barbiturates such as phenobarbital.[2][3][4][5]
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Alphenal, Efrodal, Prophenal, Sanudorm |
| Other names | 5-Phenyl-5-allylbarbituric acid |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | Barbiturate |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.718 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C13H12N2O3 |
| Molar mass | 244.250 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
LD50: Mouse (Oral): 280 mg/kg
References
edit- ^ DE 526854, "Verfahren zur Darstellung von C,C-disubstituierten Barbitursaeuren", issued 11 June 1931, assigned to Hoffmann La Roche
- ^ Carissimi M (1962). "Nuovi Barbiturici Alogenati Farmaco". Ediozione Scientifica. 17 (6): 390–413.
- ^ Martin JR, Godel T, Hunkeler W, Jenck F, Moreau JL, Sleight AJ, Widmer U (December 2000). "Psychopharmacological Agents". Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. doi:10.1002/0471238961.1619250313011820.a01. ISBN 0471238961.
- ^ Brandenberger H, Maes RA (1997). Analytical Toxicology: For Clinical, Forensic, and Pharmaceutical Chemists. Walter de Gruyter. p. 348. ISBN 978-3-11-010731-9. Retrieved 19 May 2012.
- ^ García PC, Cruz SV, Mirón CE (28 January 2005). Fundamentos de síntesis de fármacos. Edicions Universitat Barcelona. p. 161. ISBN 978-84-475-2876-9. Retrieved 19 May 2012.