| Physics Portal Main Page | Physics Textbook | Wikiprojects and things to do |
The Physics Portal

Physics is the scientific study of matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. Physics is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines. A scientist who specializes in the field of physics is called a physicist.
Physics is one of the oldest academic disciplines. Over much of the past two millennia, physics, chemistry, biology, and certain branches of mathematics were a part of natural philosophy, but during the Scientific Revolution in the 17th century, these natural sciences branched into separate research endeavors. Physics intersects with many interdisciplinary areas of research, such as biophysics and quantum chemistry, and the boundaries of physics are not rigidly defined. New ideas in physics often explain the fundamental mechanisms studied by other sciences and suggest new avenues of research in these and other academic disciplines such as mathematics and philosophy.
Advances in physics often enable new technologies. For example, advances in the understanding of electromagnetism, solid-state physics, and nuclear physics led directly to the development of technologies that have transformed modern society, such as television, computers, domestic appliances, and nuclear weapons; advances in thermodynamics led to the development of industrialization; and advances in mechanics inspired the development of calculus. (Full article...)

Josiah Willard Gibbs (/ɡɪbz/; February 11, 1839 – April 28, 1903) was an American scientist who made significant theoretical contributions to physics, chemistry, and mathematics. His work on the applications of thermodynamics was instrumental in transforming physical chemistry into a rigorous deductive science. Together with James Clerk Maxwell and Ludwig Boltzmann, he created statistical mechanics (a term that he coined), explaining the laws of thermodynamics as consequences of the statistical properties of ensembles of the possible states of a physical system composed of many particles. Gibbs also worked on the application of Maxwell's equations to problems in physical optics. As a mathematician, he created modern vector calculus (independently of the British scientist Oliver Heaviside, who carried out similar work during the same period) and described the Gibbs phenomenon in the theory of Fourier analysis.
In 1863, Yale University awarded Gibbs the first American doctorate in engineering. After a three-year sojourn in Europe, Gibbs spent the rest of his career at Yale, where he was a professor of mathematical physics from 1871 until his death in 1903. Working in relative isolation, he became the earliest theoretical scientist in the United States to earn an international reputation and was praised by Albert Einstein as "the greatest mind in American history". In 1901, Gibbs received what was then considered the highest honor awarded by the international scientific community, the Copley Medal of the Royal Society of London, "for his contributions to mathematical physics". (Full article...)
Did you know -

- ...that while Albert Einstein is most famous for his Theory of Relativity, he was awarded the Nobel Prize for his explanation of the photoelectric effect?
- ...that gravitational tidal accelerations are the result of the curvature of spacetime?
- ...that the blue glow of the Cherenkov effect is due to electrons moving faster than the speed of light in water?
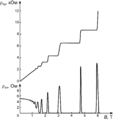
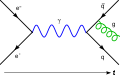
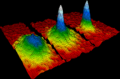
Selected image -

Related portals
November anniversaries
- 1952 - detonation of the first Hydrogen bomb, code named "Ivy Mike".
- 1947 - invention of the first transistor, between November 17 to December 23. APS.
- 1930 - Patent granted for Einstein-Szilard refrigerator designed by Albert Einstein and Leó Szilárd. APS.
- 1919 - Elmer Imes's published work presented the first accurate measurement of the distance between atoms in molecules with high resolution infrared spectroscopy. APS.
- 1915 – Einstein's presentation to the Prussian Academy of Science specifies how the geometry of space and time is influenced by whatever matter is present. (see: General relativity and APS)
- 1895 - Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen discovers X-rays.
- 1887 - Michelson–Morley experiment provided strong evidence against the luminiferous ether. APS.
- 1872 - death of Mary Somerville who gained an international reputation as a scientist in the intervals of raising a family of six children. APS
- 1783 - John Michell predicted the existence of black holes, and the possibility of a luminous twin to aid in detection. APS
- 1676 – using his first quantitative measurement of the speed of light, Ole Rømer accurately predicts the delay of eclipse of Io
Births
- 1934 – Carl Sagan
- 1932 - Melvin Schwartz
- 1929 - Richard E. Taylor
- 1925 - Simon van der Meer
- 1902 - Eugene Wigner
- 1837 - Johannes Diderik van der Waals
- 1867 - Marie Curie (Nov. 7)
- 1828 - Balfour Stewart
- 1878 - Lise Meitner (Nov. 7)
- 1887 - Henry Moseley
- 1888 - C V Raman (Nov. 7)
- 1892 - Dmitri Skobeltsyn (Nov. 24)
General images
Categories

Fundamentals: Concepts in physics | Constants | Physical quantities | Units of measure | Mass | Length | Time | Space | Energy | Matter | Force | Gravity | Electricity | Magnetism | Waves
Basic physics: Mechanics | Electromagnetism | Statistical mechanics | Thermodynamics | Quantum mechanics | Theory of relativity | Optics | Acoustics
Specific fields: Acoustics | Astrophysics | Atomic physics | Molecular physics | Optical physics | Computational physics | Condensed matter physics | Nuclear physics | Particle physics | Plasma physics
Tools: Detectors | Interferometry | Measurement | Radiometry | Spectroscopy | Transducers
Background: Physicists | History of physics | Philosophy of physics | Physics education | Physics journals | Physics organizations
Other: Physics in fiction | Physics lists | Physics software | Physics stubs
Physics topics
Classical physics traditionally includes the fields of mechanics, optics, electricity, magnetism, acoustics and thermodynamics. The term Modern physics is normally used for fields which rely heavily on quantum theory, including quantum mechanics, atomic physics, nuclear physics, particle physics and condensed matter physics. General and special relativity are usually considered to be part of modern physics as well.
More recognized content
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus